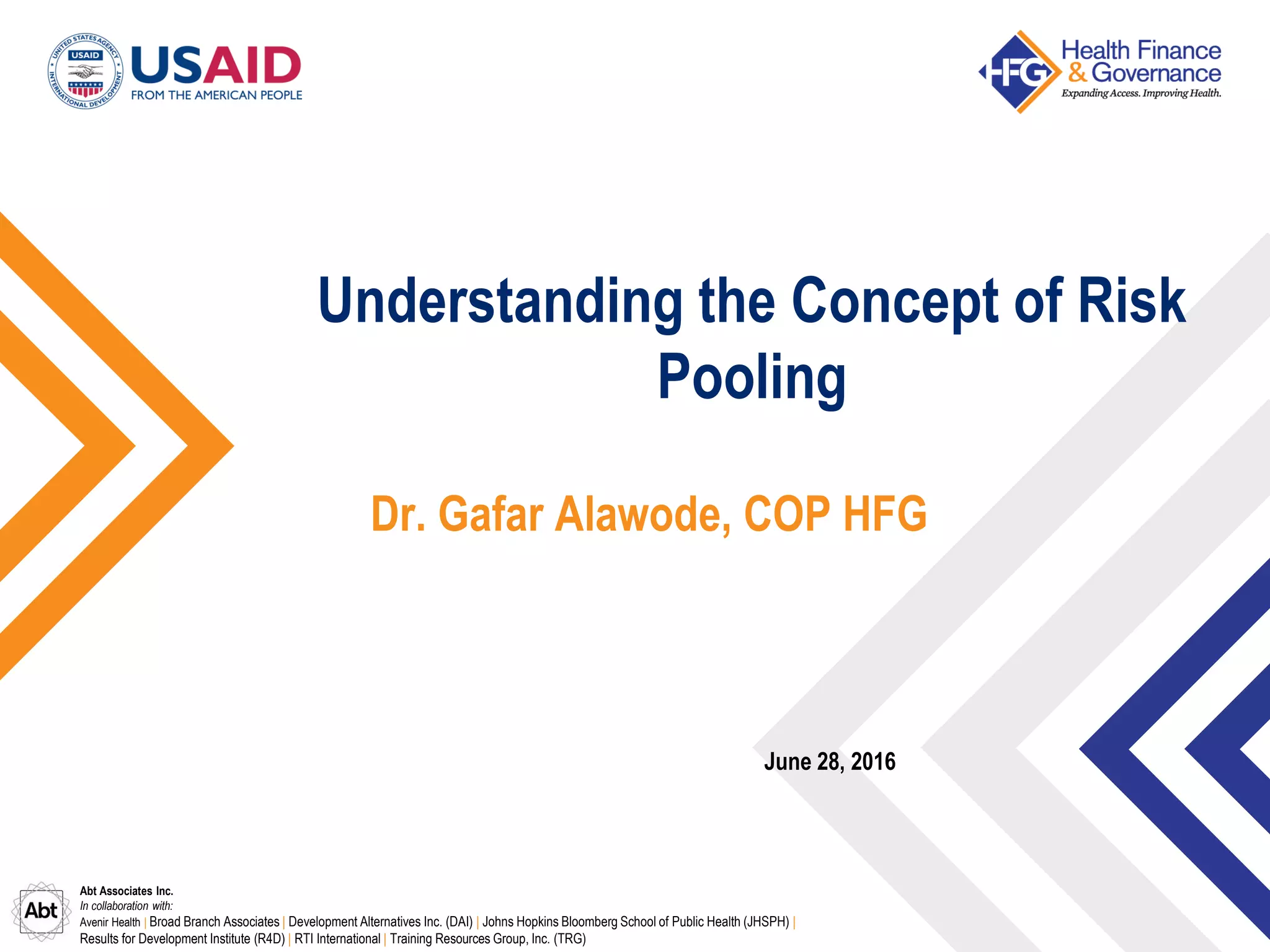
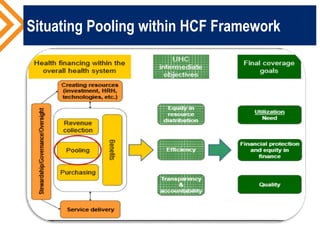
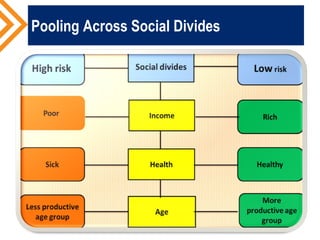
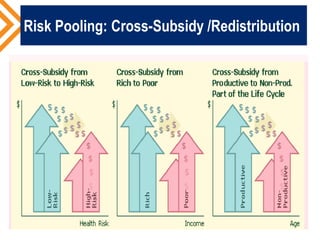
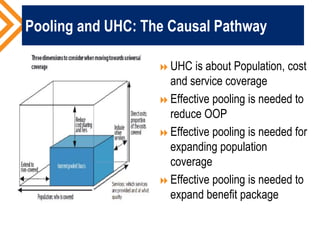
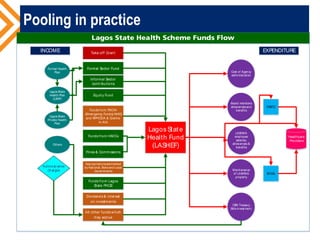
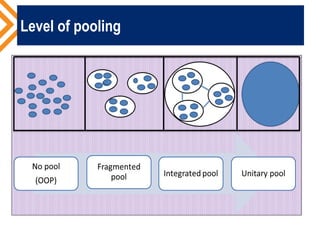
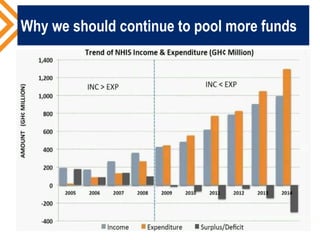
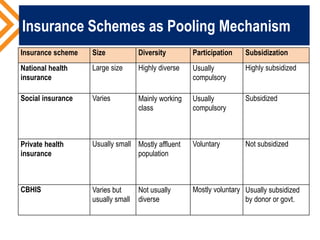
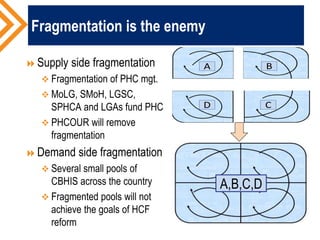
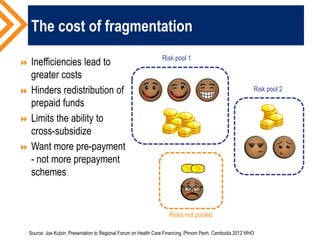
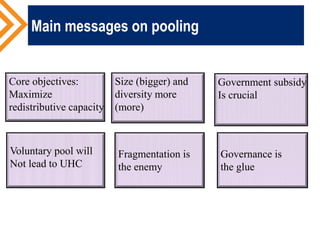
The document outlines the concept of risk pooling as a critical function of health financing, emphasizing its role in achieving universal health coverage (UHC) through the collection and redistribution of prepaid resources. It discusses characteristics of effective pooling, the necessity to avoid fragmentation in health insurance schemes, and the importance of governance and strategic purchasing to enhance health equity and economic prosperity. Key recommendations include aligning policies with objectives, expanding inclusive pools, and ensuring government subsidization to support vulnerable groups.