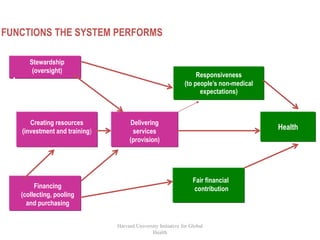
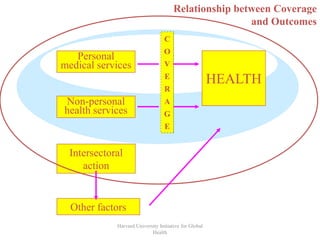
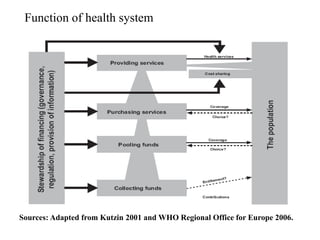
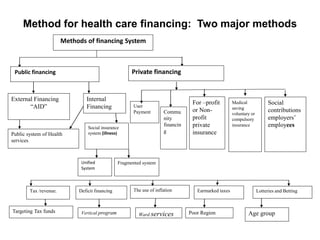
The document discusses health systems and financing. It begins by defining a health system as all actors, institutions, and resources that undertake health actions, with the primary intent of improving health. Not all policies that influence health are part of the health system. The document then discusses the goals of health systems, including improving health and ensuring financial contribution. It outlines the key functions of health systems as stewardship, financing, resource generation, and service delivery. The document emphasizes the importance of aligning financing with national health plans to avoid fragmentation. It also discusses concepts of coverage, effectiveness, and factors that influence health outcomes.