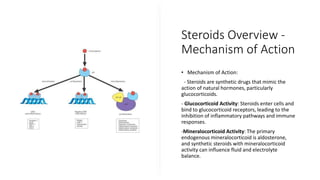
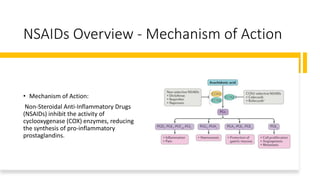
The document discusses the mechanisms, uses, indications, contraindications, and side effects of steroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Steroids, which mimic natural hormones, are used for various inflammatory and autoimmune conditions but have significant side effects and contraindications, including infections and gastric ulcers. NSAIDs work by inhibiting cyclooxygenase enzymes to reduce pain and inflammation but can also lead to gastrointestinal, renal, and cardiovascular issues.