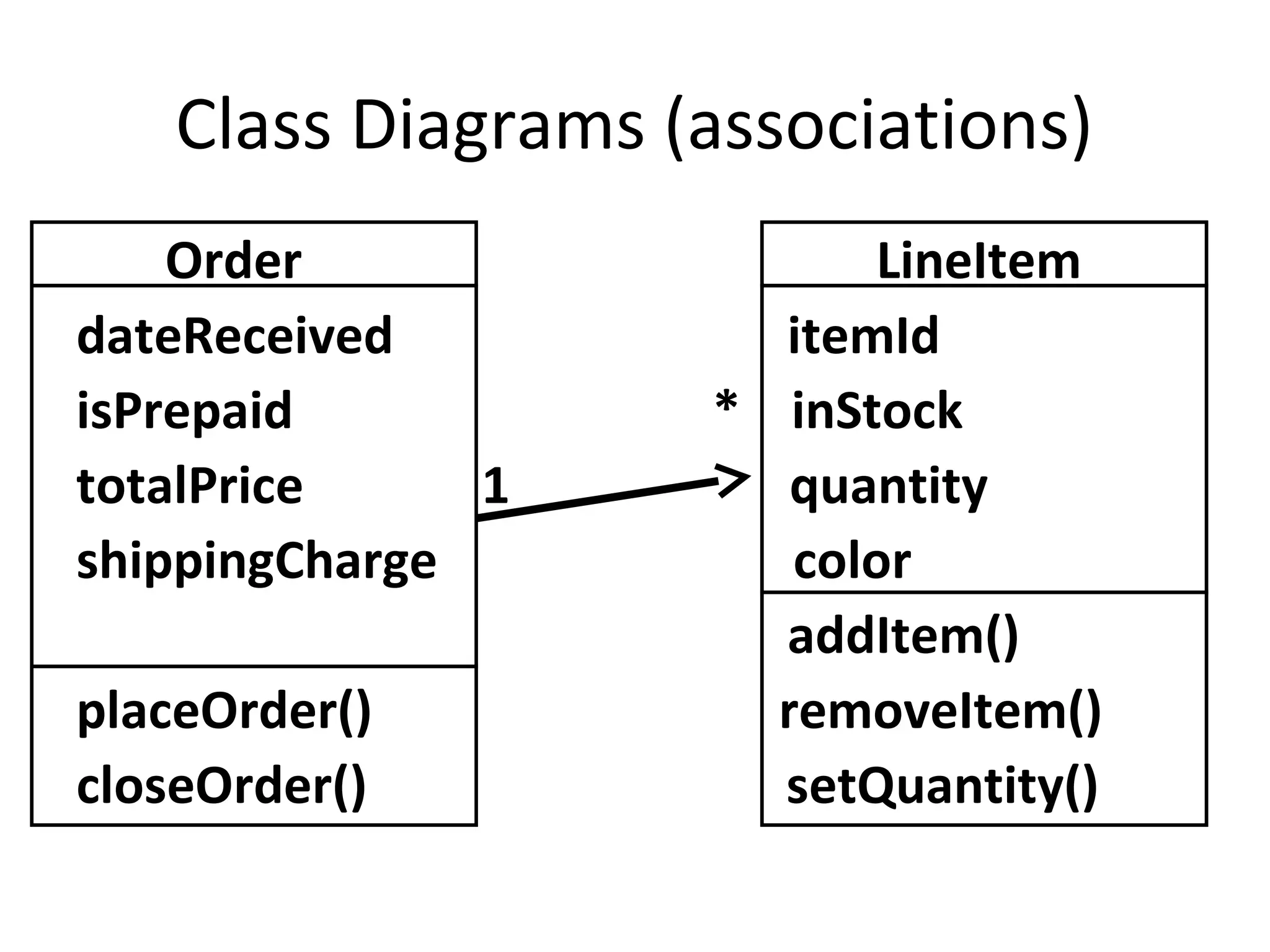
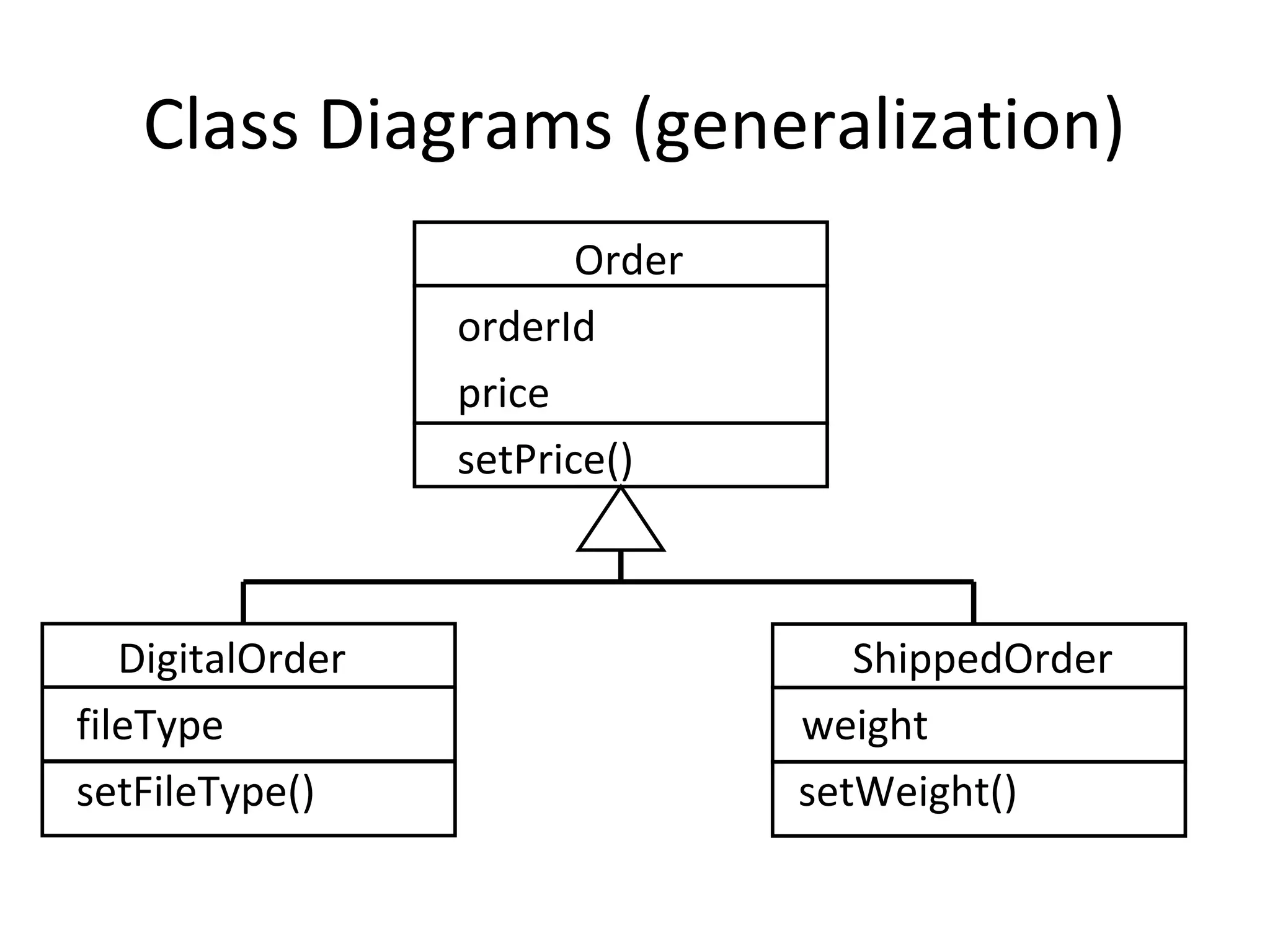
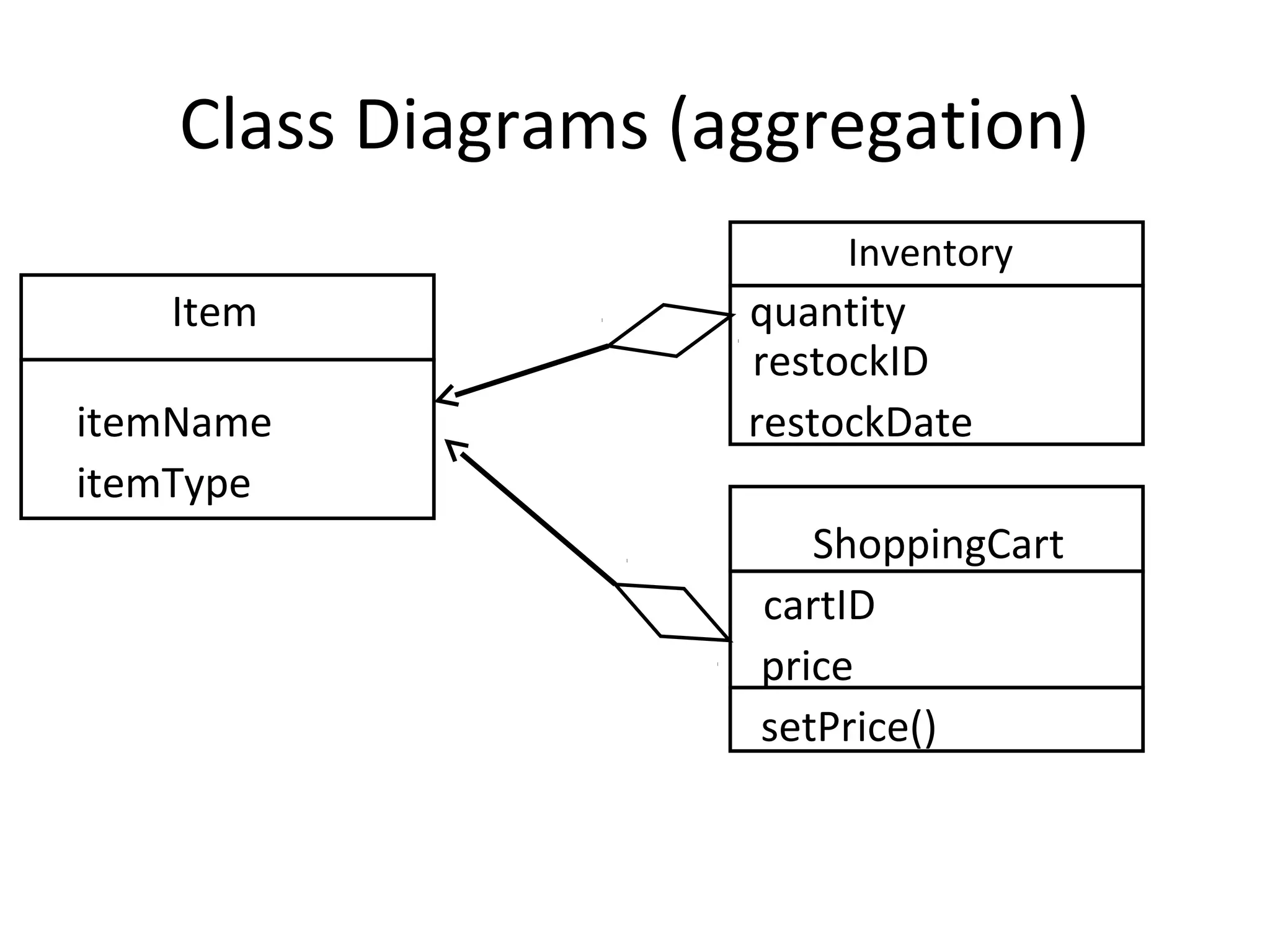
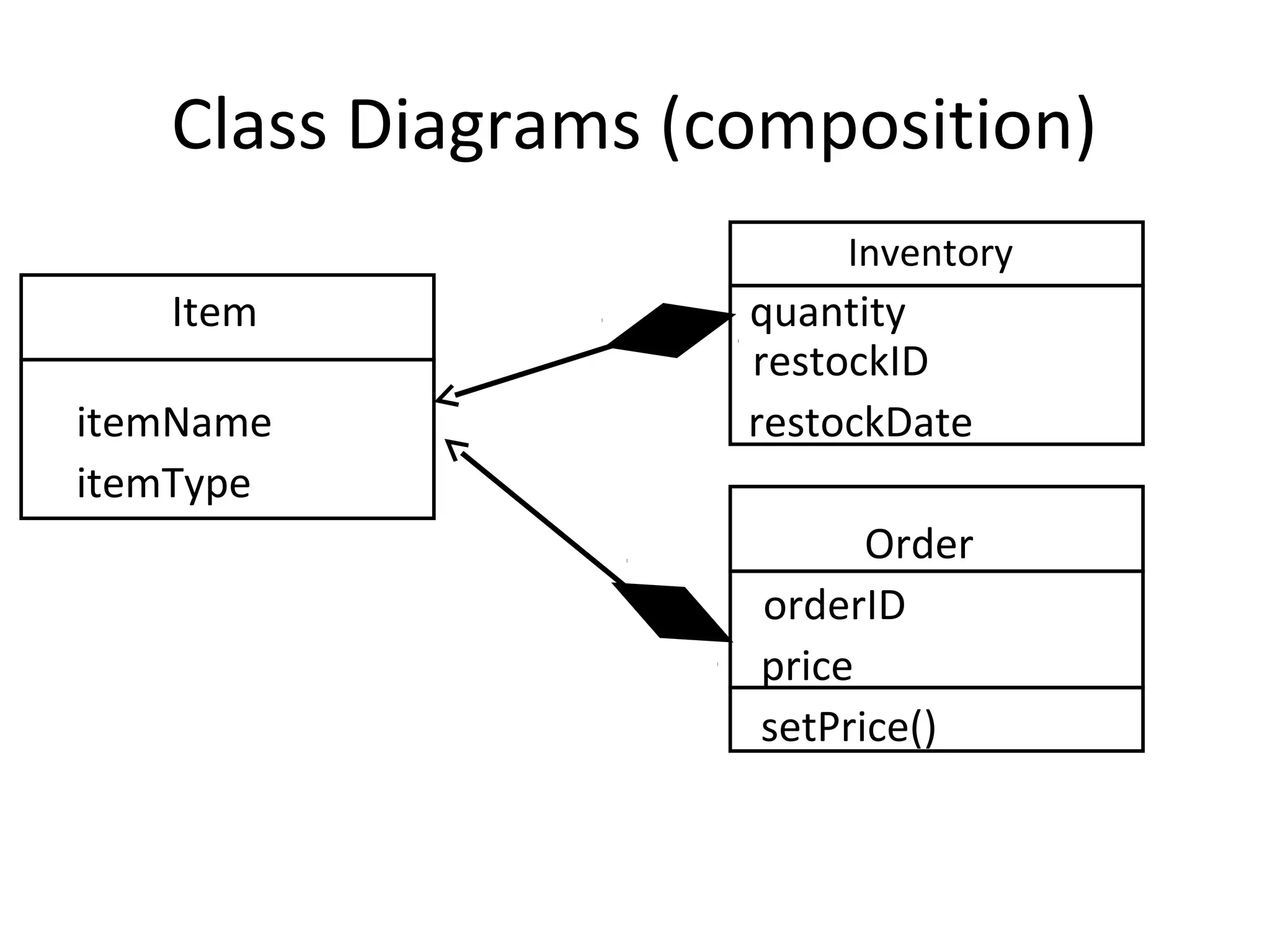
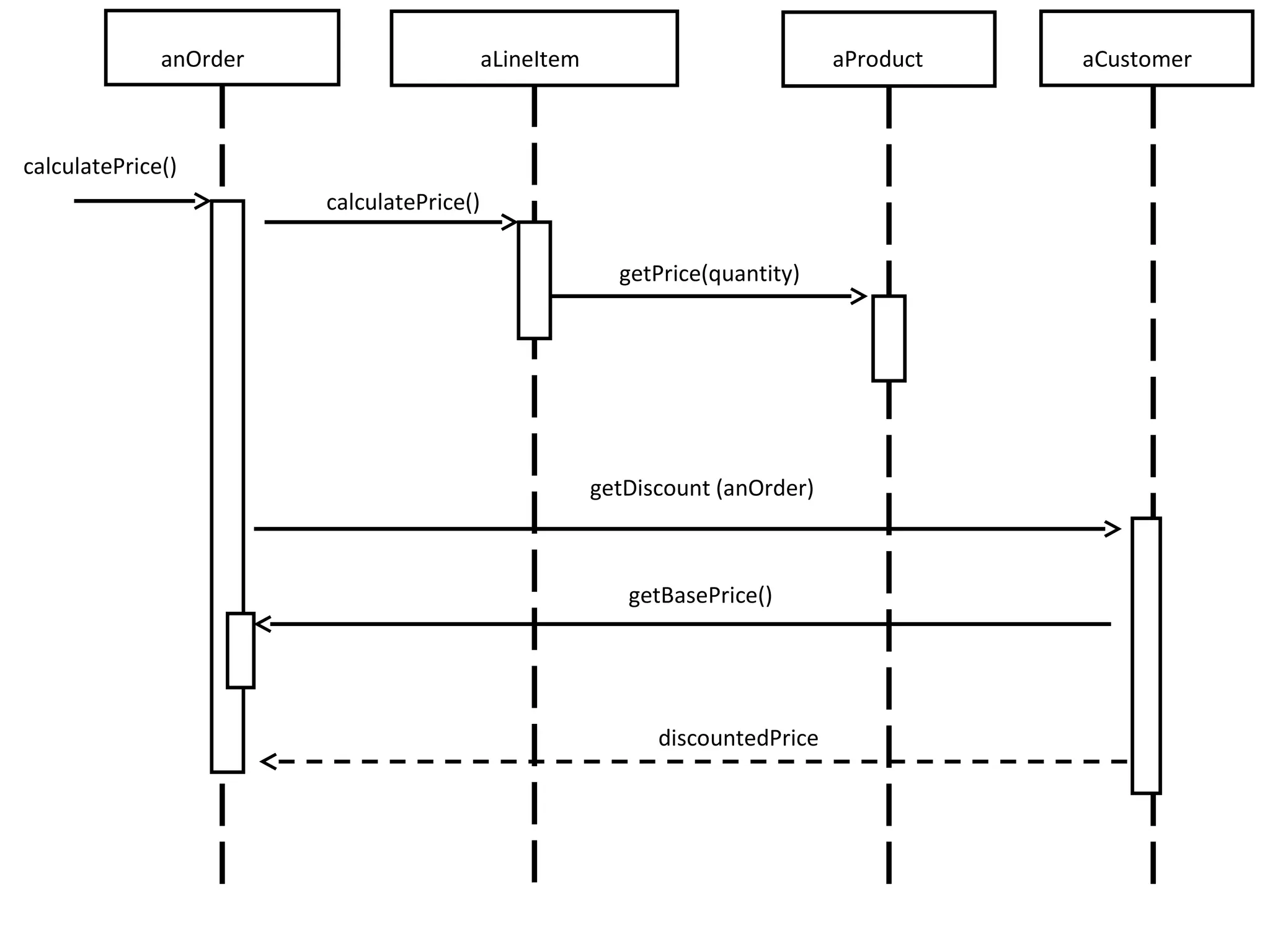
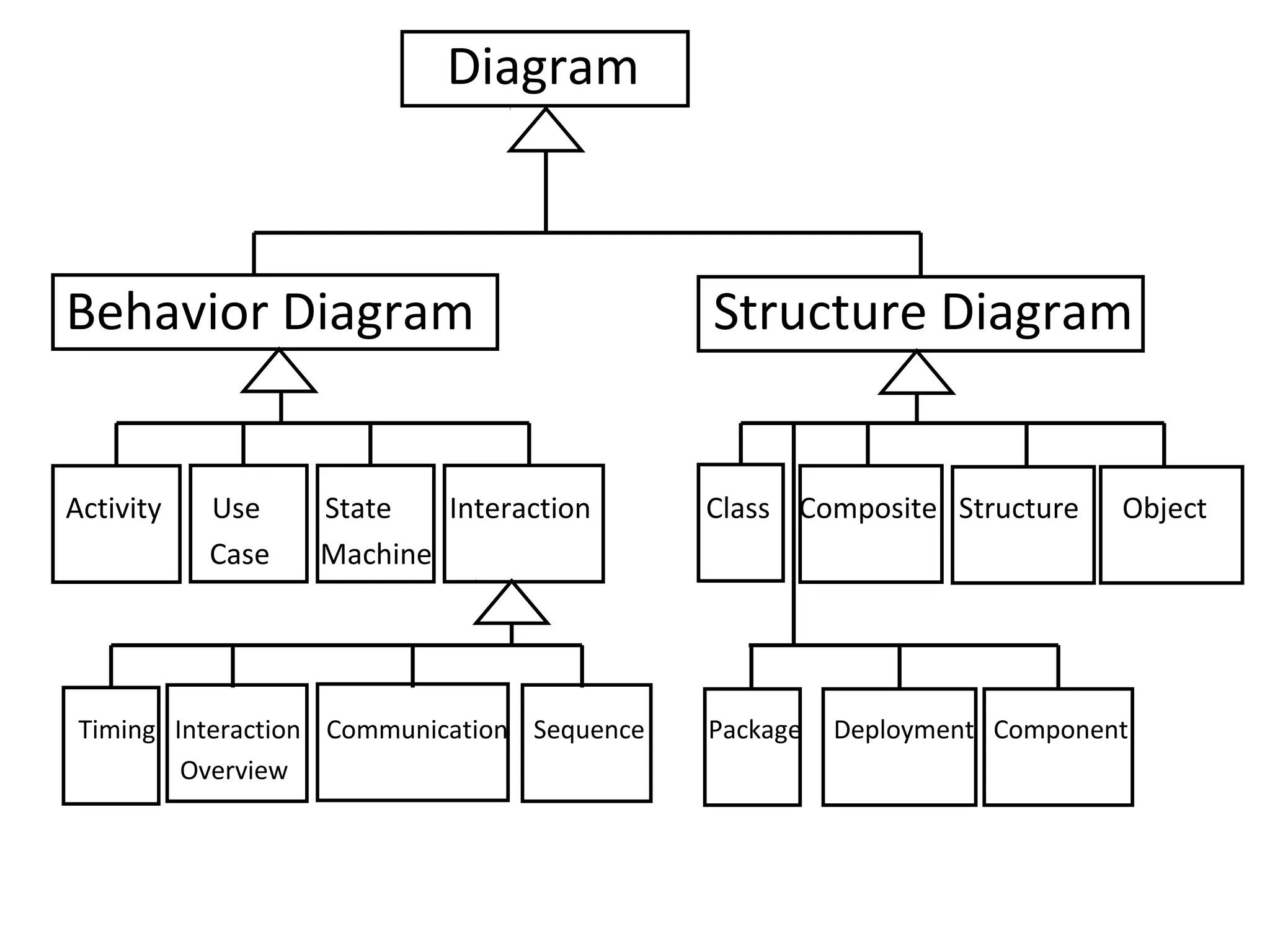
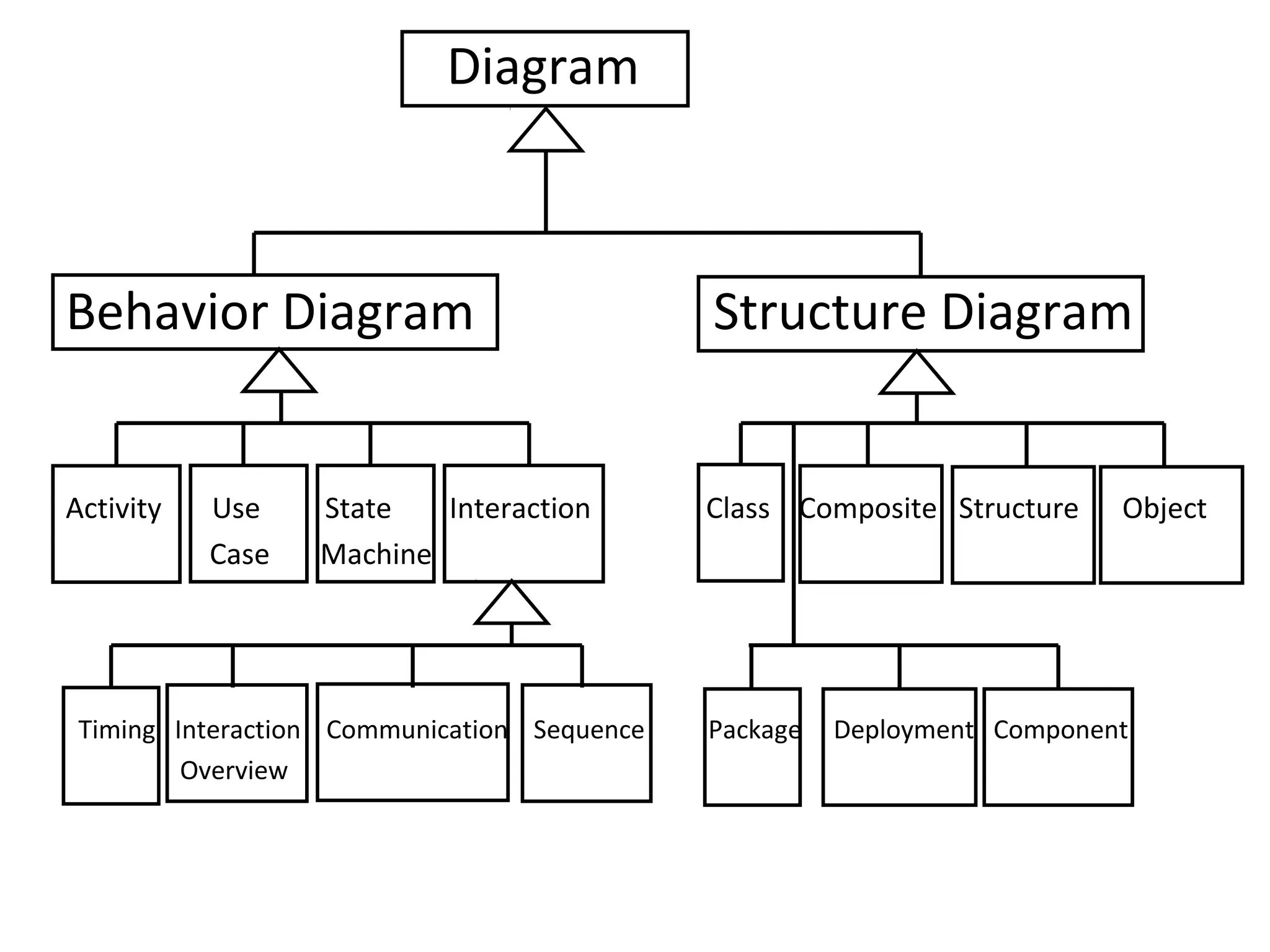
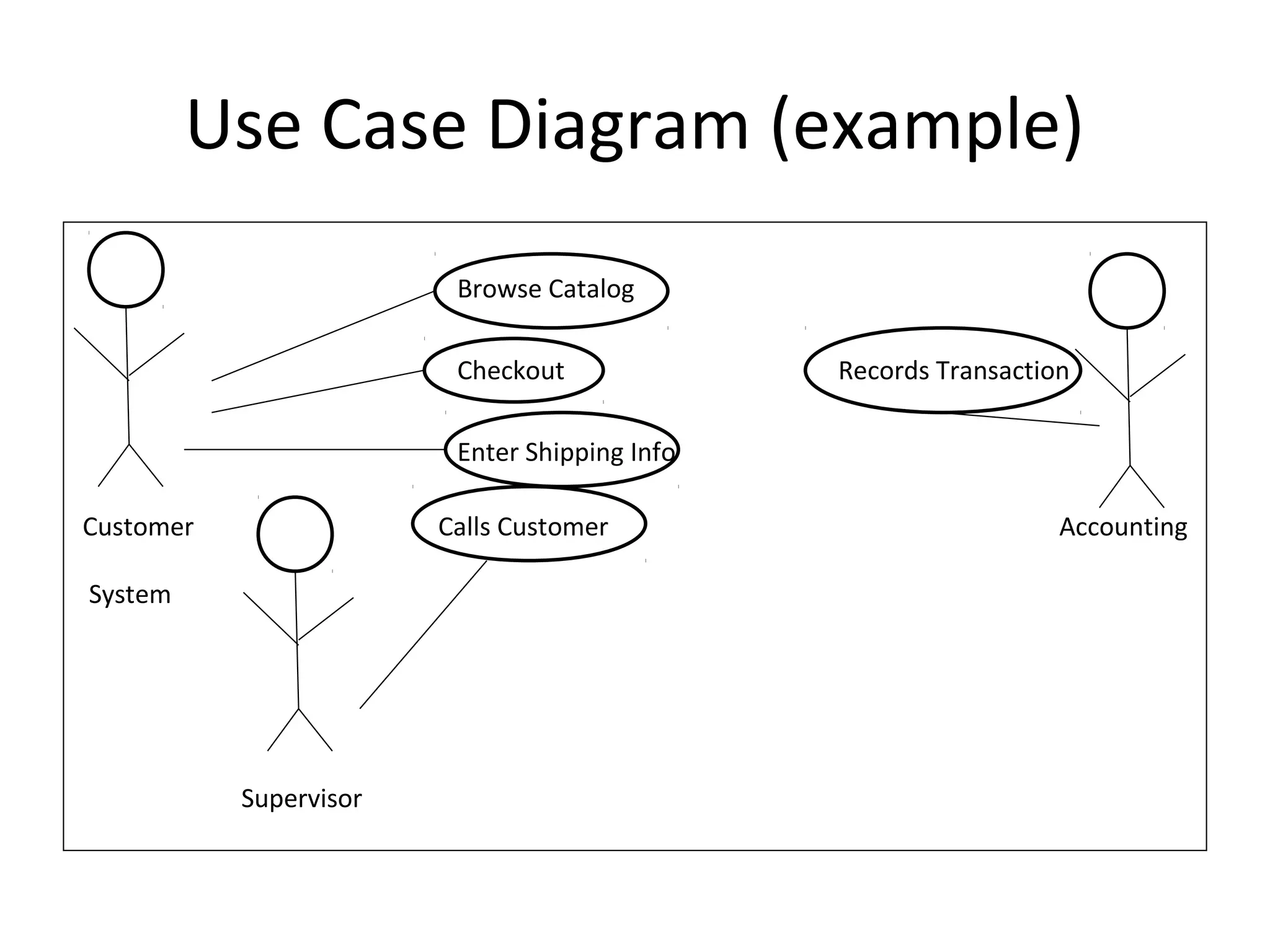
The document provides an overview of the Unified Modeling Language (UML) by discussing its history, purpose, common diagrams, and basic concepts. UML was created in 1997 by combining existing modeling languages. It is a standard graphical modeling language used to communicate and visualize ideas through diagrams like use case diagrams, class diagrams, and sequence diagrams. The document recommends using UML as a sketch to plan systems and explains some key UML concepts like the difference between classes and objects.













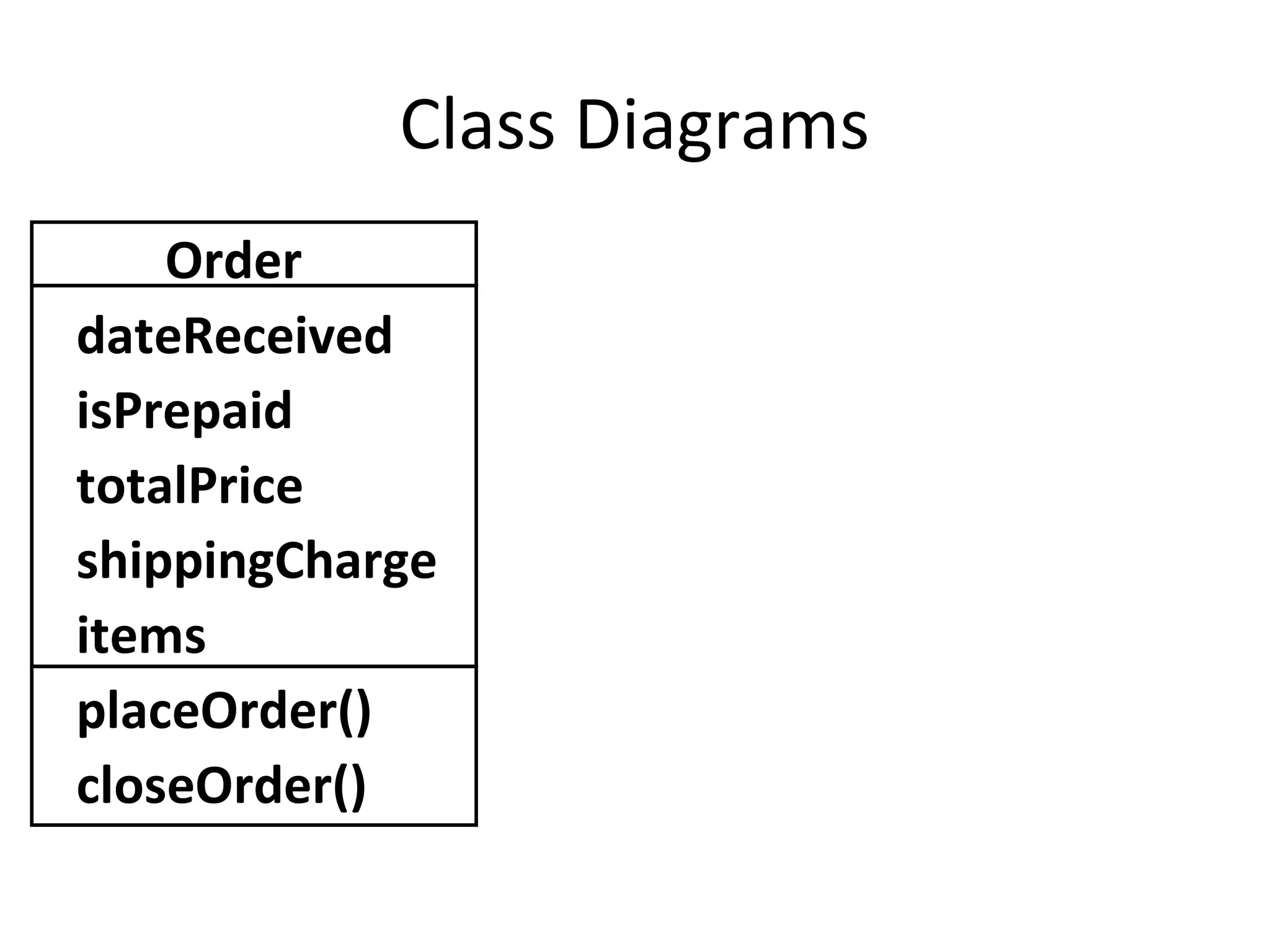
![Class Diagrams
Order
+ dateReceived: Date[1]
- isPrepaid: Boolean [0..1]
+ totalPrice: Float[1]
# shippingCharge: Float [1]
+ items: LineItem [*]
+ placeOrder(int: orderId): Boolean
+ closeOrder(): Boolean](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umlandyou-130123101355-phpapp02/75/UML-and-You-18-2048.jpg)
![Class Diagrams
Order Class name
+ dateReceived: Date[1]
- isPrepaid: Boolean [0..1]
+ totalPrice: Float[1] Attributes
# shippingCharge: Float [1]
+ items: LineItem [*]
+ placeOrder(int: orderId): Boolean
+ closeOrder(): Boolean Operations
Visibility
Data Type
Multiplicity
Parameter List
Return Type](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umlandyou-130123101355-phpapp02/75/UML-and-You-19-2048.jpg)