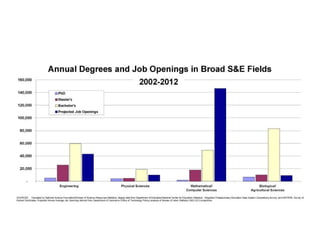
The document provides an overview of the Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County. It details the department's research funding, degree programs, course requirements, faculty credentials, and opportunities for undergraduate and graduate students. The department has over 850 undergraduate students, 230 graduate students, 35 professors with PhDs from top universities, and $6 million per year in research expenditures. The BS in Computer Science provides a rigorous education combining theory and practice in areas like software, algorithms, and data structures to prepare students for lifelong learning.




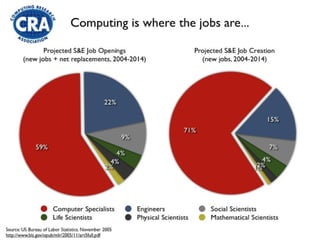
![Why computer science? It’s a broad discipline Pick your mix of engineering, science, math and the arts It’s practical relatively strong job market [next slides] It’s important information technology is changing the world It’s interesting and fun](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/umbc-undergraduate-computer-science-program-2414/85/UMBC-undergraduate-computer-science-program-5-320.jpg)