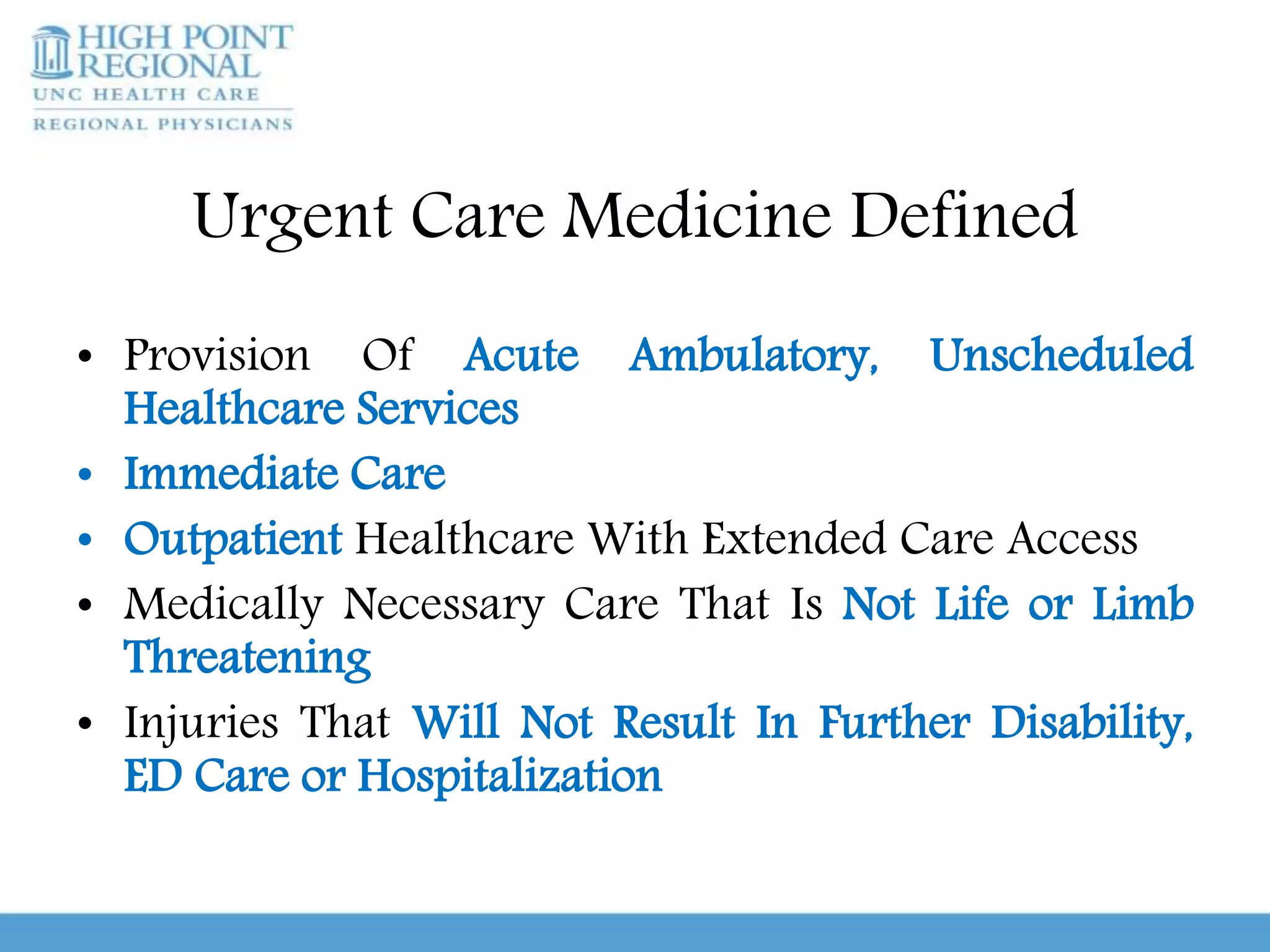
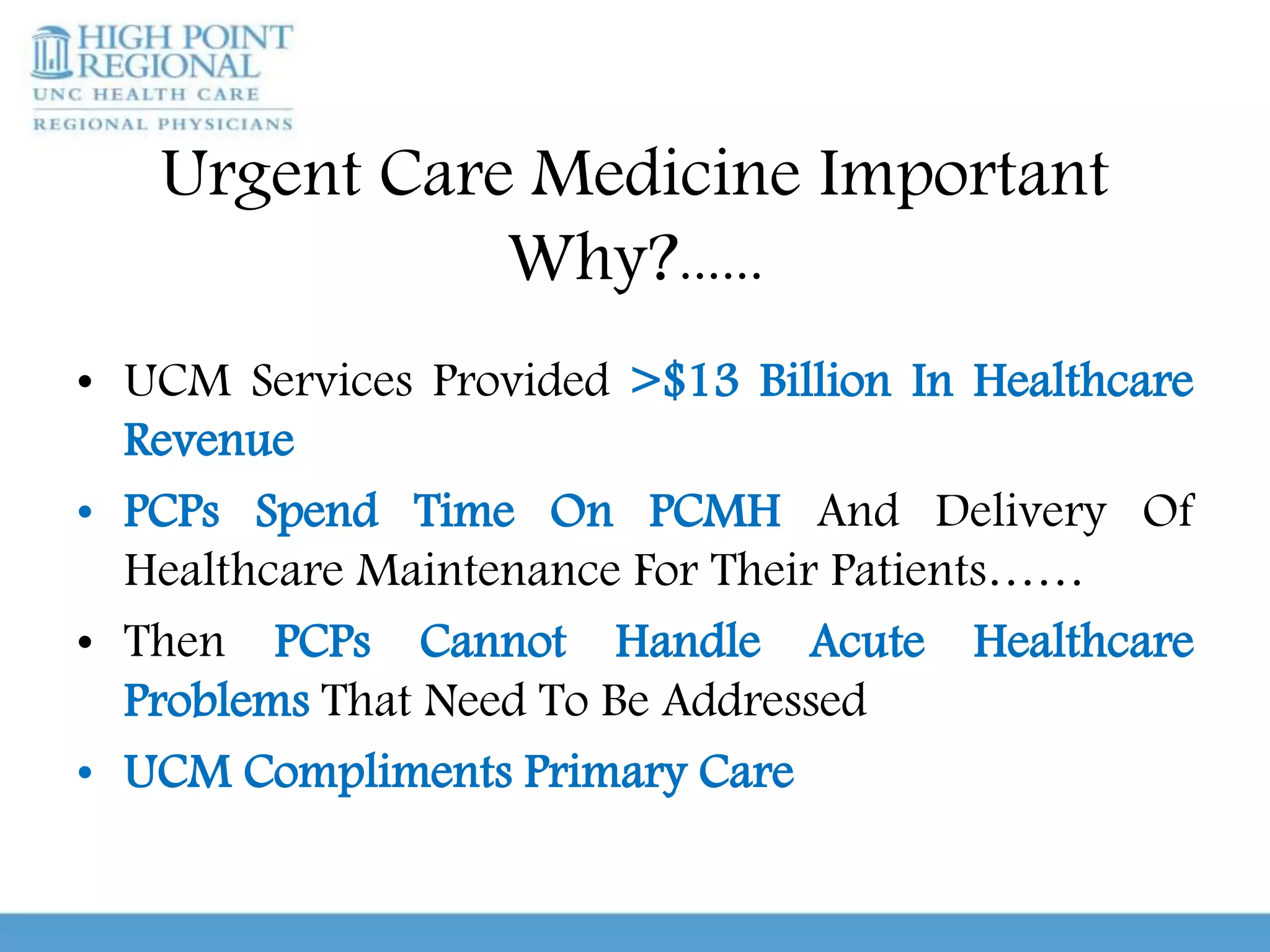
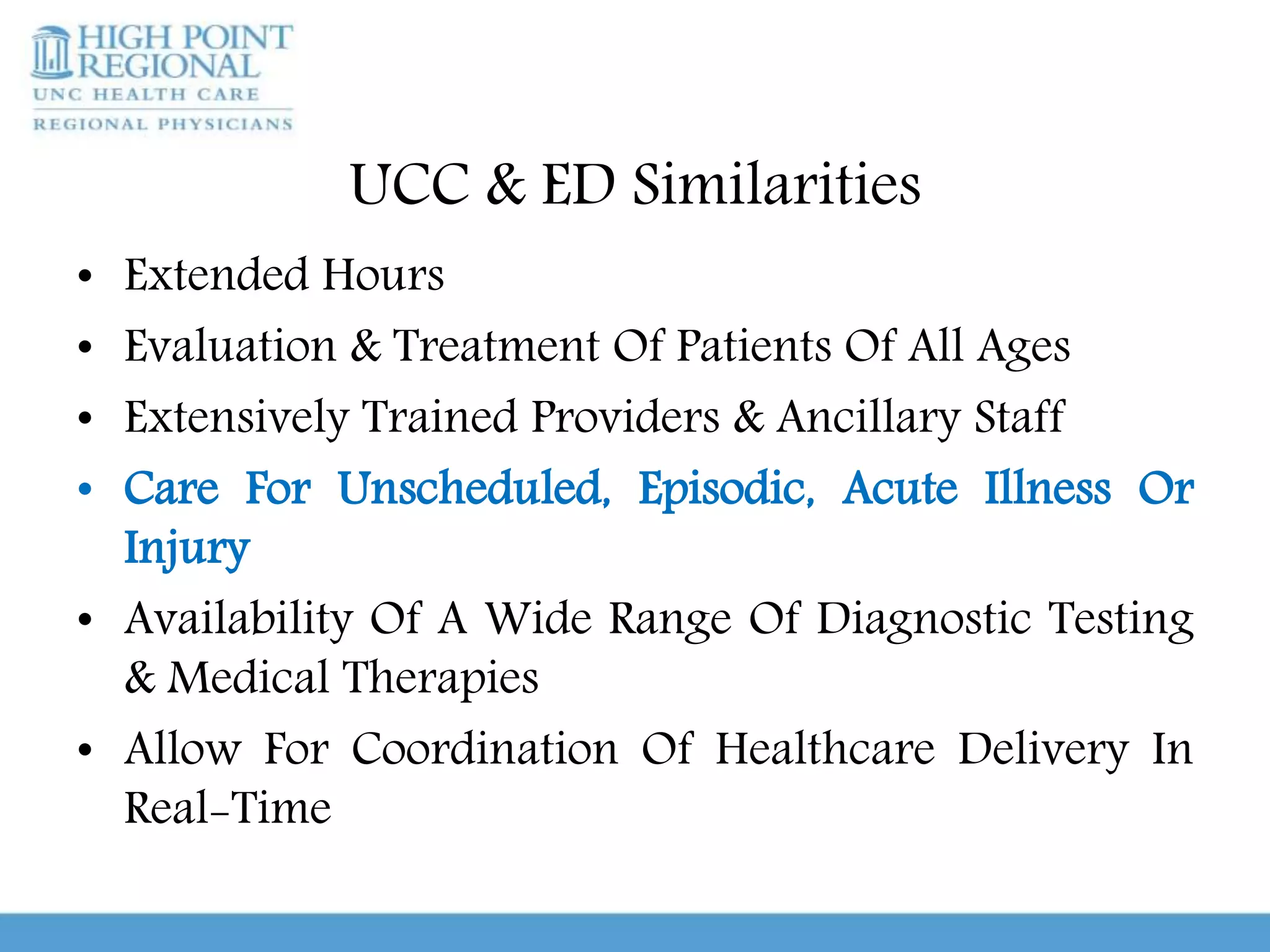
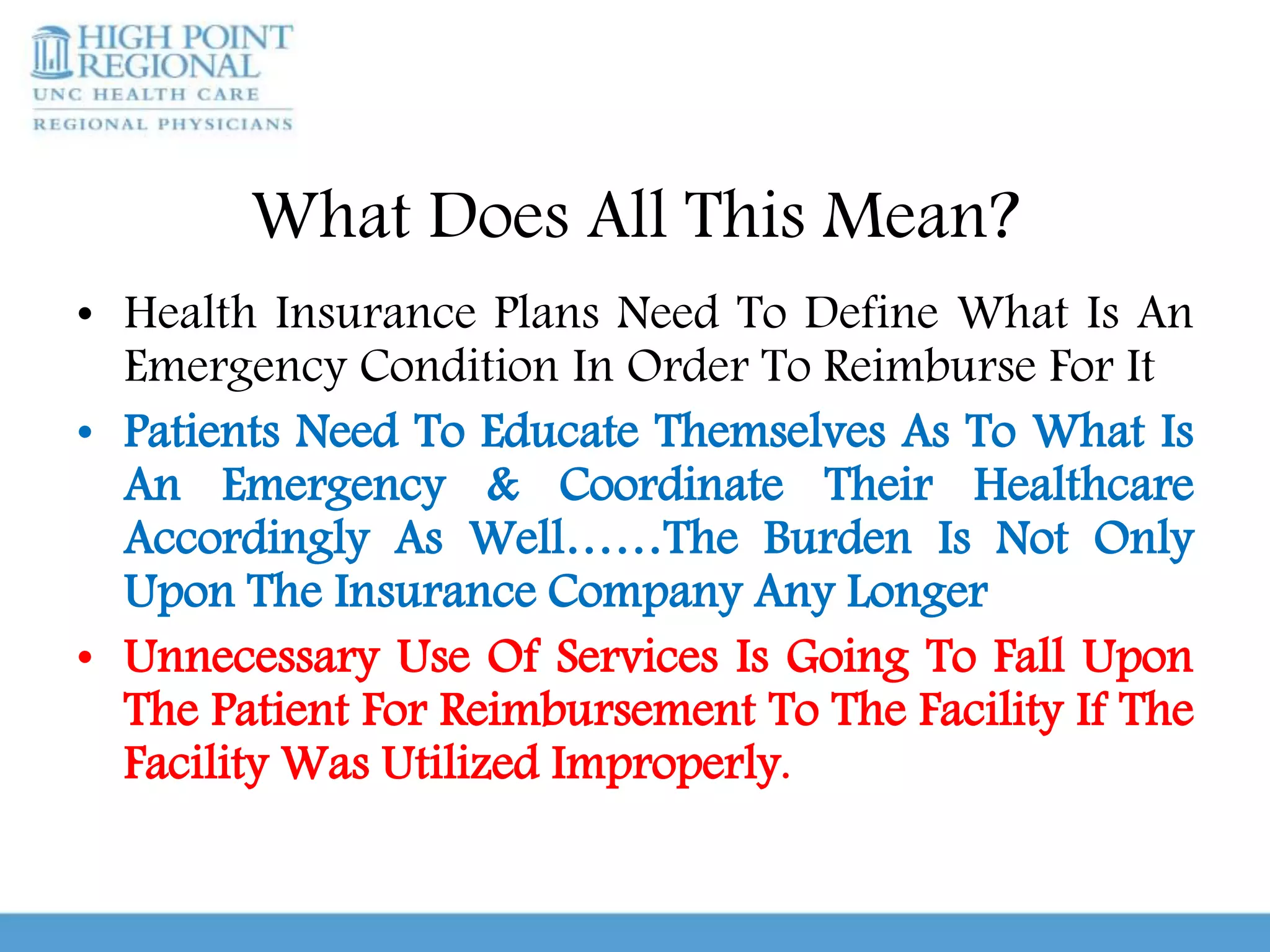
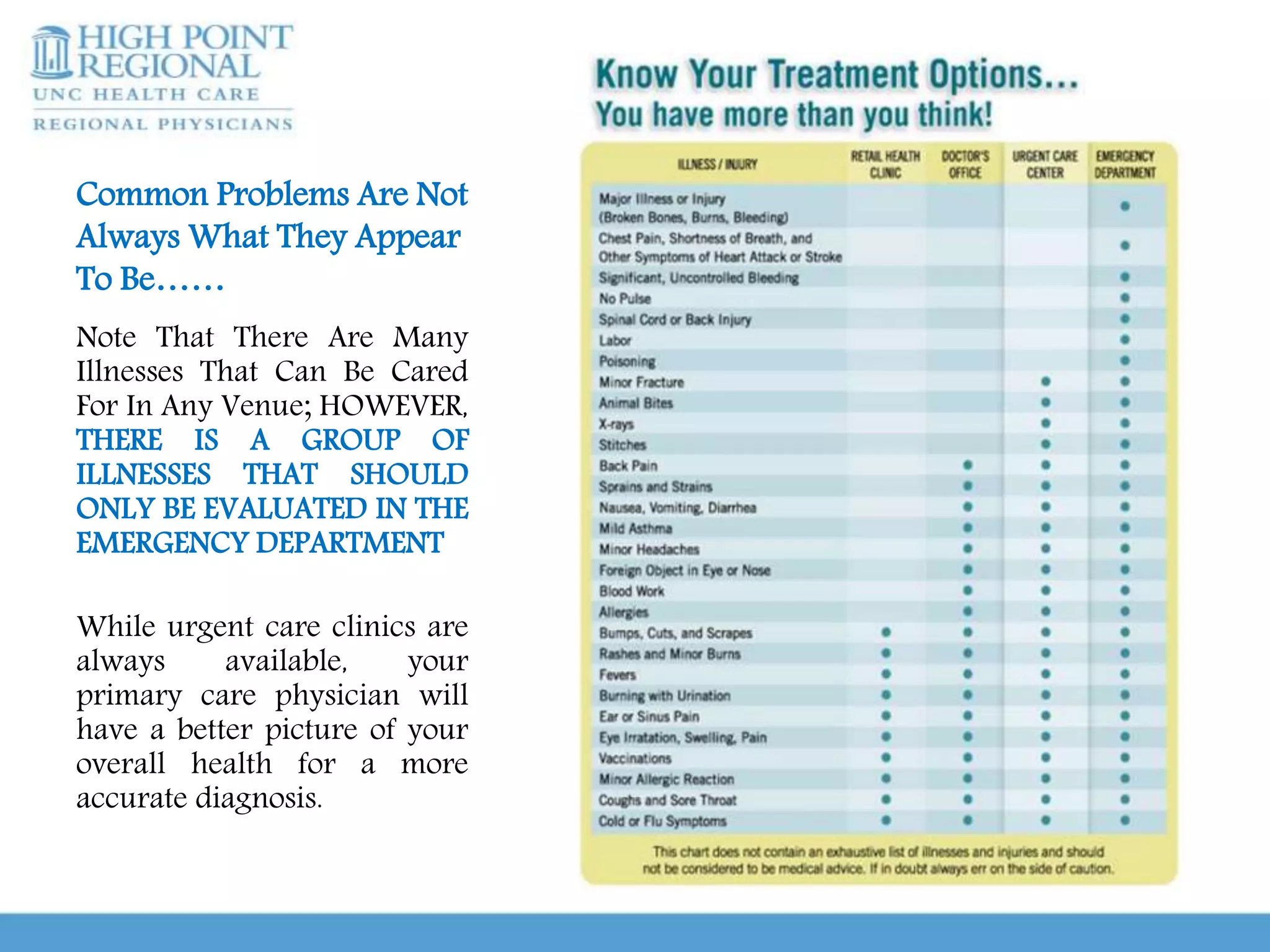
Urgent care clinics and emergency departments provide similar services like extended hours, treatment for all ages, diagnostic testing, and coordination of care. However, they differ in important ways. Urgent care clinics are best for non-emergent care and offer low-cost, high-efficiency treatment, while emergency departments are intended for true medical emergencies and acute issues that could threaten life or limb. It is important for patients to educate themselves on when to use urgent care versus an emergency room in order to receive the right treatment in the right setting. Conditions that generally require emergency care include chest pain, difficulty breathing, severe abdominal pain, injuries, and other issues listed. With guidance and knowledge of options, patients can make