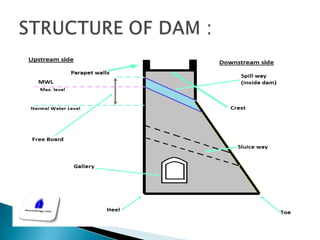
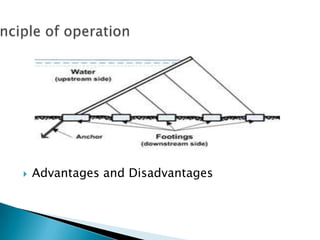
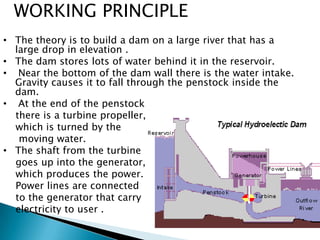
This document summarizes different types of dams and how hydroelectricity works. It describes the main types of dams as arch dams, gravity dams, arch-gravity dams, and embankment dams. It then explains how hydroelectricity is produced by building a dam to store water in a reservoir, which is then released through a turbine to generate electricity. The document also notes some advantages and disadvantages of large hydroelectric plants.