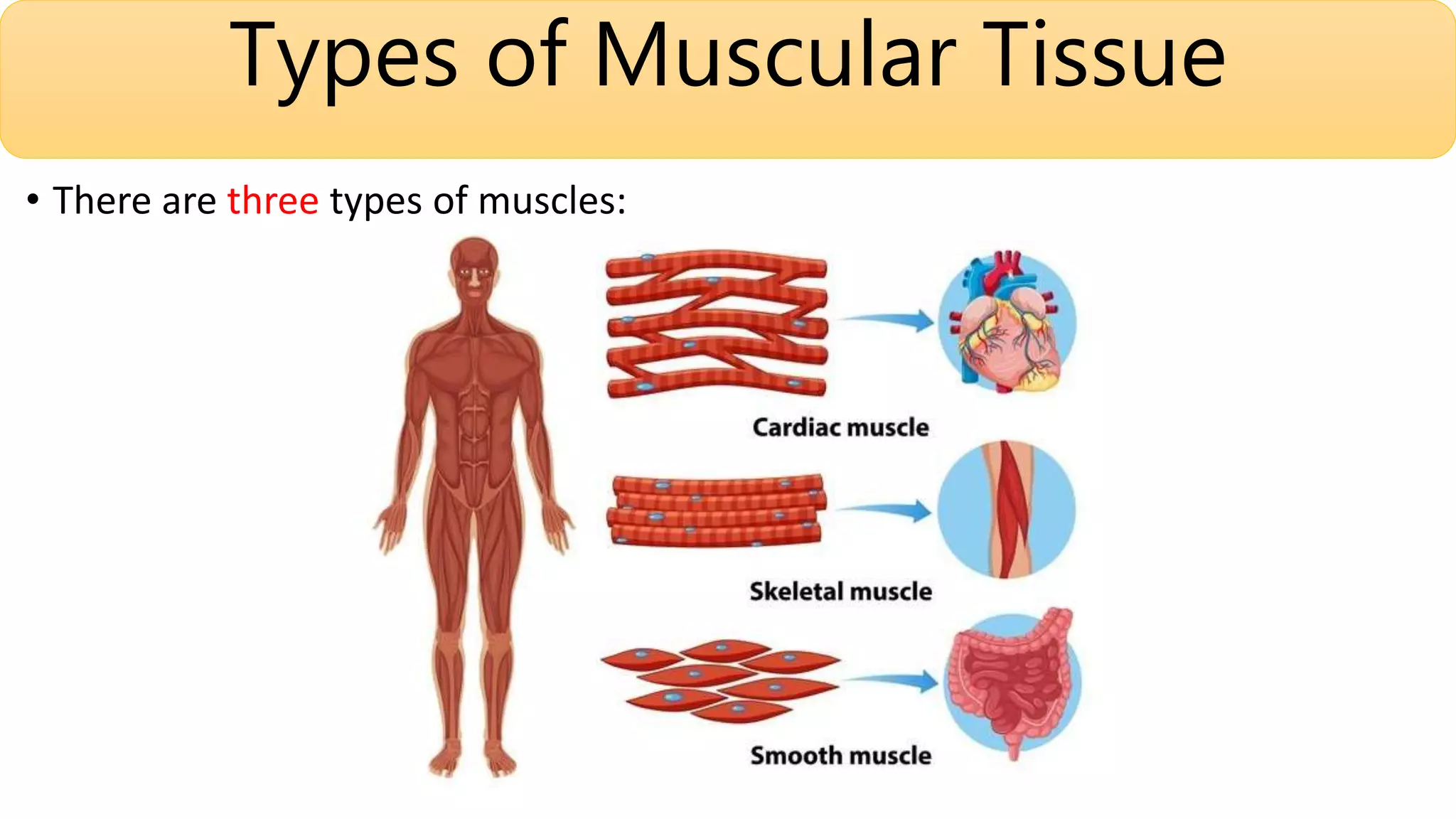
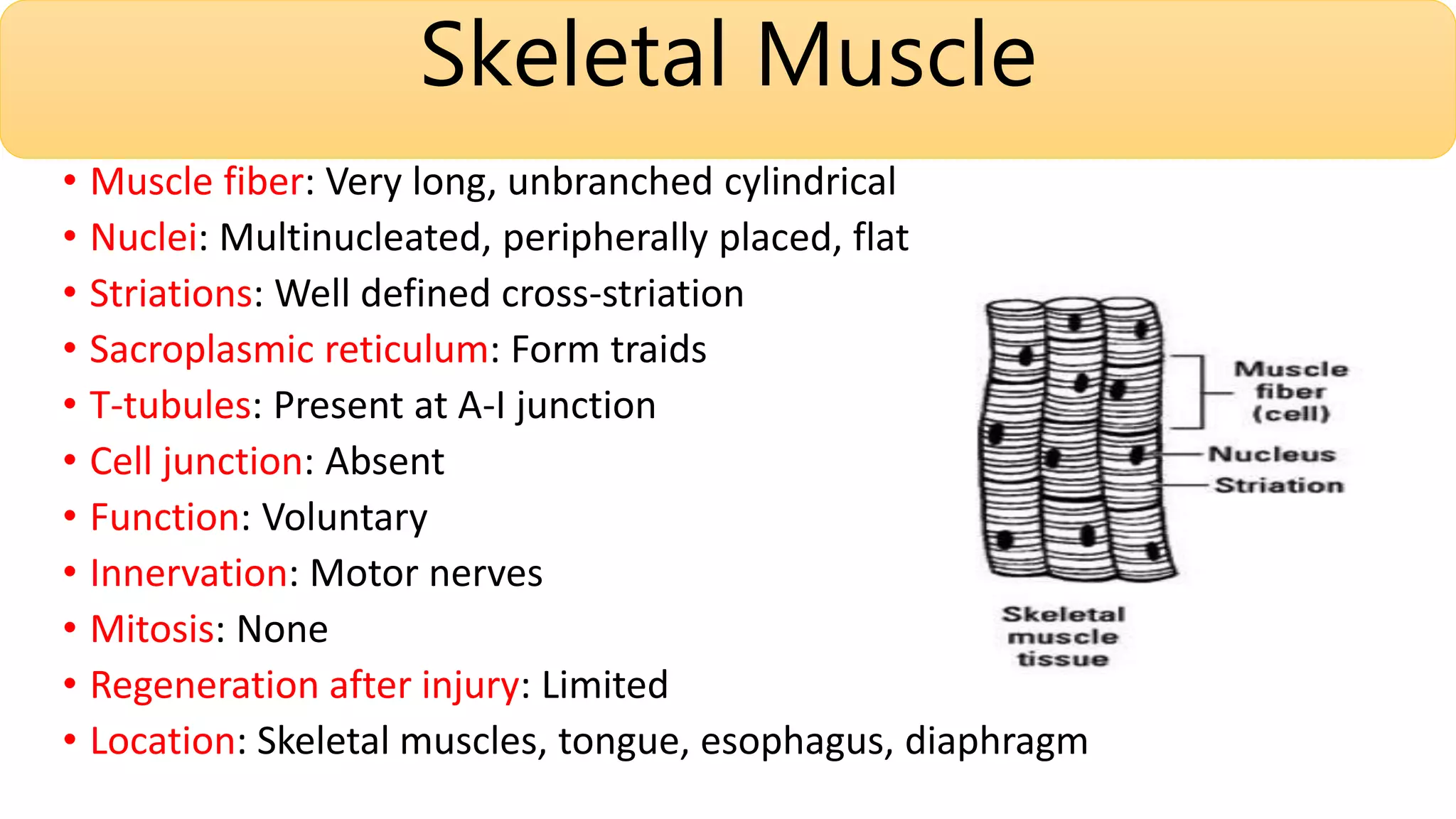
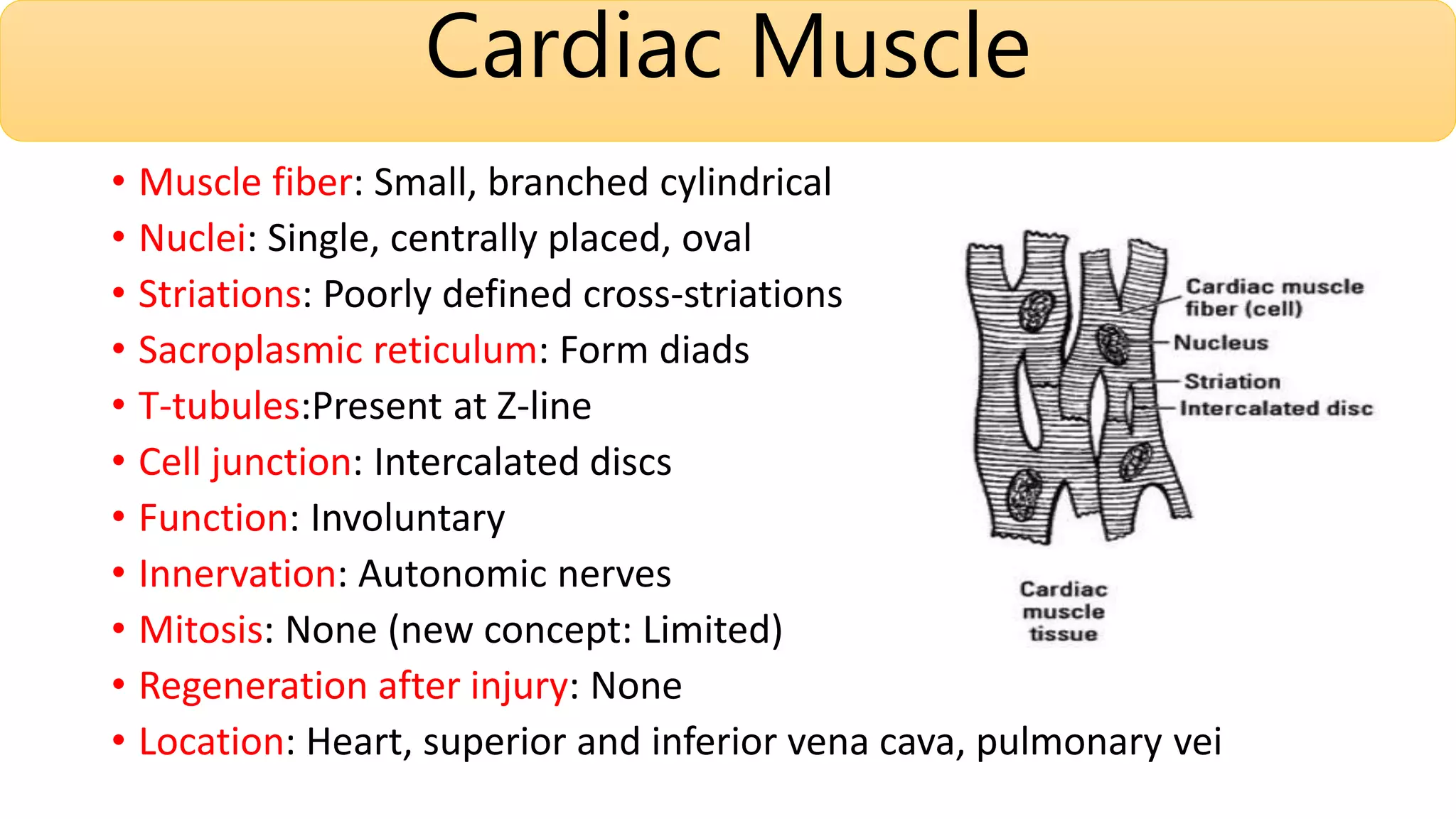
This document summarizes the three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is striated, voluntary, and found in locations like the tongue and diaphragm. Cardiac muscle is found in the heart and has intercalated discs. Smooth muscle is spindle-shaped, involuntary, and regenerates after injury in locations such as blood vessels. Each type of muscle tissue has distinct characteristics including nuclear shape, presence of striations, junction type, and regeneration ability.