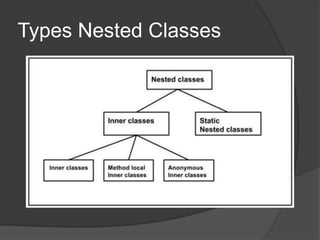
The document explains nested classes in Java, detailing how they are defined within another class, termed the outer class. It distinguishes between non-static nested classes and static nested classes, including subtypes like inner classes, method-local inner classes, and anonymous inner classes. Additionally, it describes how static nested classes can be accessed without instantiating the outer class while noting their limitations in accessing instance variables of the outer class.