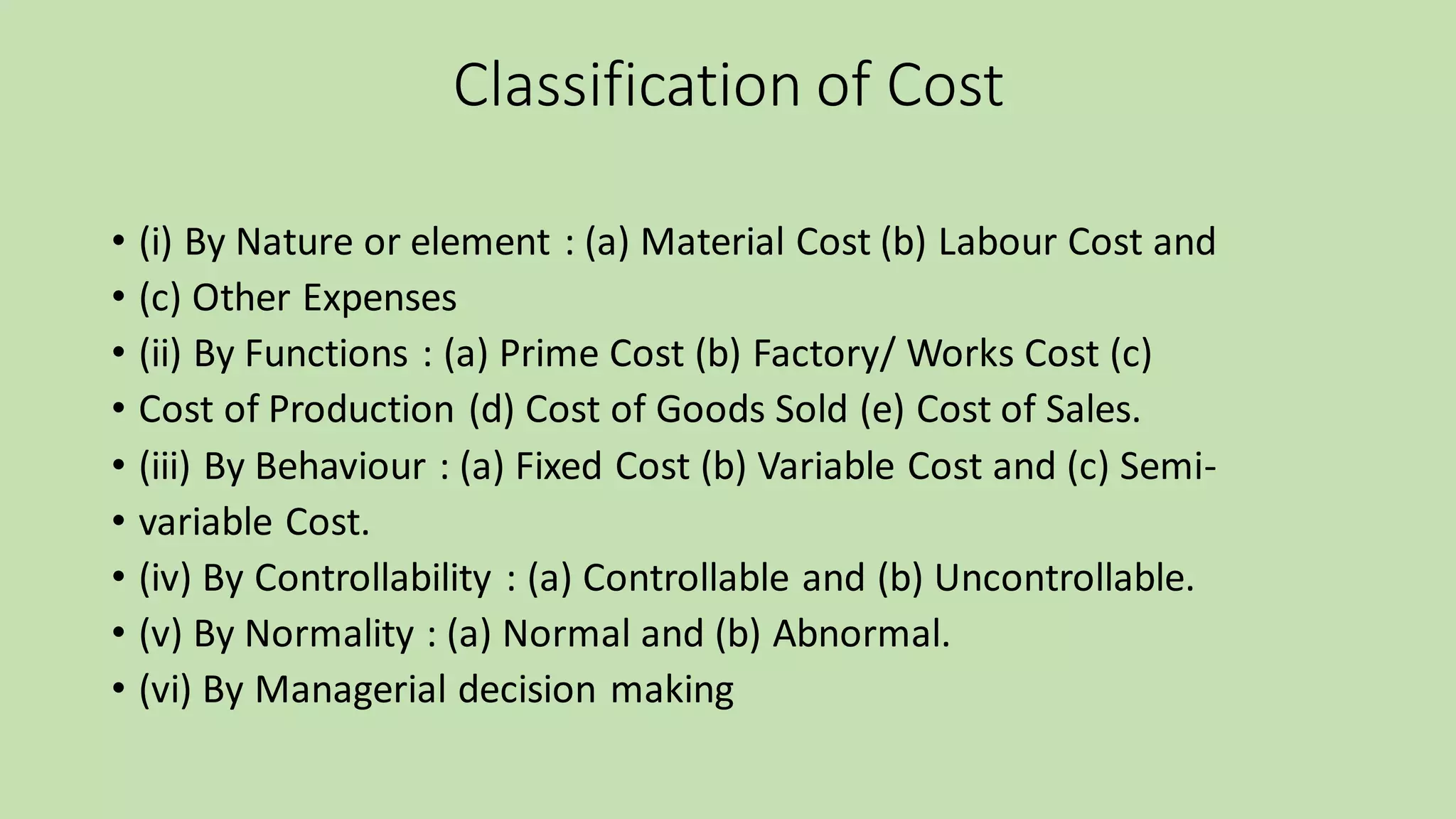
The document outlines several advantages and disadvantages of costing, classifications of costs, types of costs relevant for managerial decision making, methods of costing, and techniques of costing. The key advantages listed are cost determination, helping reduce costs, product profitability analysis, and providing information for decision making. The disadvantages include the expense of setting up an accounting system and potential duplication of recording costs. Costs are classified by nature, function, behavior, controllability, normality, and for decision making. Methods include job, process, batch, contract, and single/output costing. Techniques include uniform, marginal, standard/variance, historical, direct, and absorption costing.