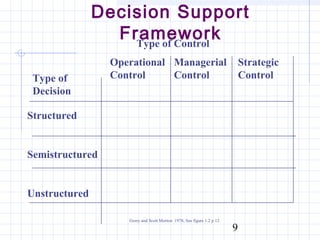
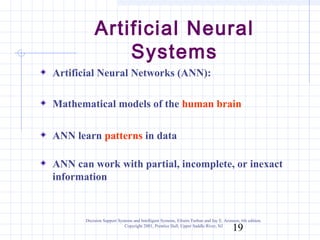
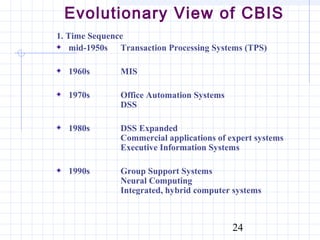
The document discusses various types of management support systems that can help with managerial decision making, including decision support systems, expert systems, intelligent agents, neural networks, and knowledge management systems. It covers the evolution of these computerized decision aids from early transaction processing to more advanced integrated and hybrid systems. The goal of management support systems is to improve the quality, speed, and consistency of managerial decisions through leveraging data, models, and artificial intelligence technologies.