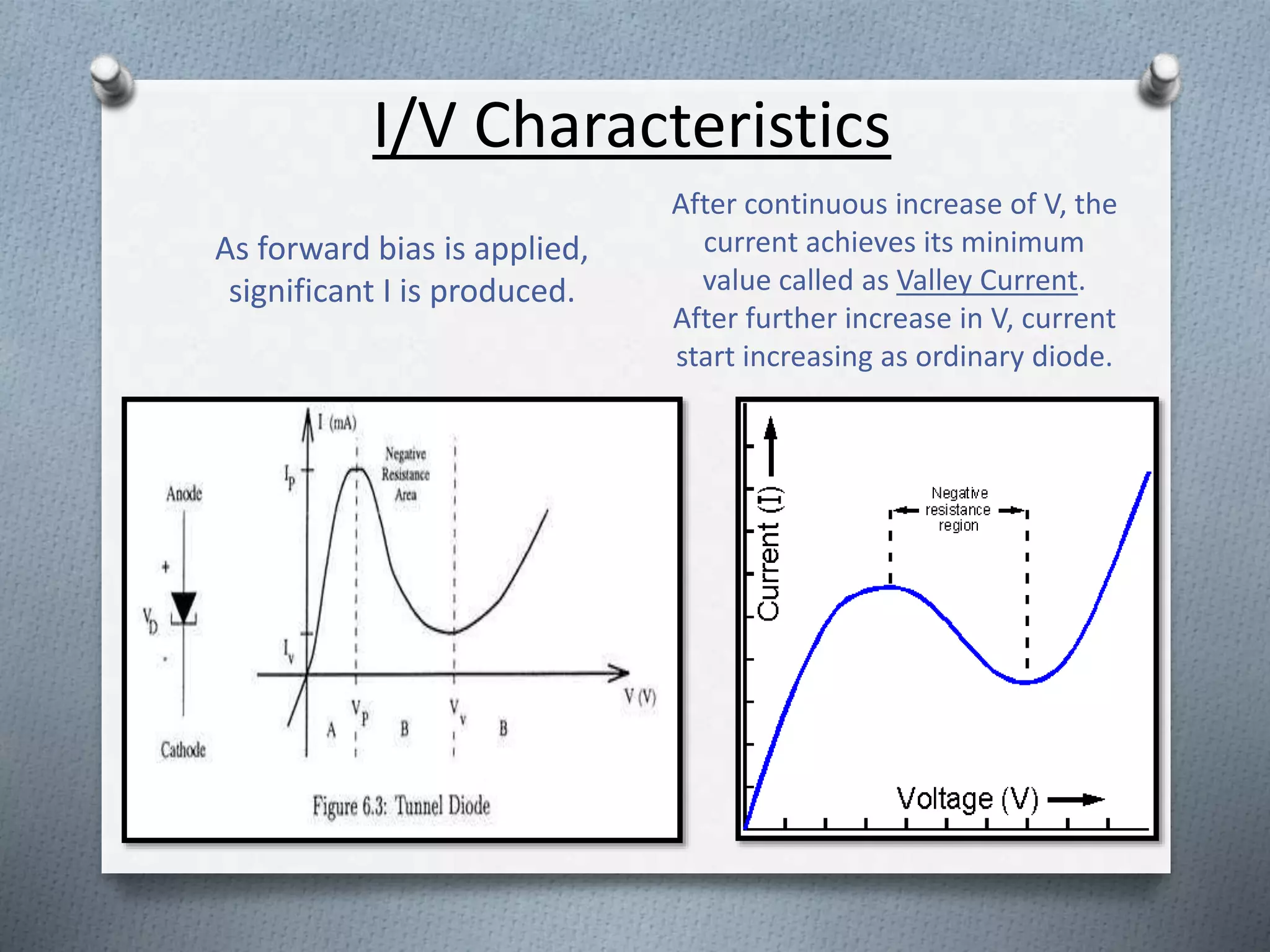
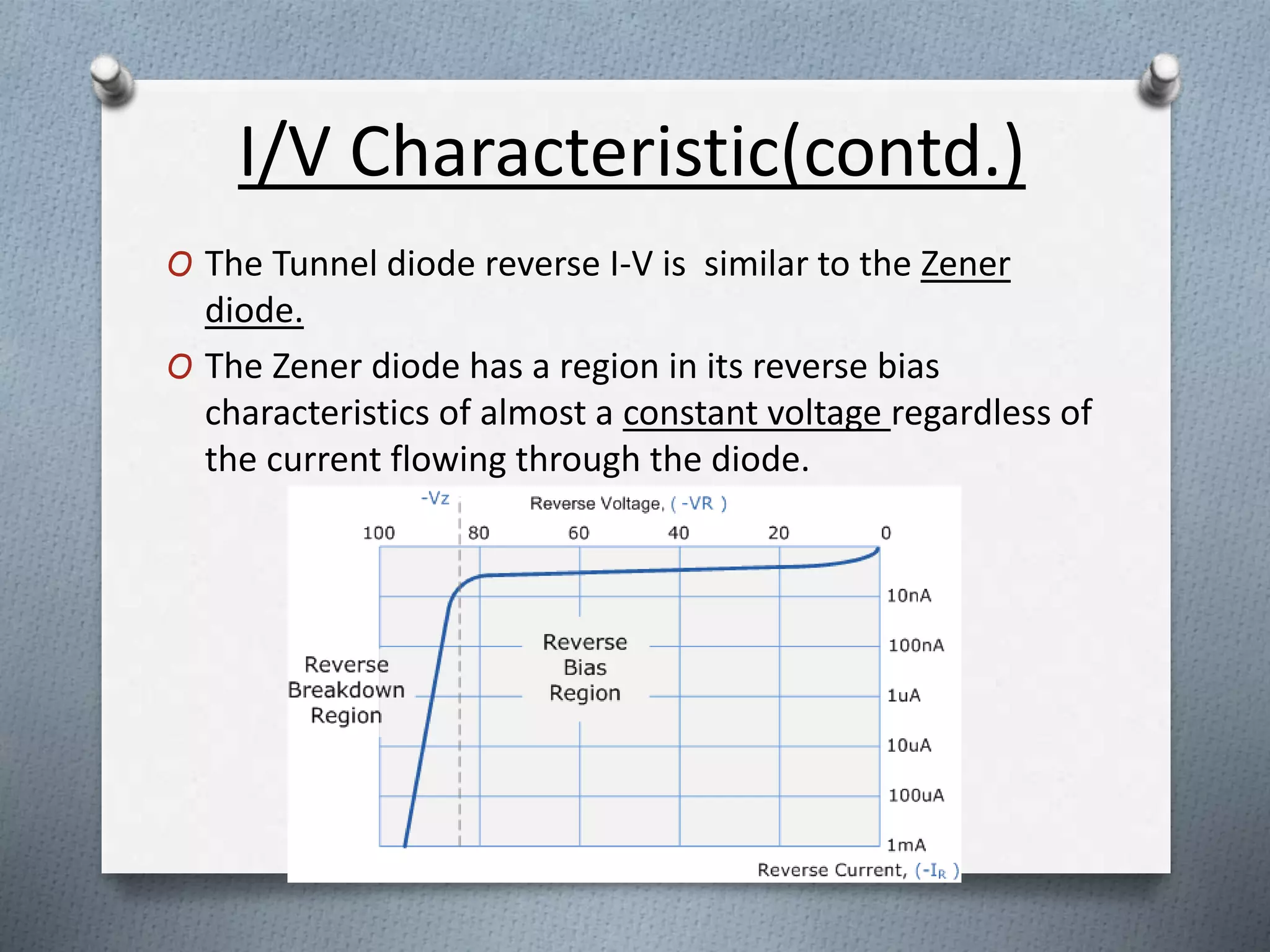
The document describes the tunnel diode, which was invented in 1958 and exhibits negative resistance. It consists of a heavily doped PN junction with doping density around 1000 times greater than a regular diode. This heavy doping reduces the depletion width and voltage barrier, allowing electrons to tunnel through the junction even without forward voltage. As voltage increases initially in the forward direction, current also increases due to tunneling but then decreases as states become misaligned, exhibiting negative resistance. Tunnel diodes find applications in oscillators, switches, and memory due to their ability to conduct at very high speeds through tunneling.