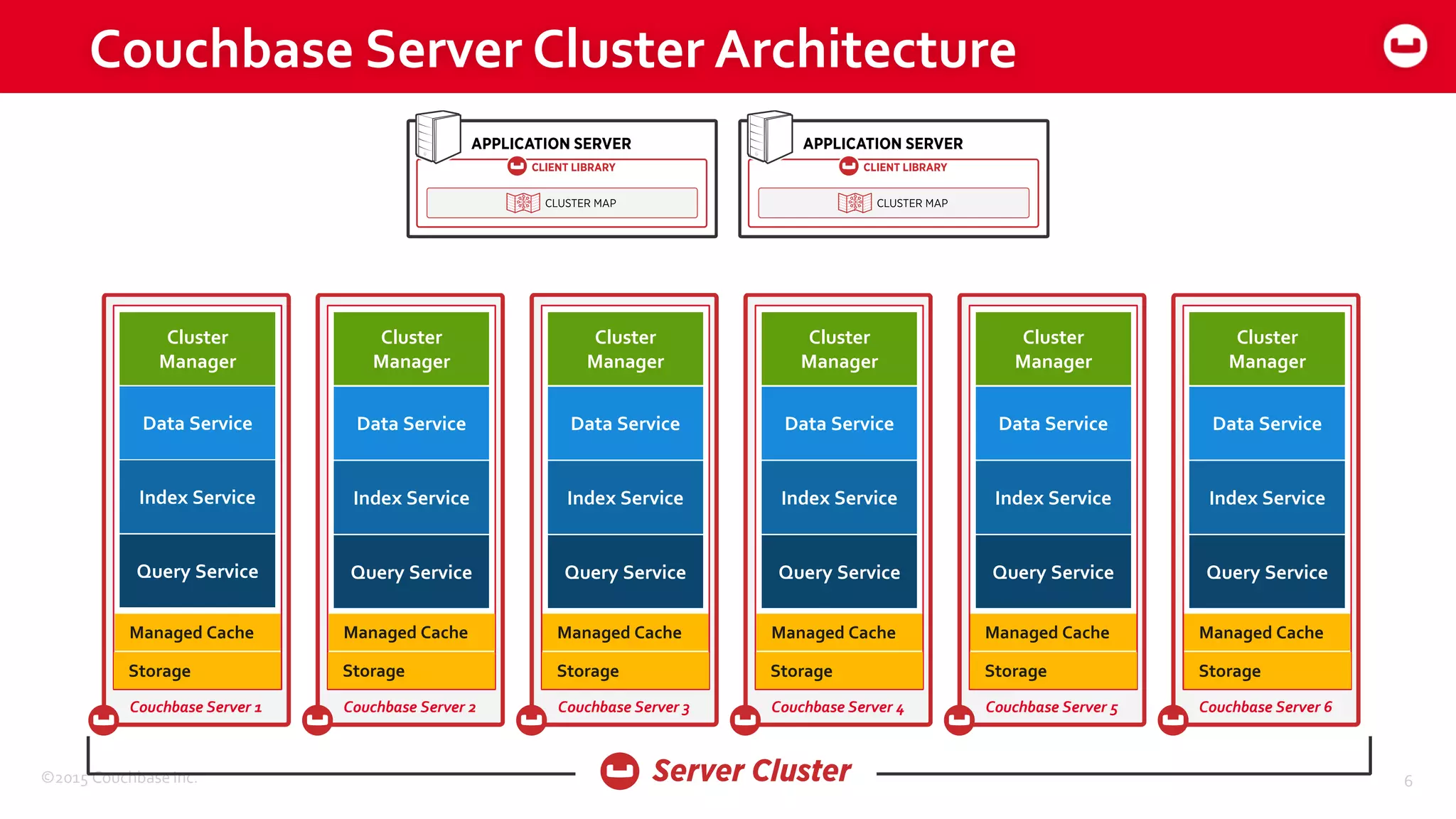
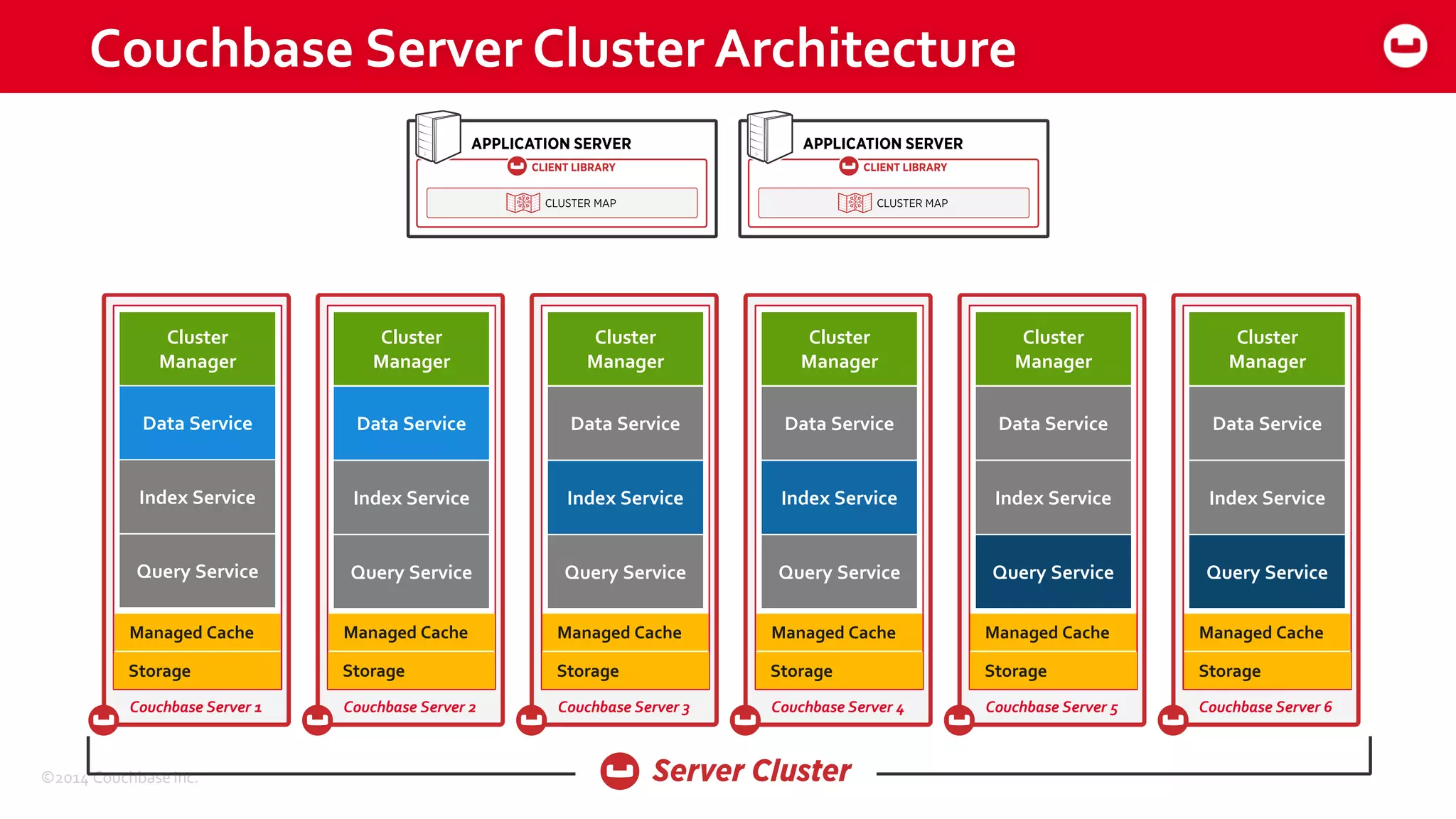
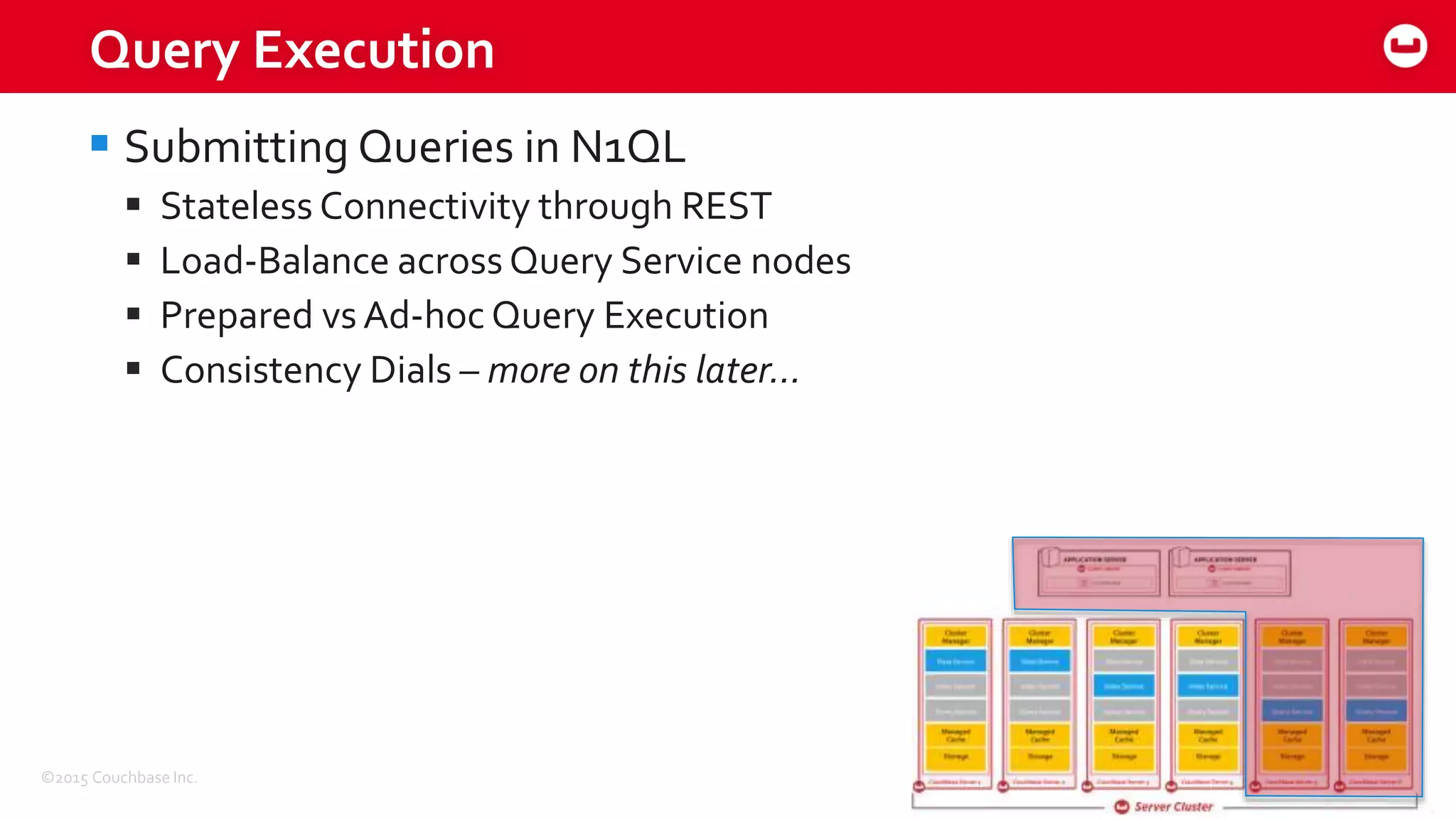
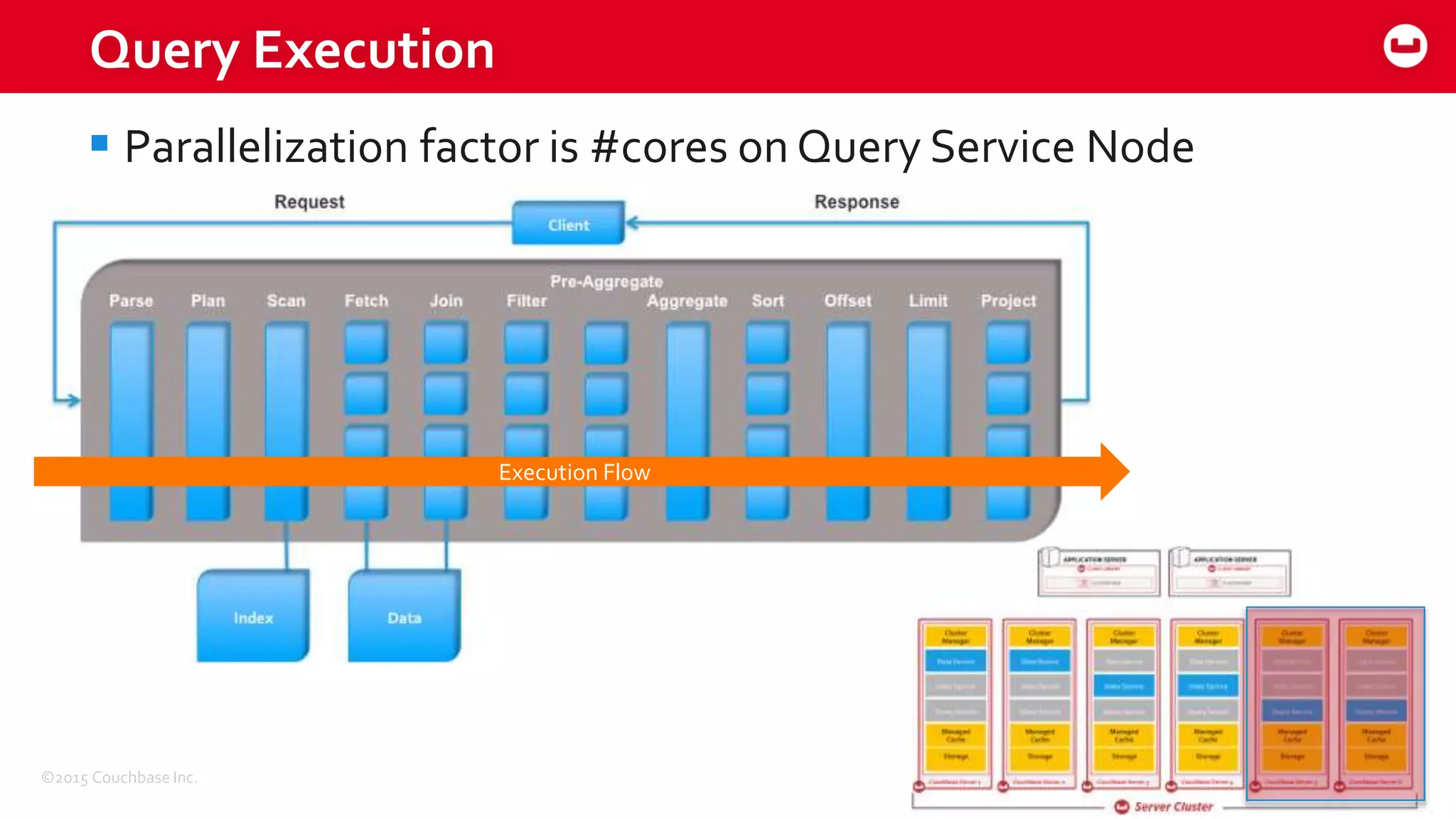
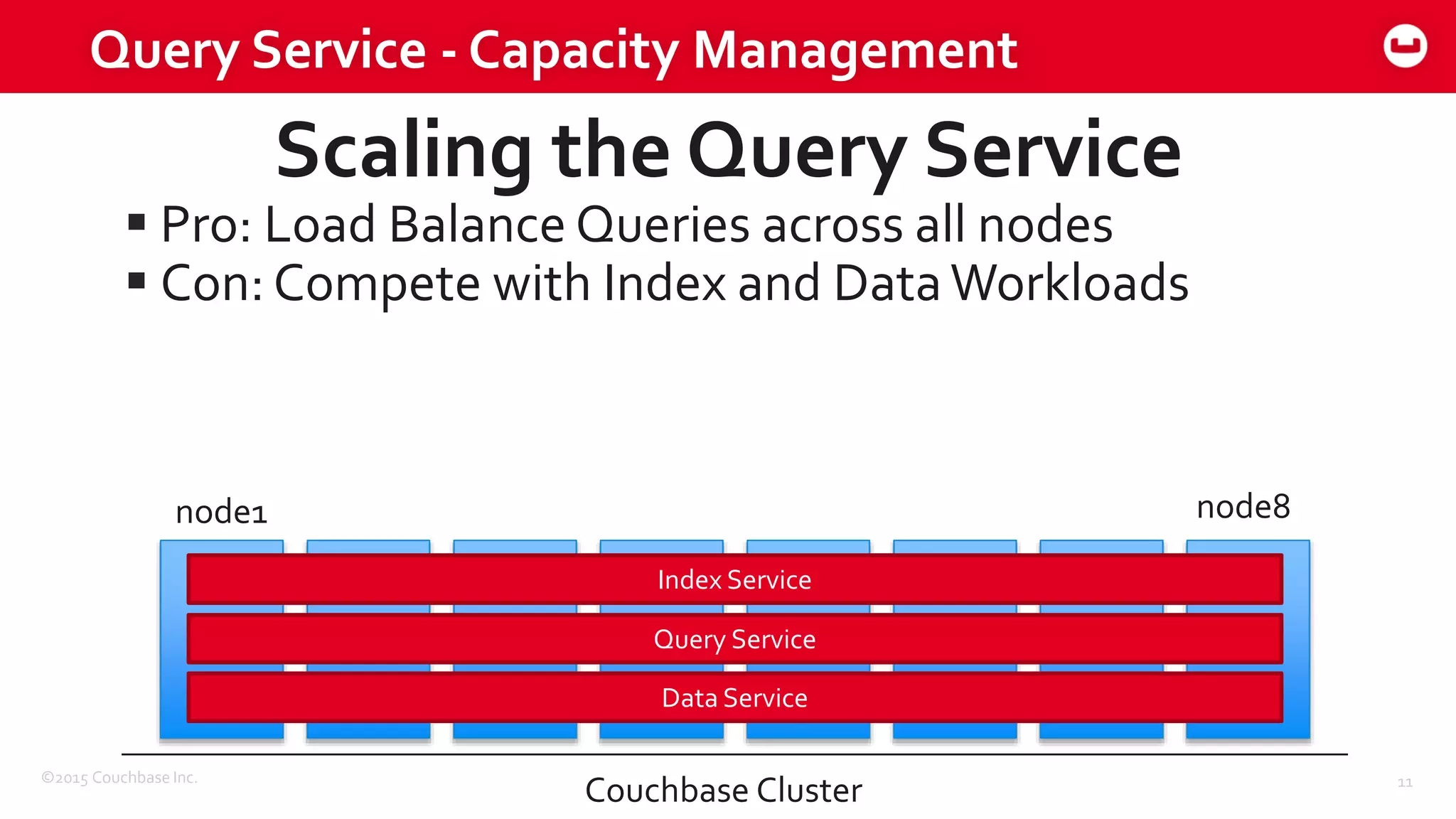
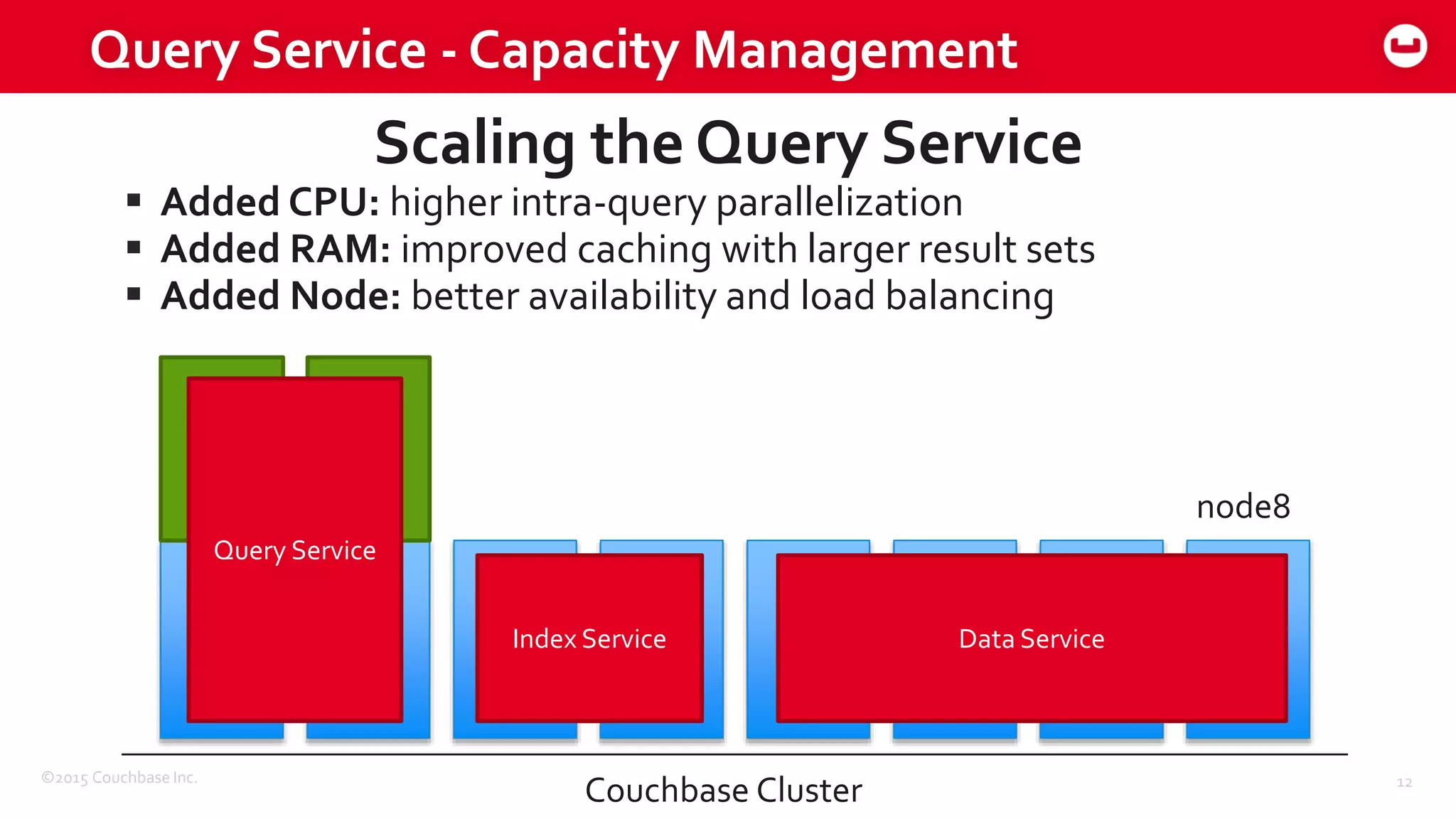
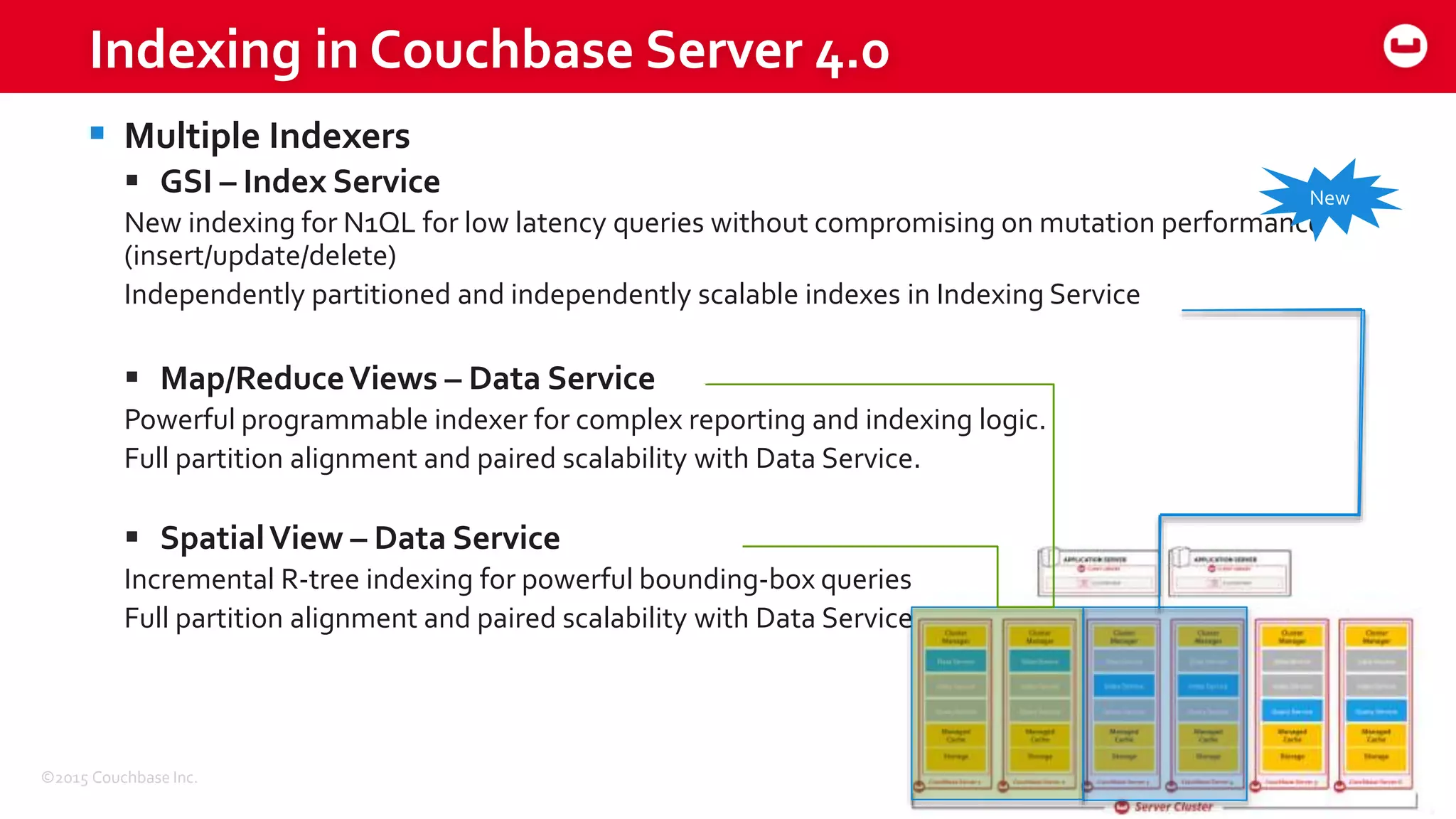
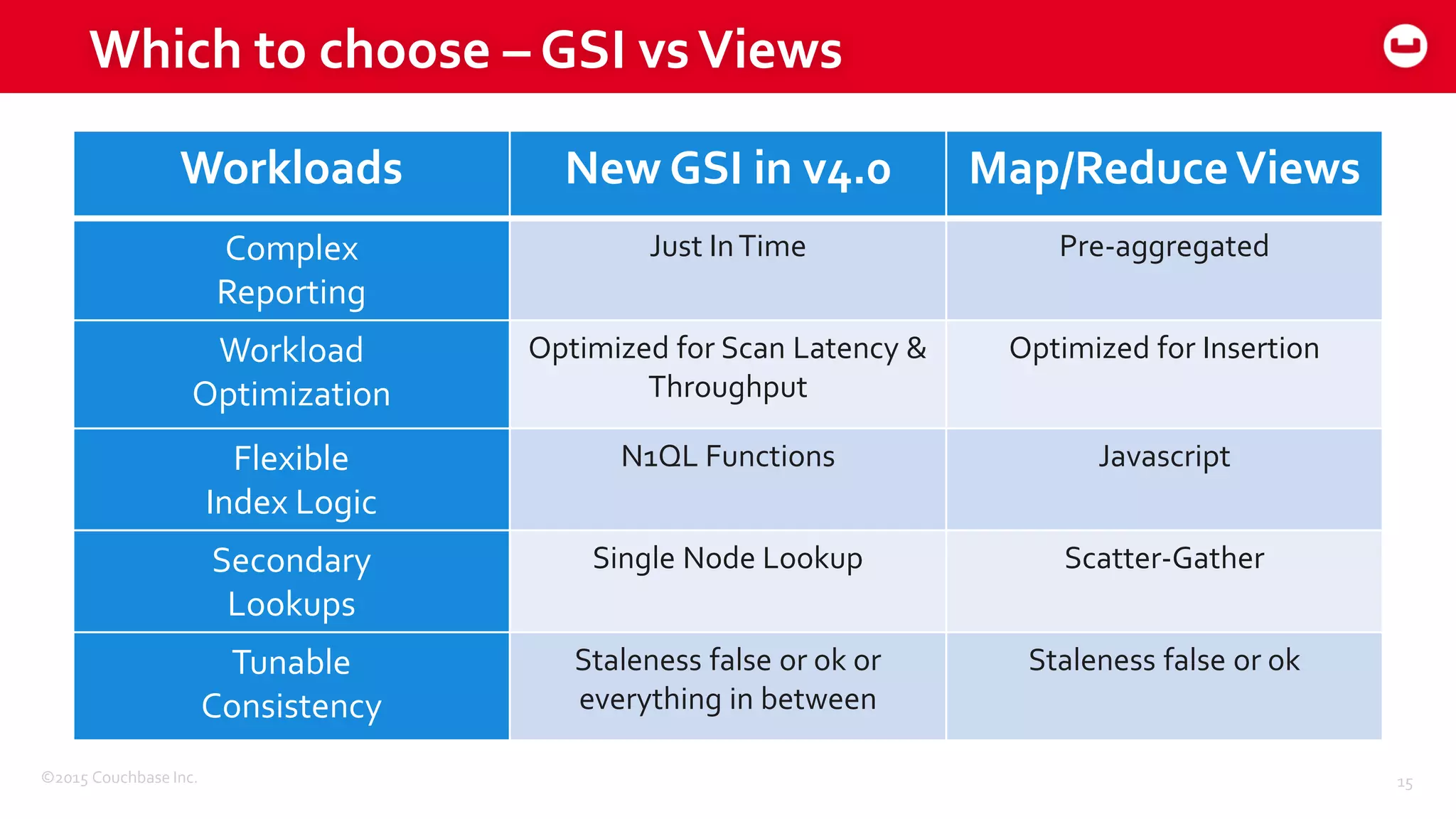
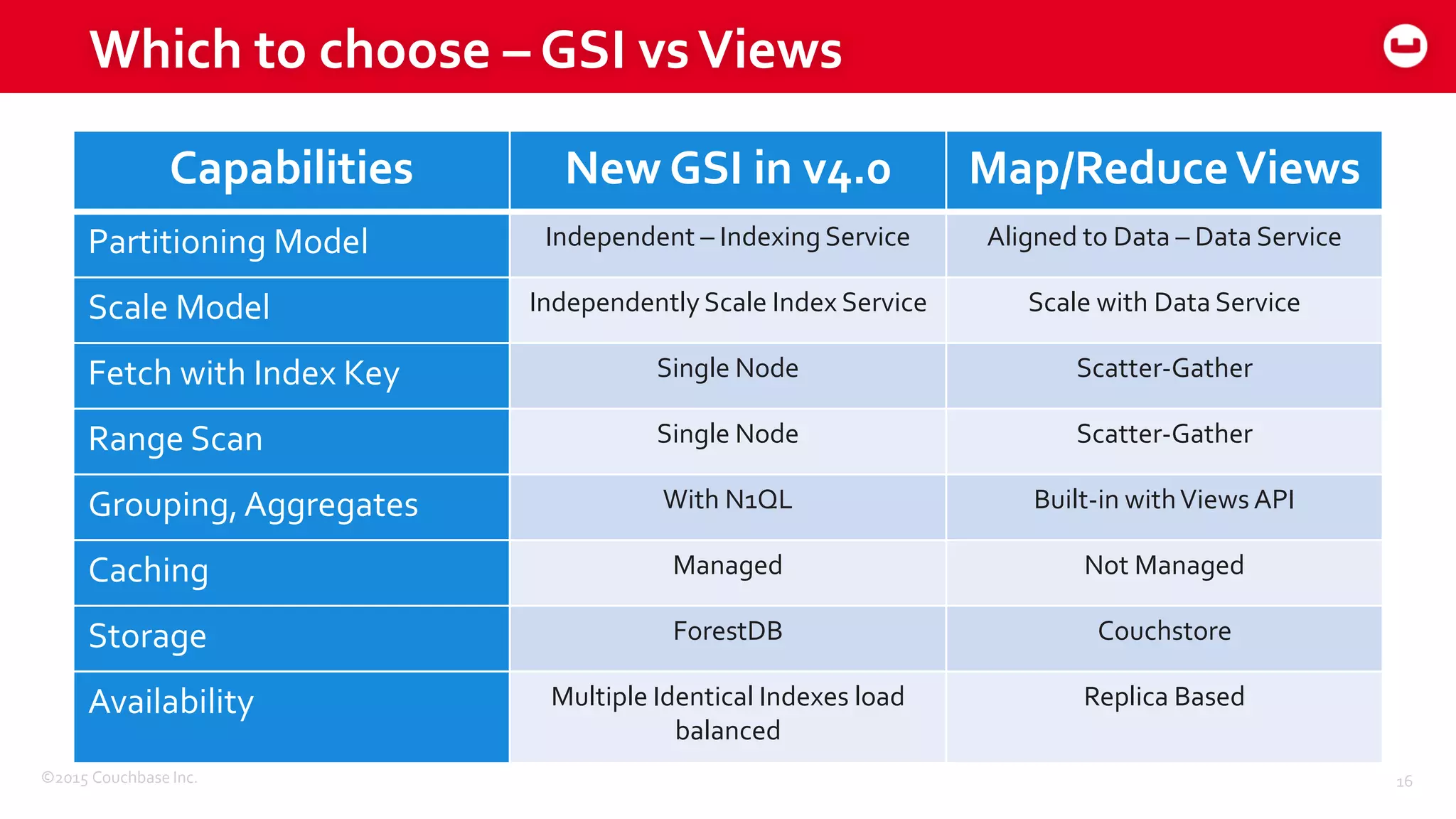
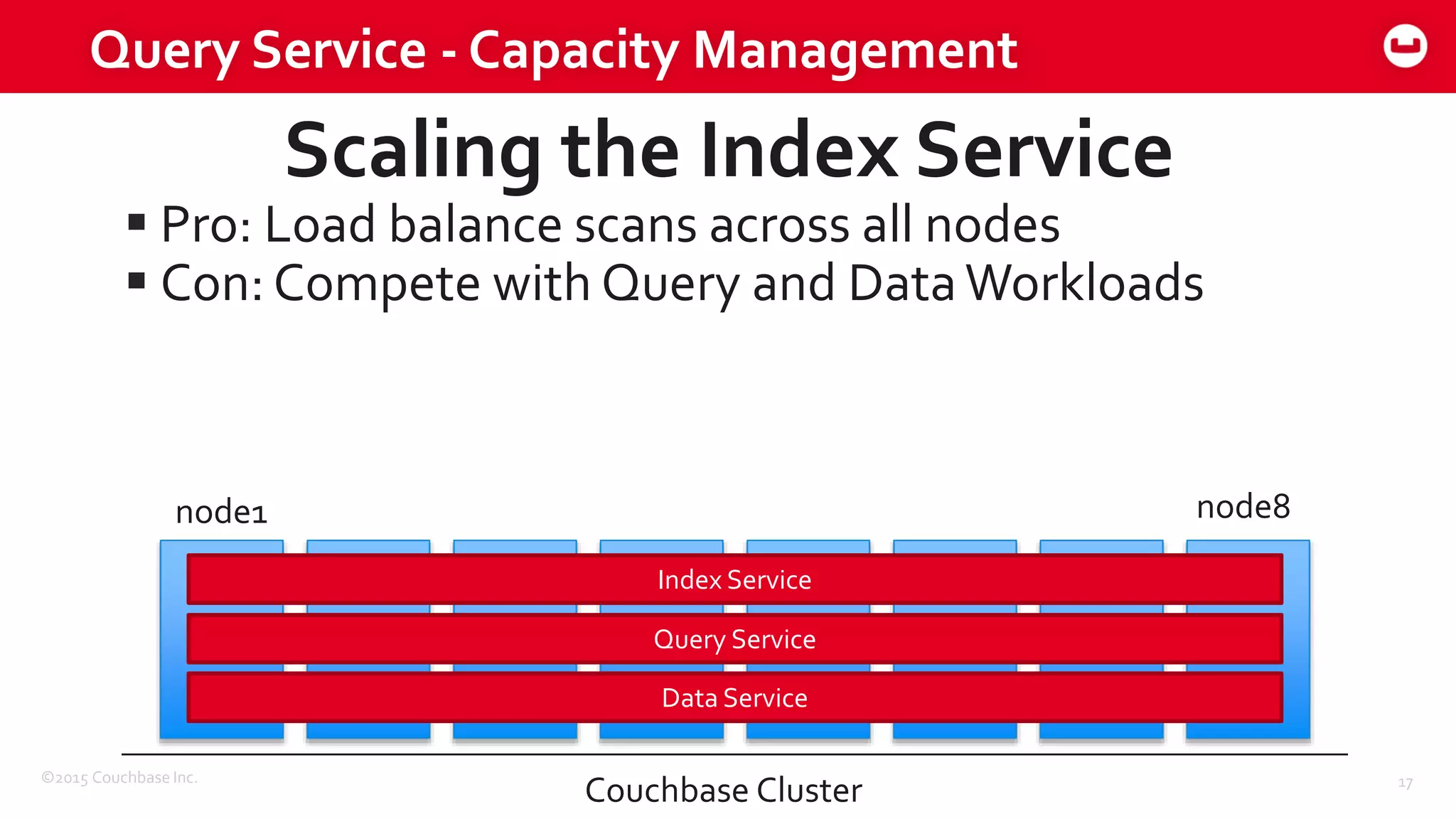
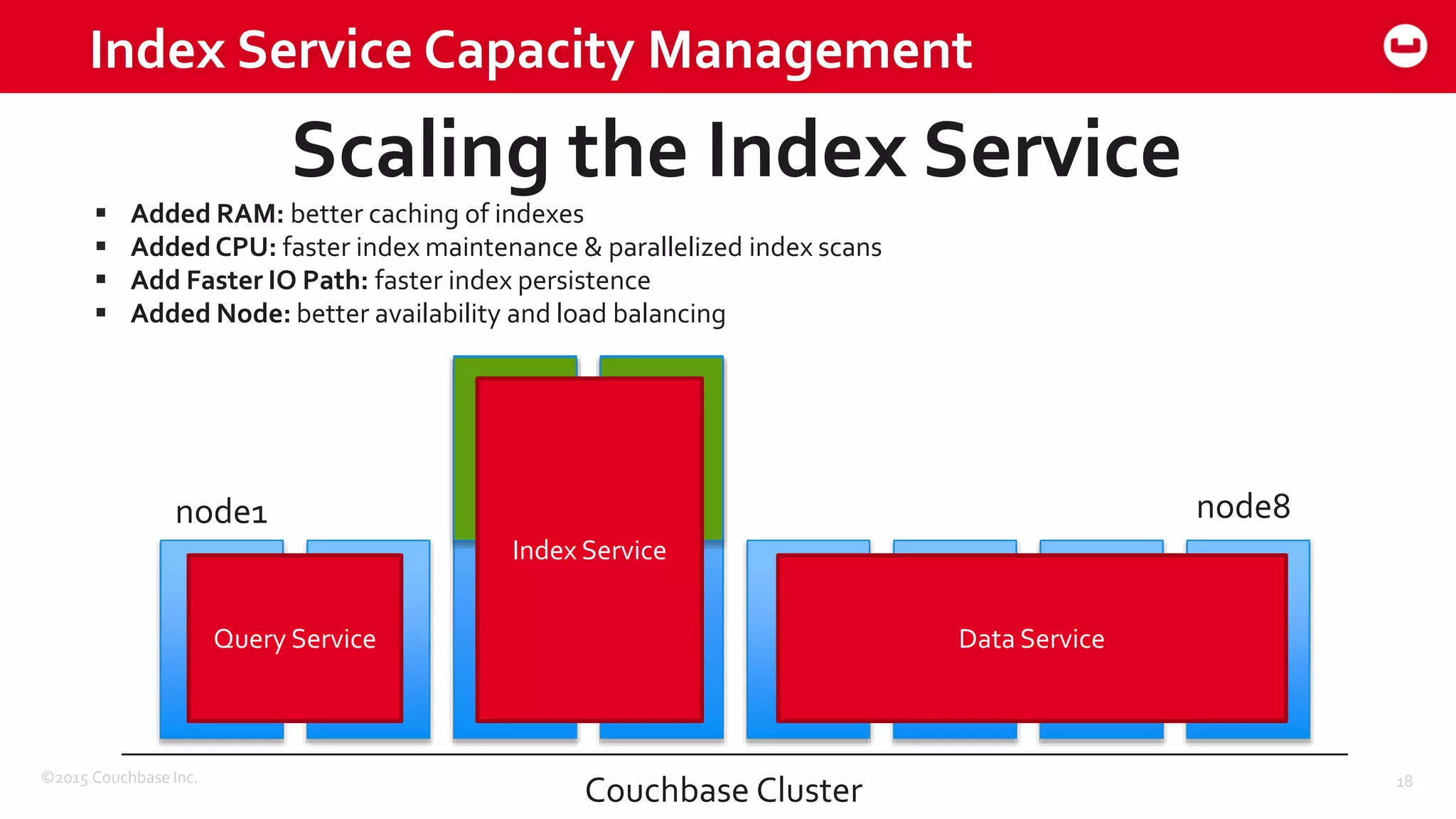
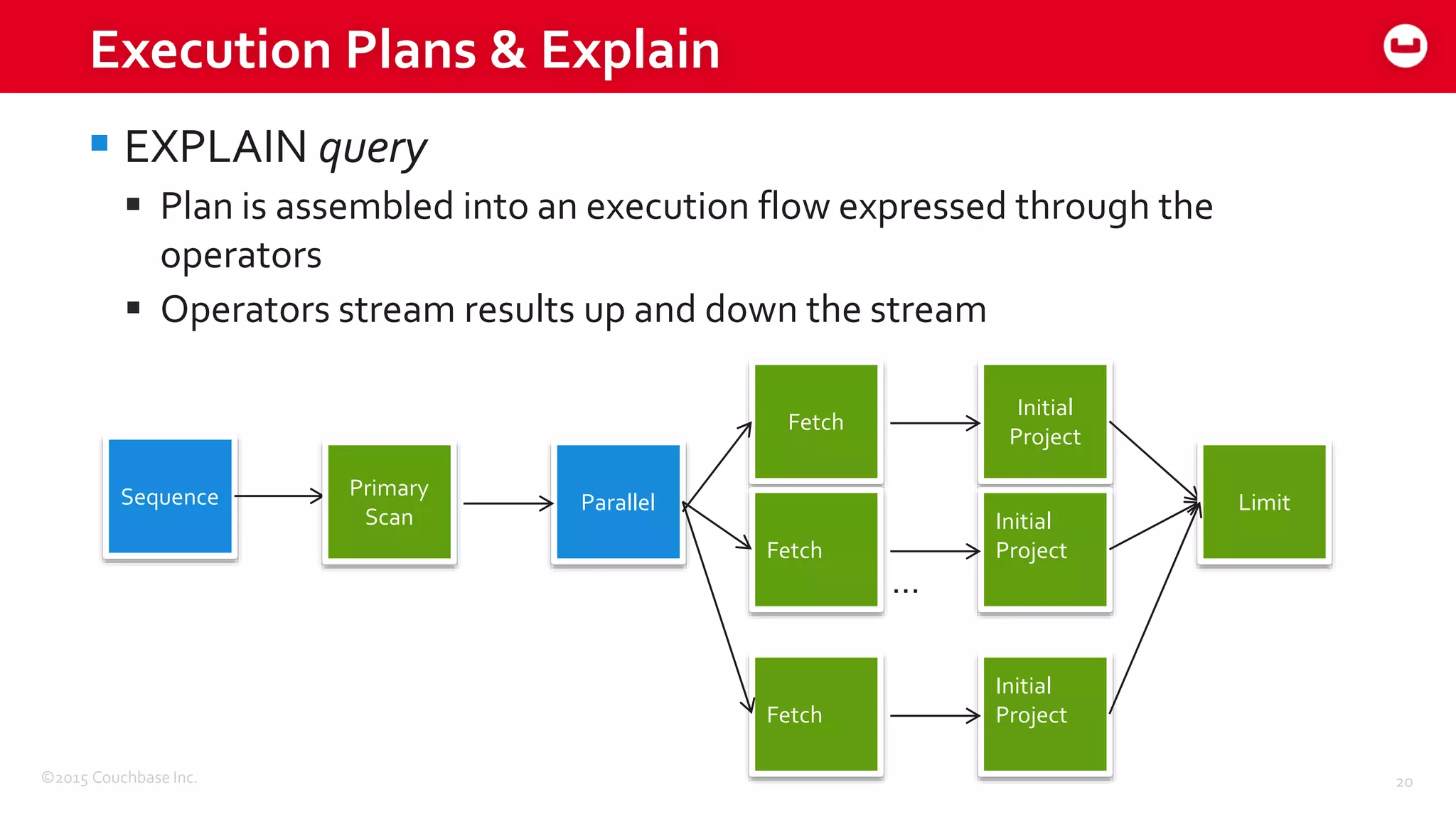
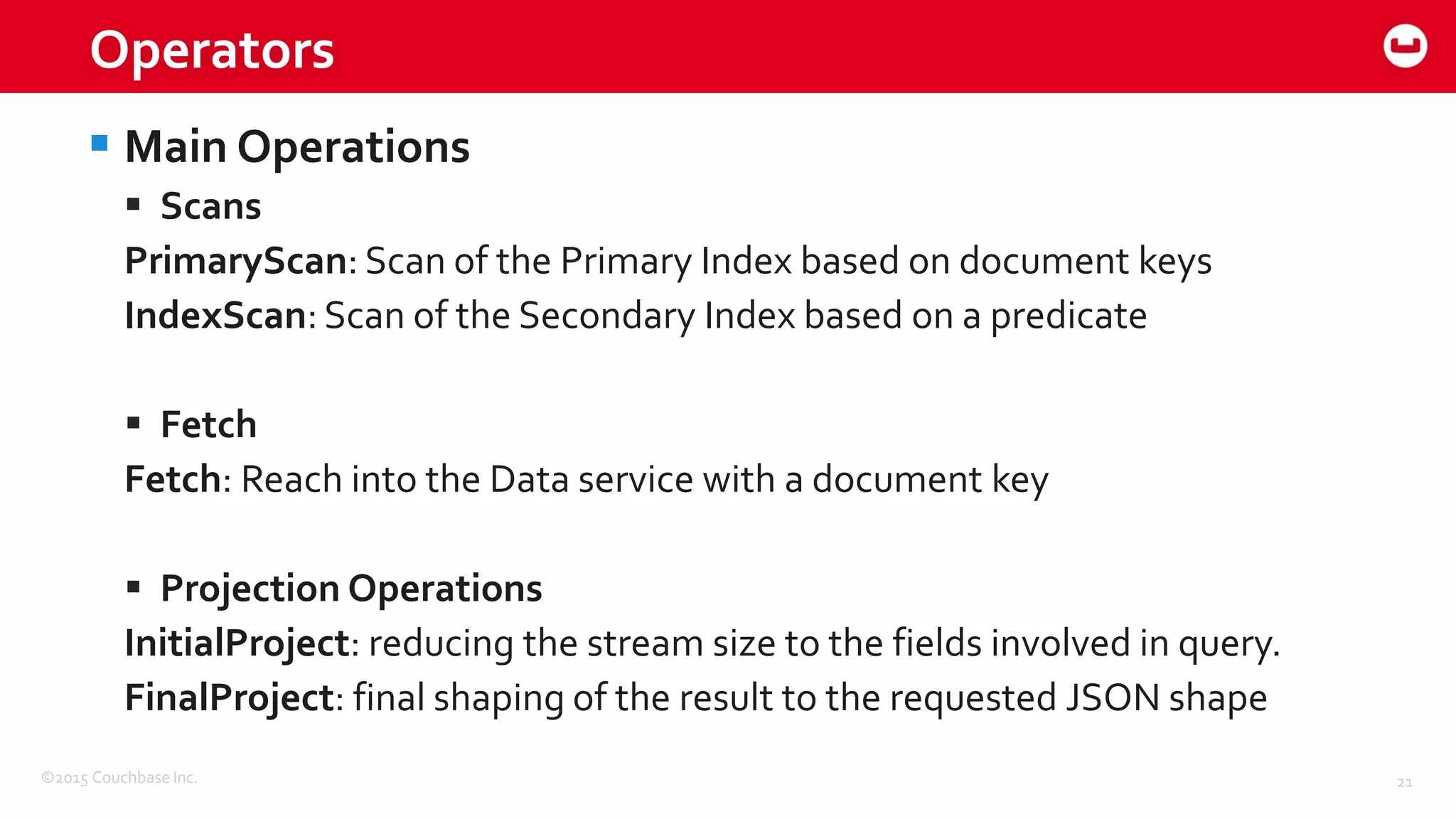
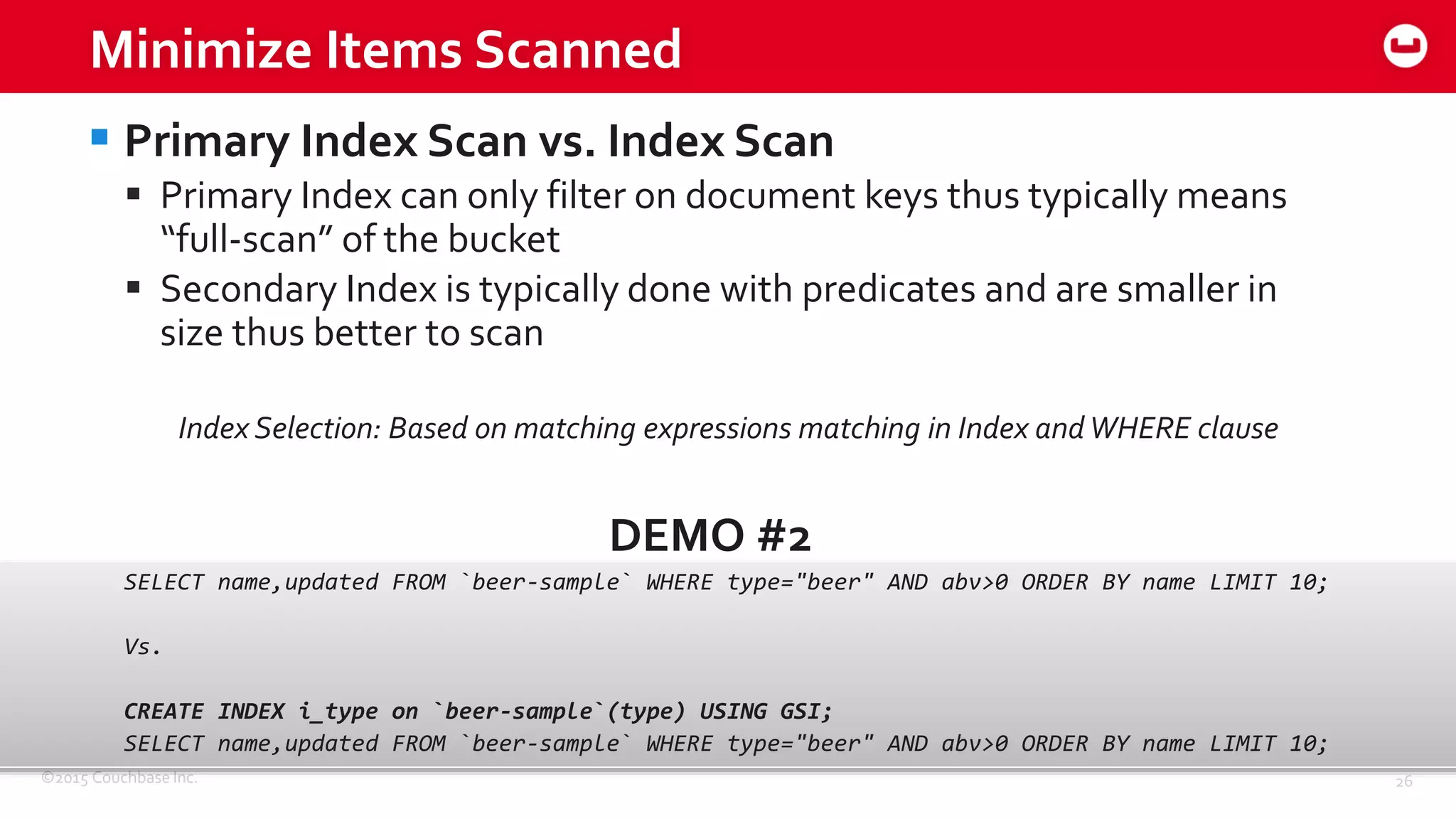
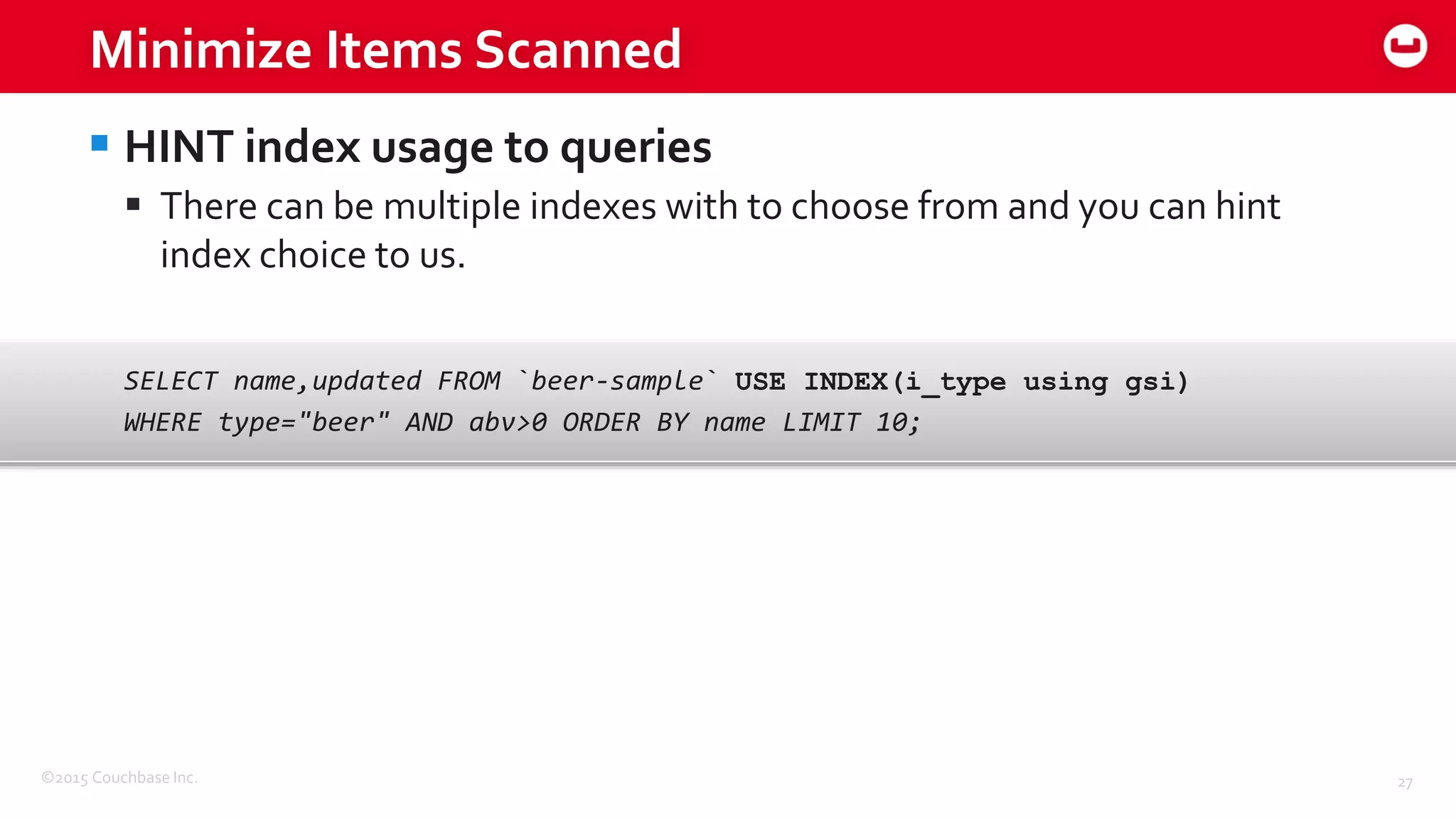
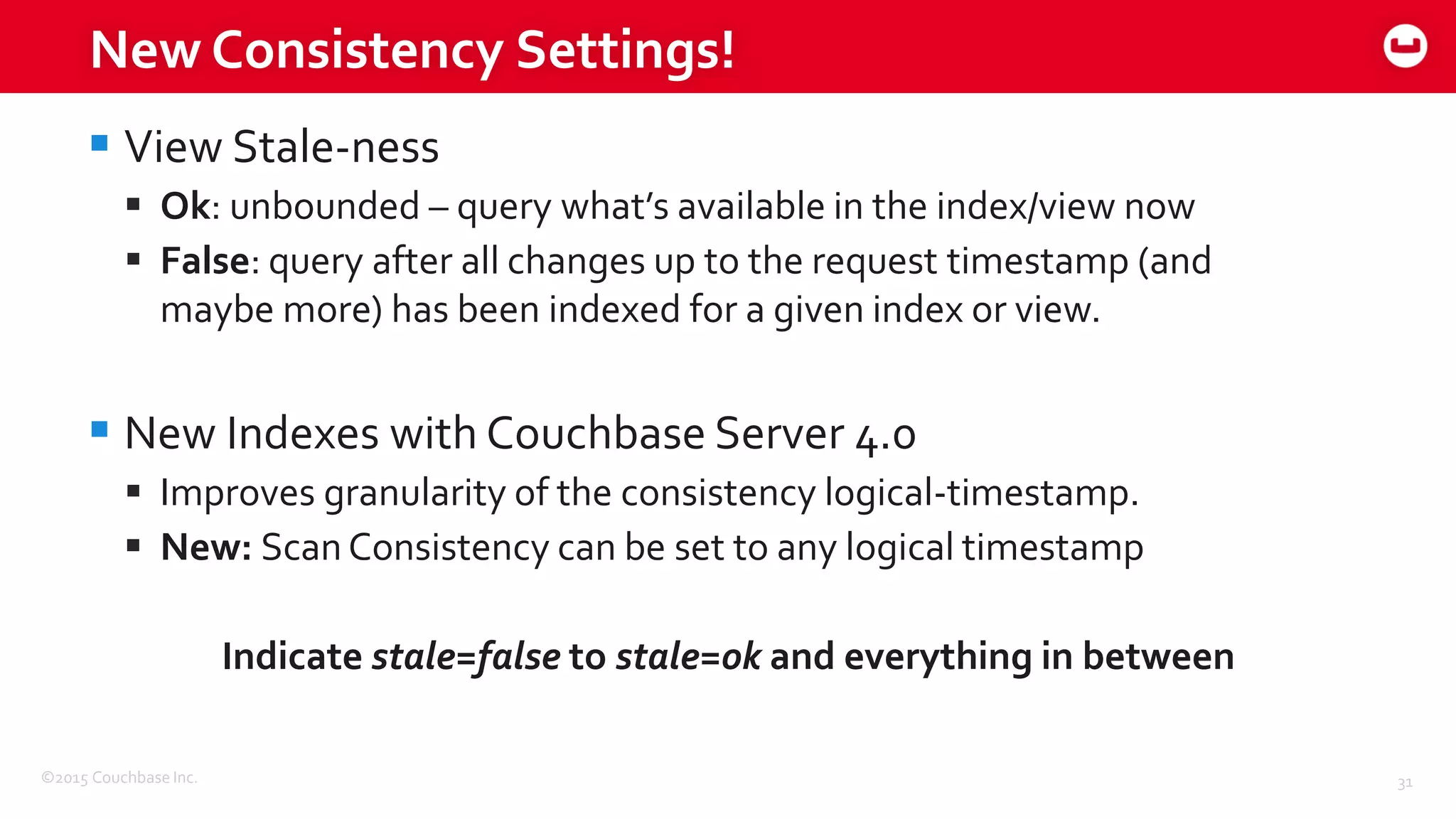
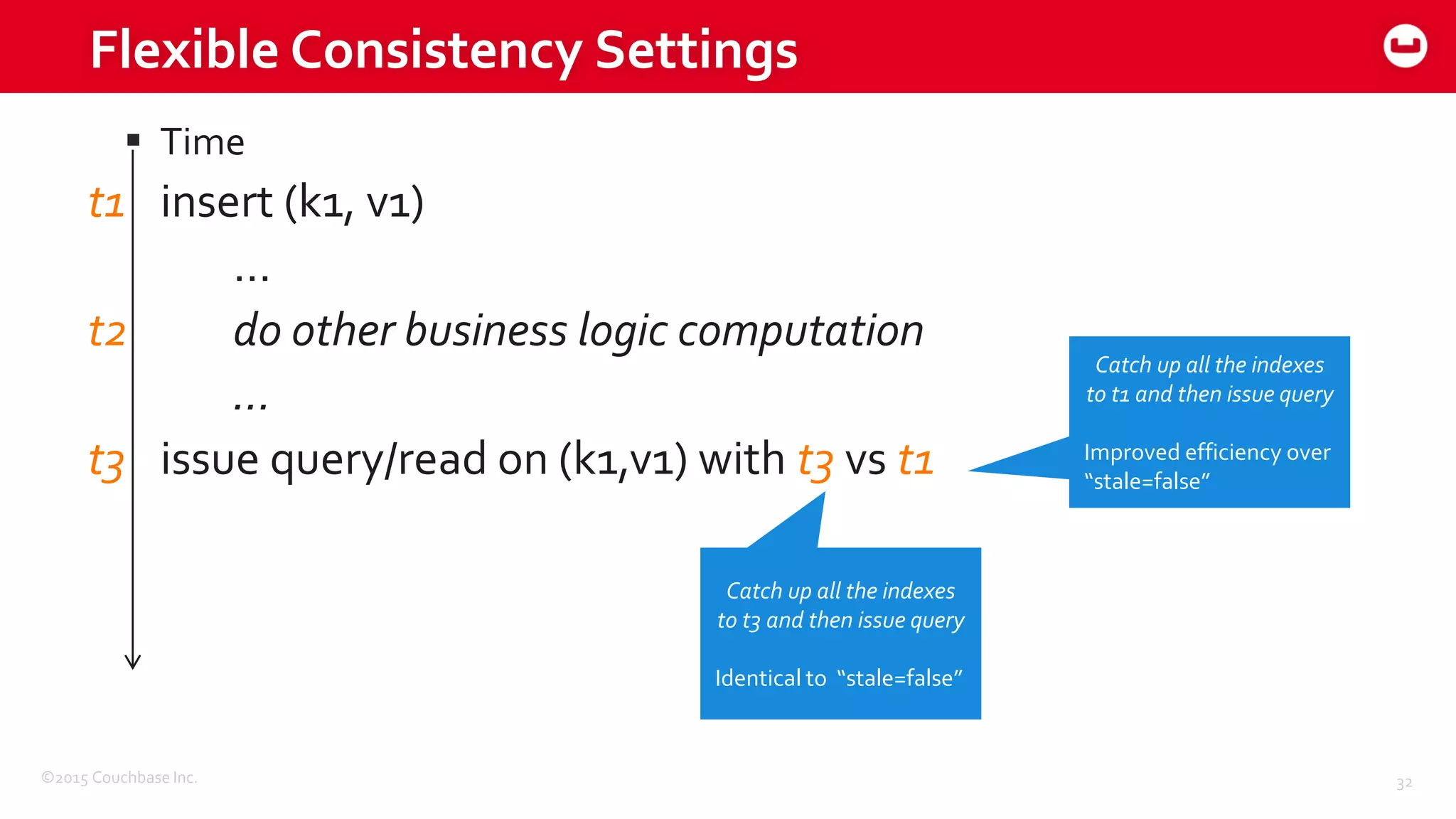
The document discusses optimizing N1QL query performance and scaling in Couchbase Server 4.0, emphasizing architectural overview, query processing, and indexing features. It outlines techniques for tuning queries, including execution plans, optimizing joins, and new consistency settings. Key advancements include improvements in indexing architecture and workload isolation, leading to better performance and scalability.