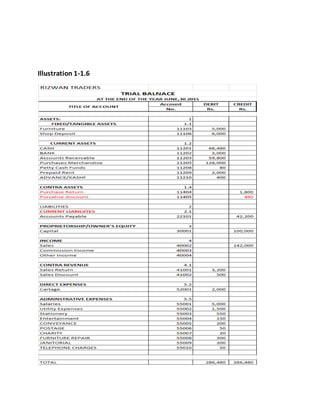
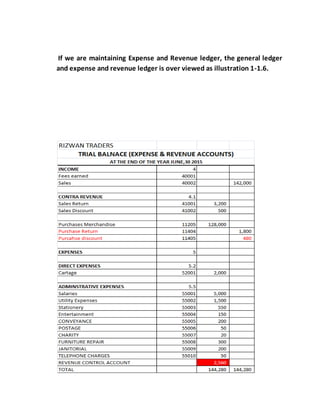
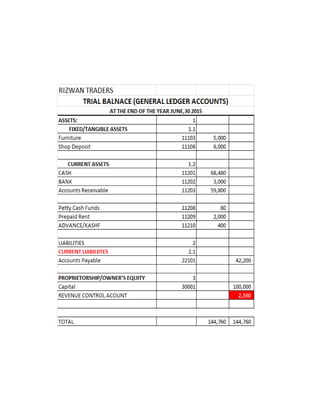
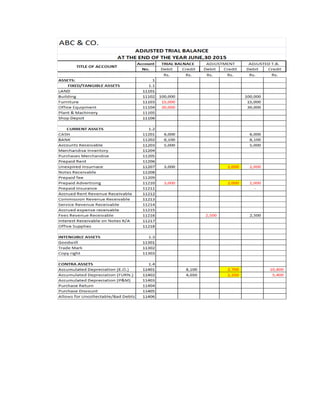
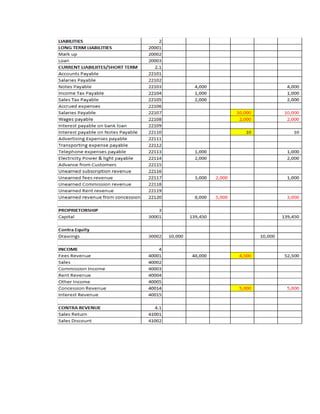
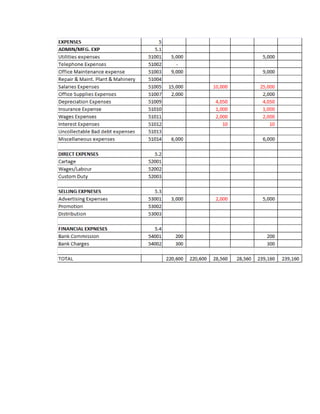
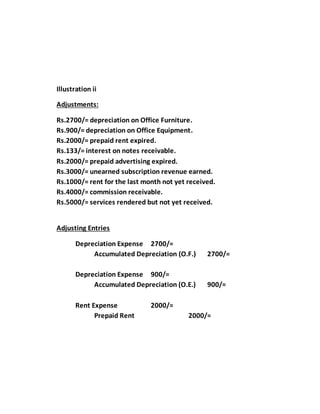
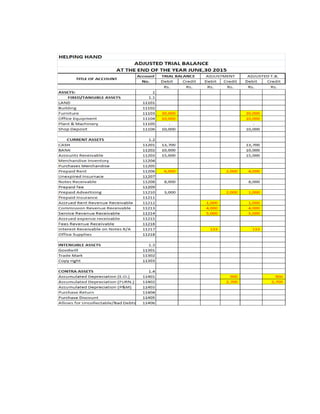
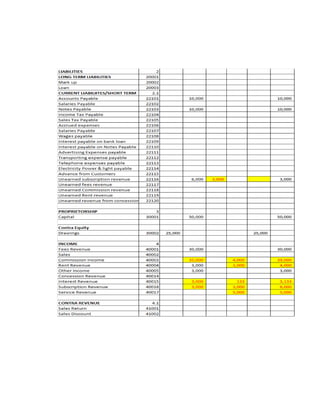
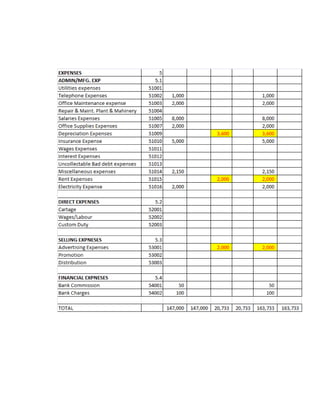
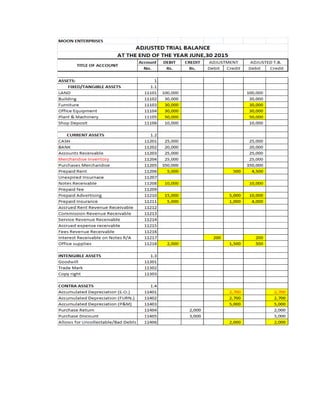
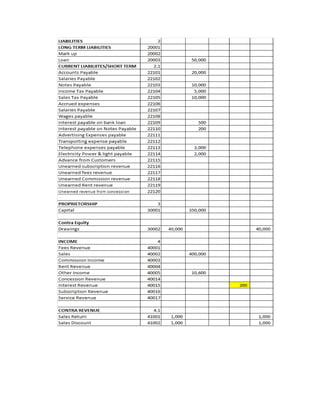
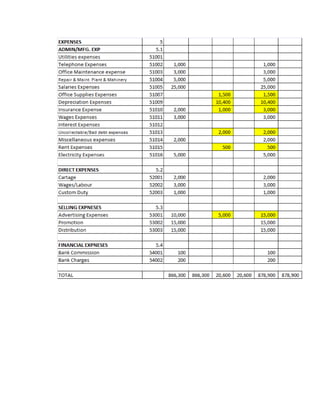
The document provides a detailed explanation of accounting processes including trial balances, adjusting entries, and the management of expenses and revenues. It outlines various adjustments like accrued expenses, unearned revenues, depreciation, and handling bad debts, as well as the steps needed to prepare an adjusted trial balance. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of correcting errors and making necessary entries to maintain accurate account records.