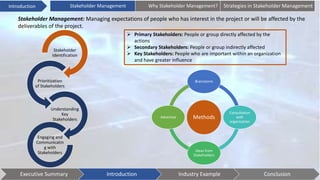
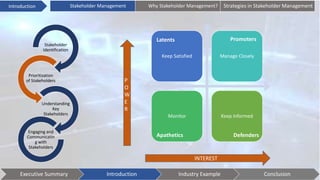
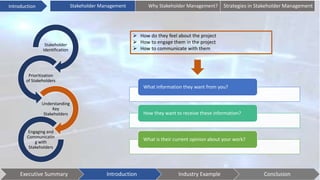
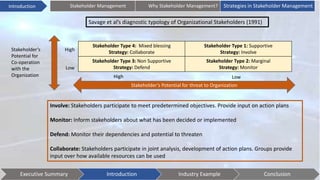
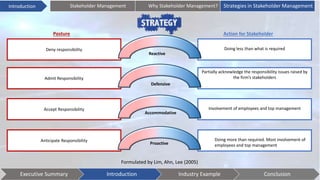
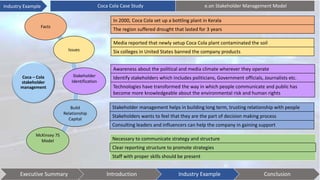
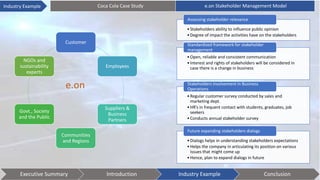
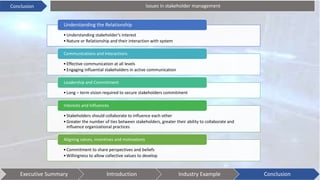
This document discusses stakeholder management. It begins by defining stakeholders and identifying primary and secondary stakeholders. It then covers strategies for stakeholder identification, prioritization, understanding stakeholders, and engaging with them. Specific techniques discussed include stakeholder mapping and categorization. The document also provides an industry example of Coca-Cola's stakeholder management challenges. It concludes with some issues to consider, such as understanding stakeholder interests, effective communication, leadership commitment, and aligning stakeholder values.