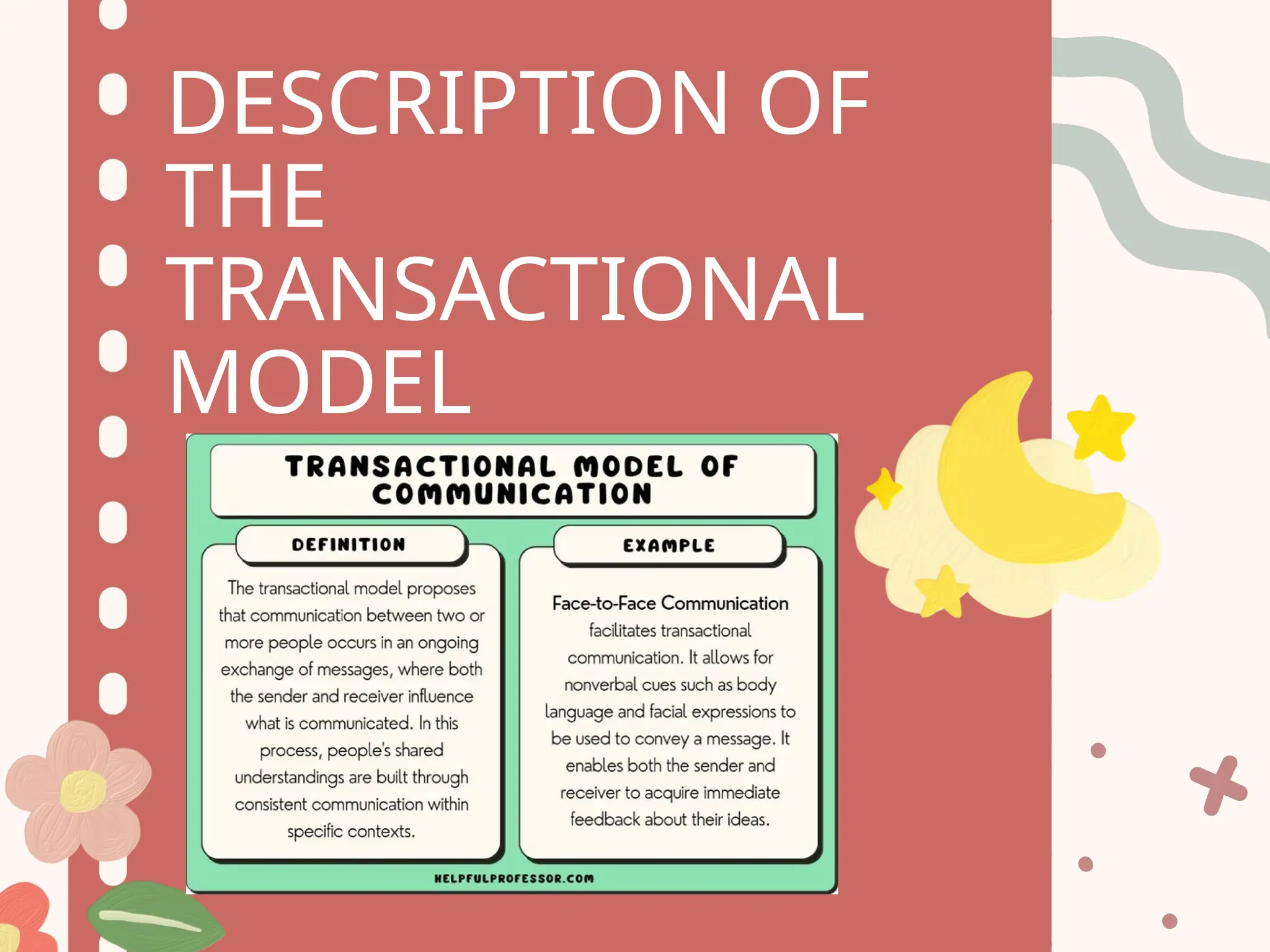
The transactional model of communication emphasizes that communication is a simultaneous process involving both 'senders' and 'receivers,' referred to as 'communicators,' who exchange messages in a context influenced by personal experiences, cultural backgrounds, and social environments. It is particularly relevant in interpersonal communication, highlighting the importance of feedback and the potential for noise during exchanges. The model's strengths lie in its recognition of contextual factors, although it also requires careful analysis and reflection on historical and social structures that impact communication.