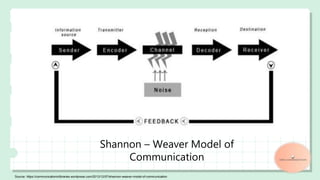
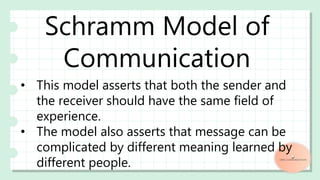
The document discusses various models of communication including linear, transactional, and interactional models. The linear model involves one-way communication from sender to receiver with no feedback, while the transactional model features simultaneous two-way communication and feedback. The interactional model allows for two-way communication and feedback but not simultaneously. Additional models covered include Aristotle's speaker-audience-message model, Shannon-Weaver's model involving sender-encoder-channel-receiver components, Schramm's model emphasizing shared experience between parties, White's cyclical eight-stage model, Berlo's model adding emotion, and the helical model portraying communication as dynamic over time.