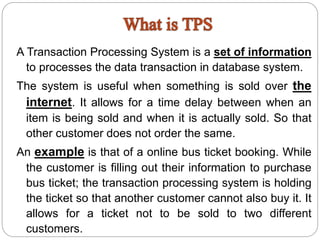
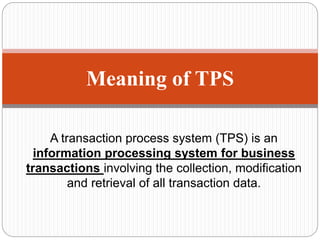
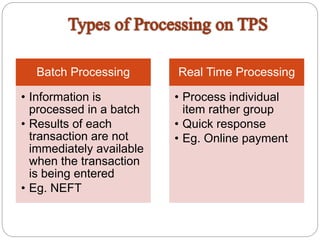
A Transaction Processing System (TPS) processes data transactions in a database system. It allows for a time delay between an item being sold and actually being sold, to prevent multiple customers from purchasing the same item. An example is an online bus ticket booking system, which holds the ticket while a customer fills out their information to prevent another customer from purchasing the same ticket. A TPS is an information processing system that collects, modifies, and retrieves transaction data for business transactions.