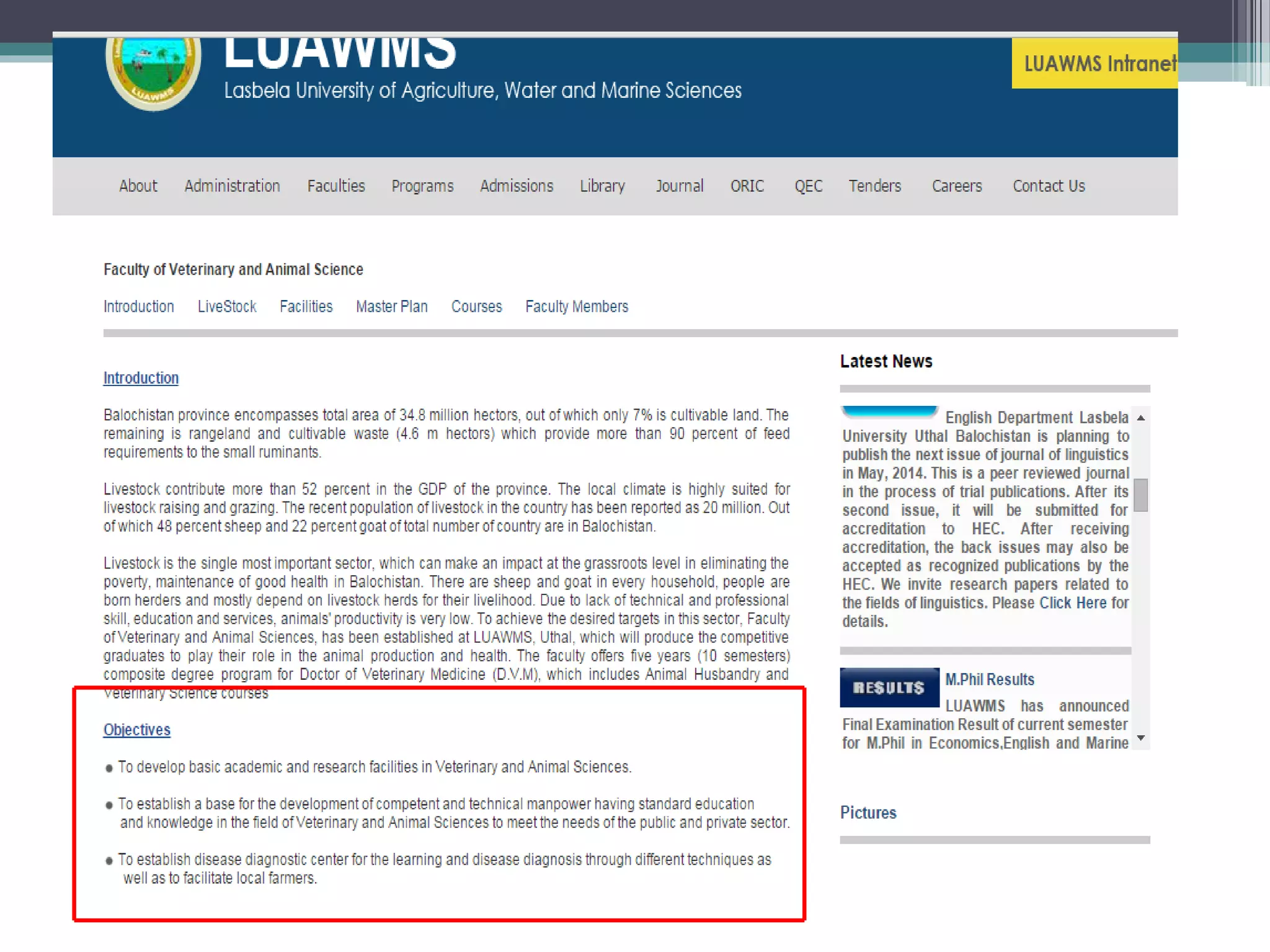
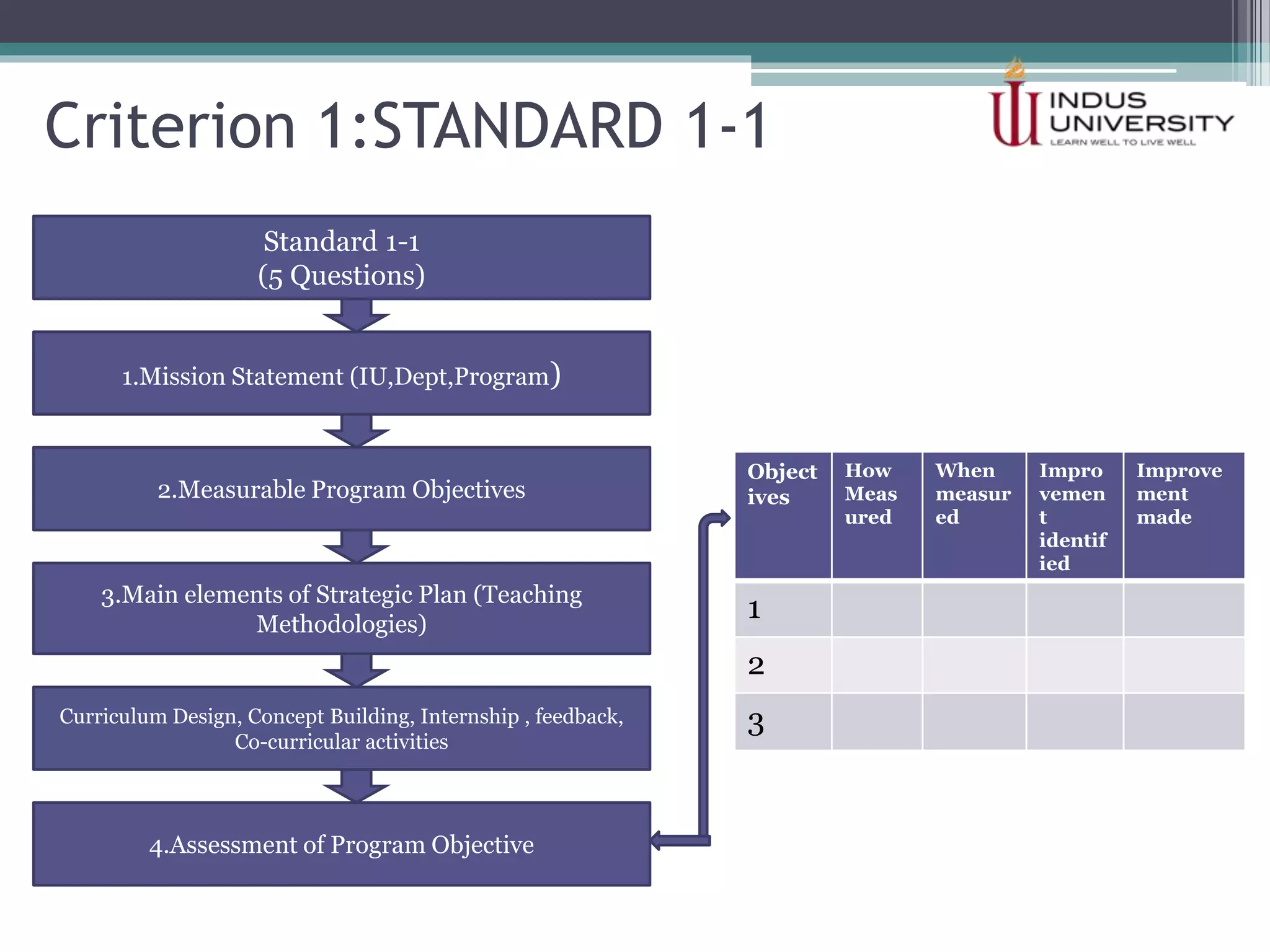
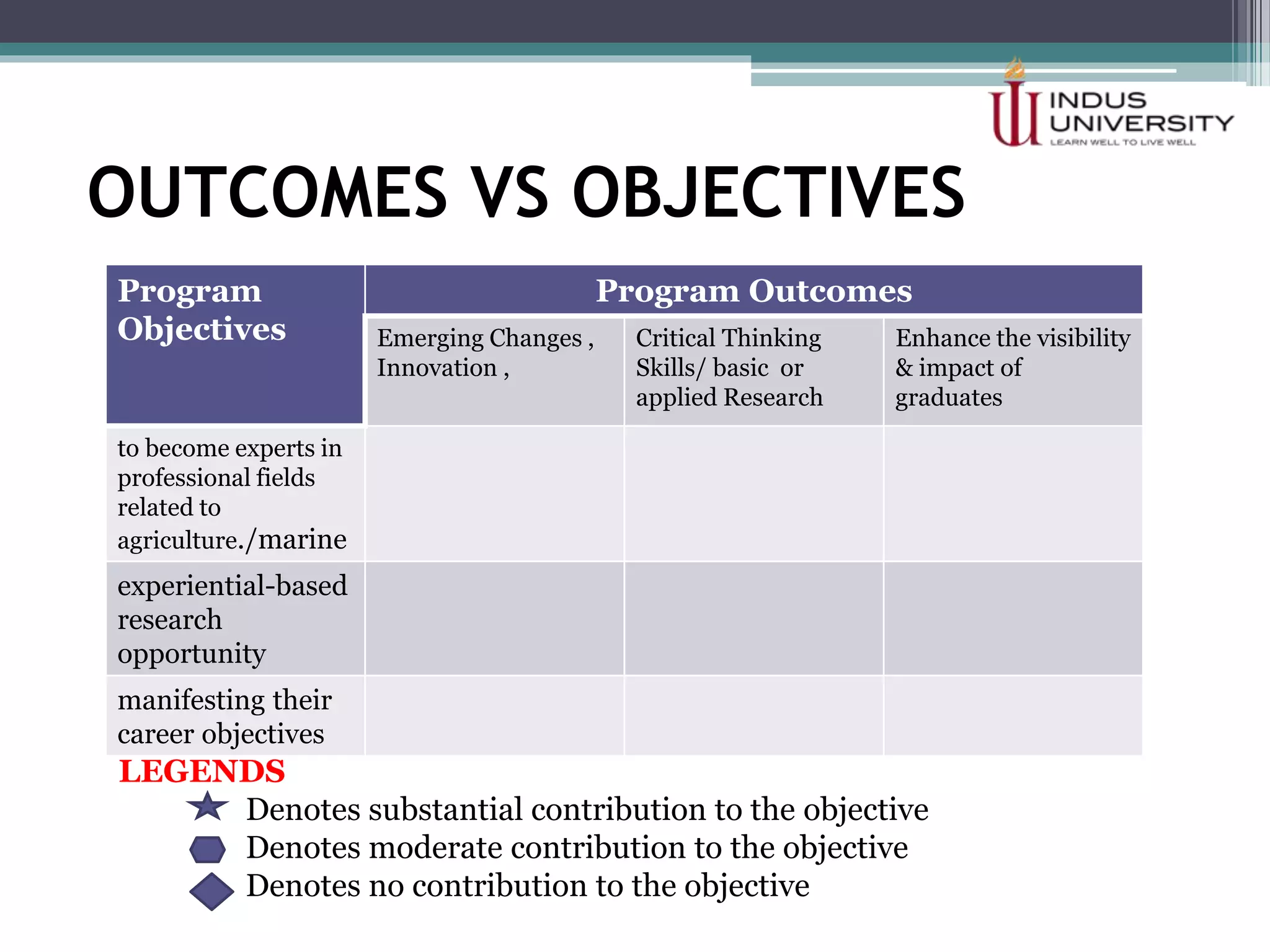
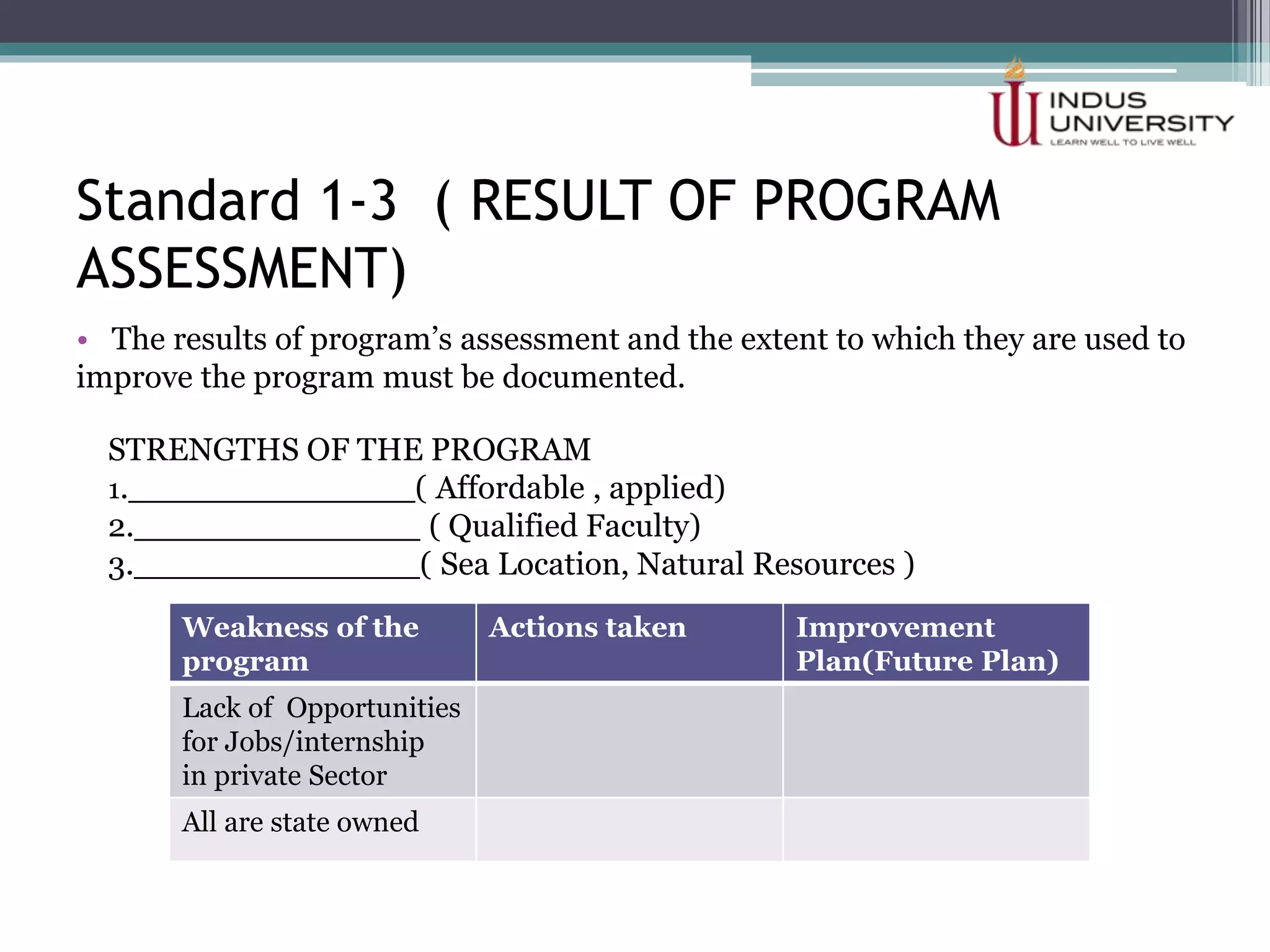
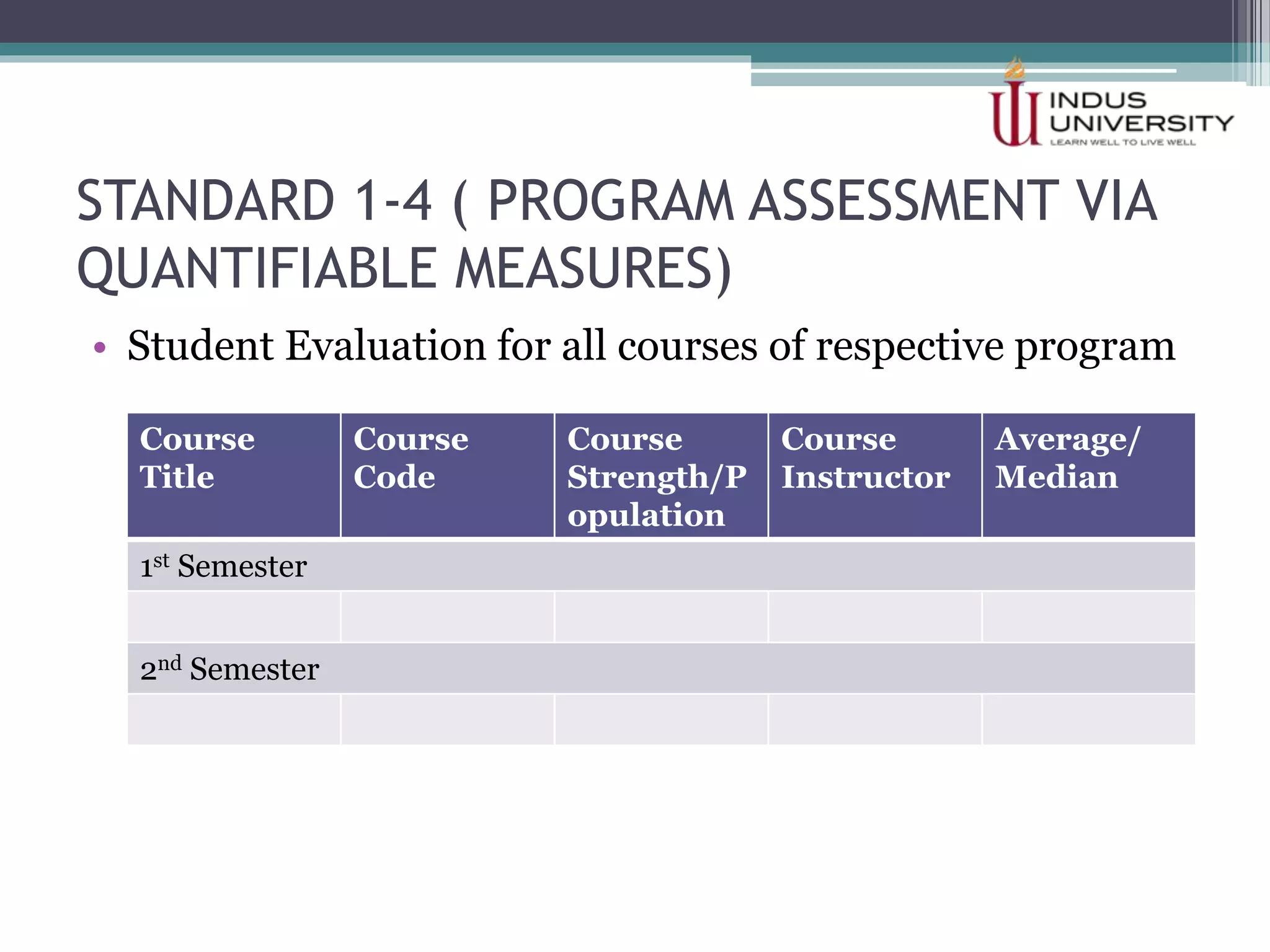
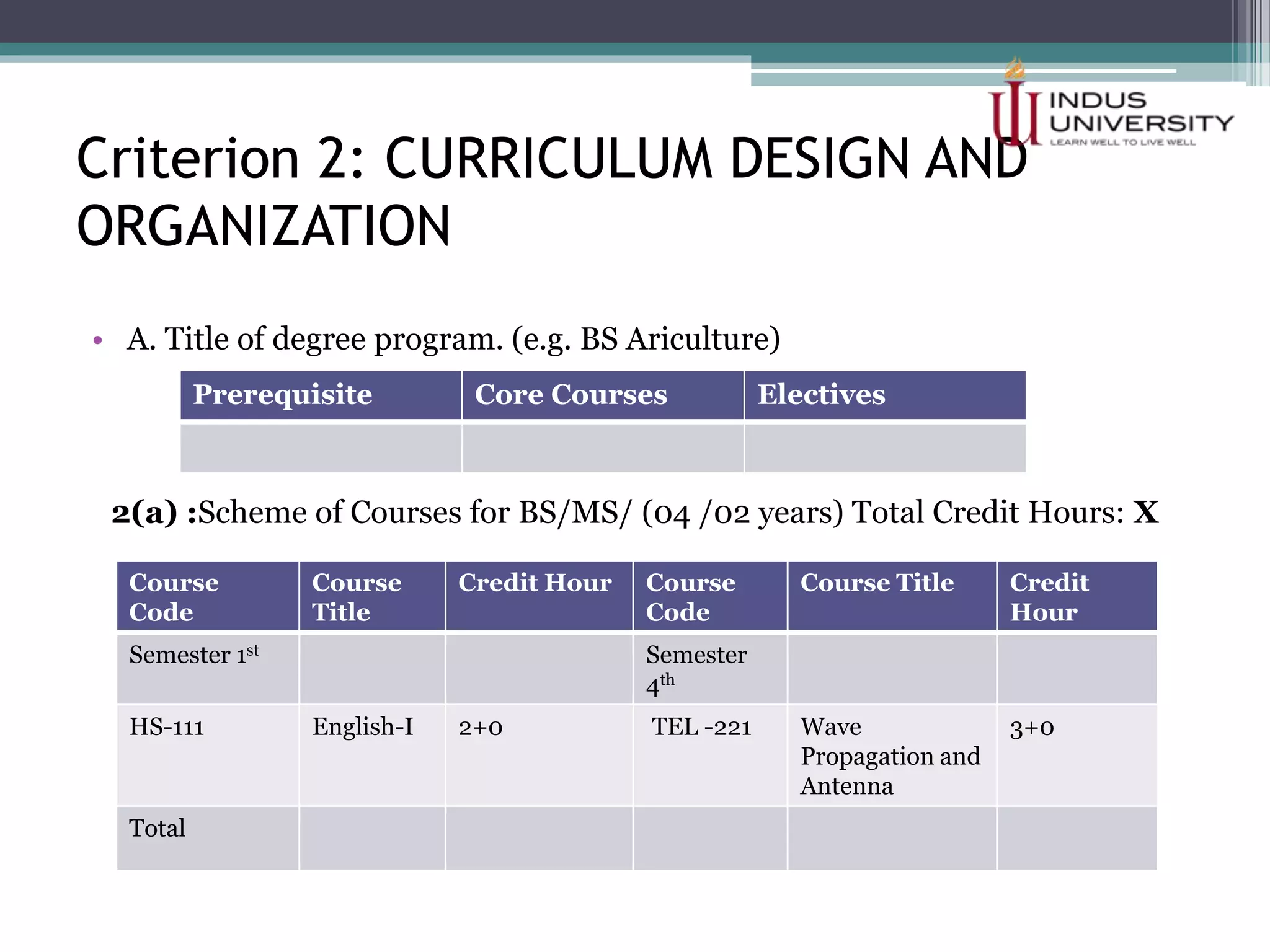
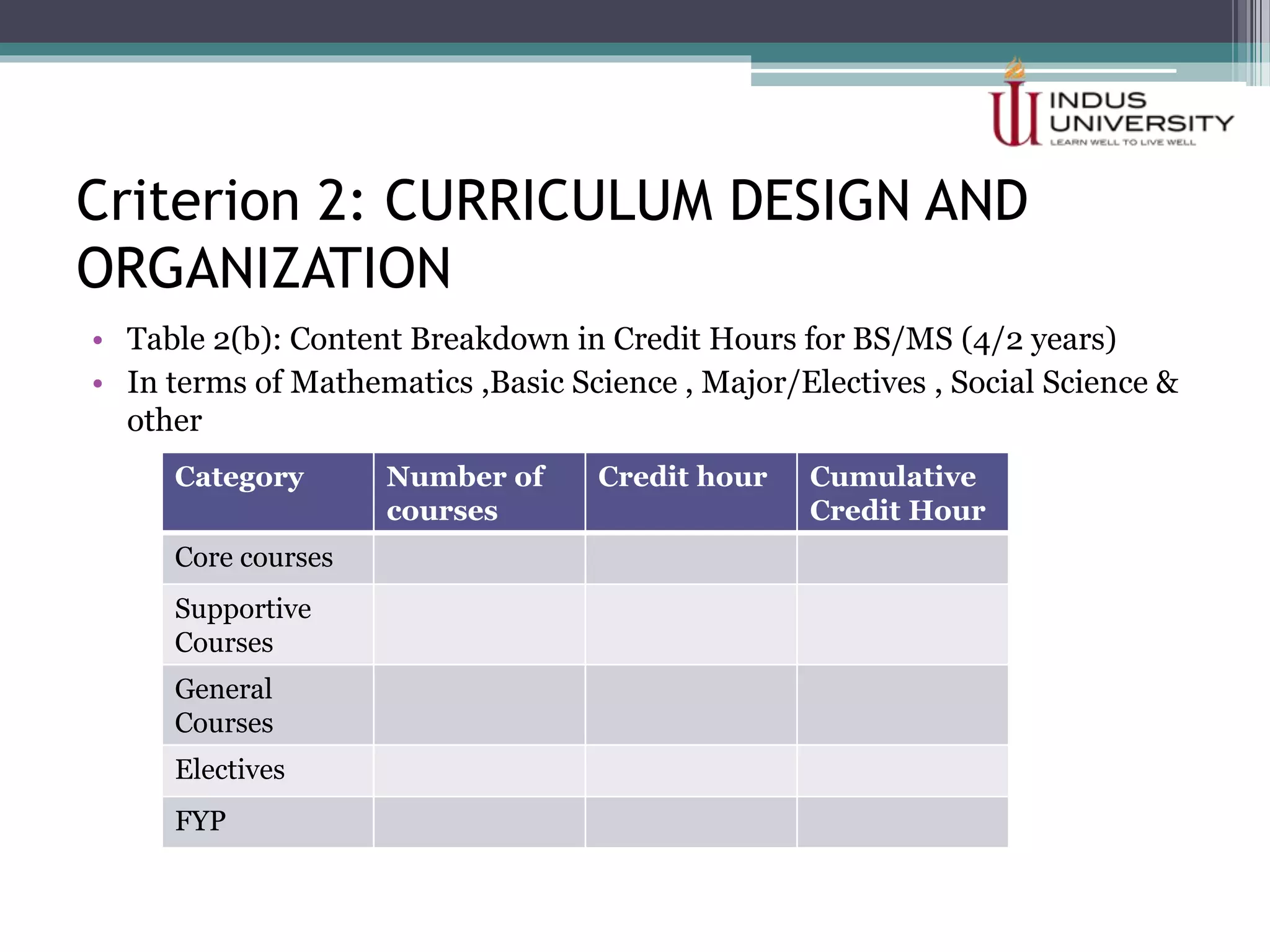
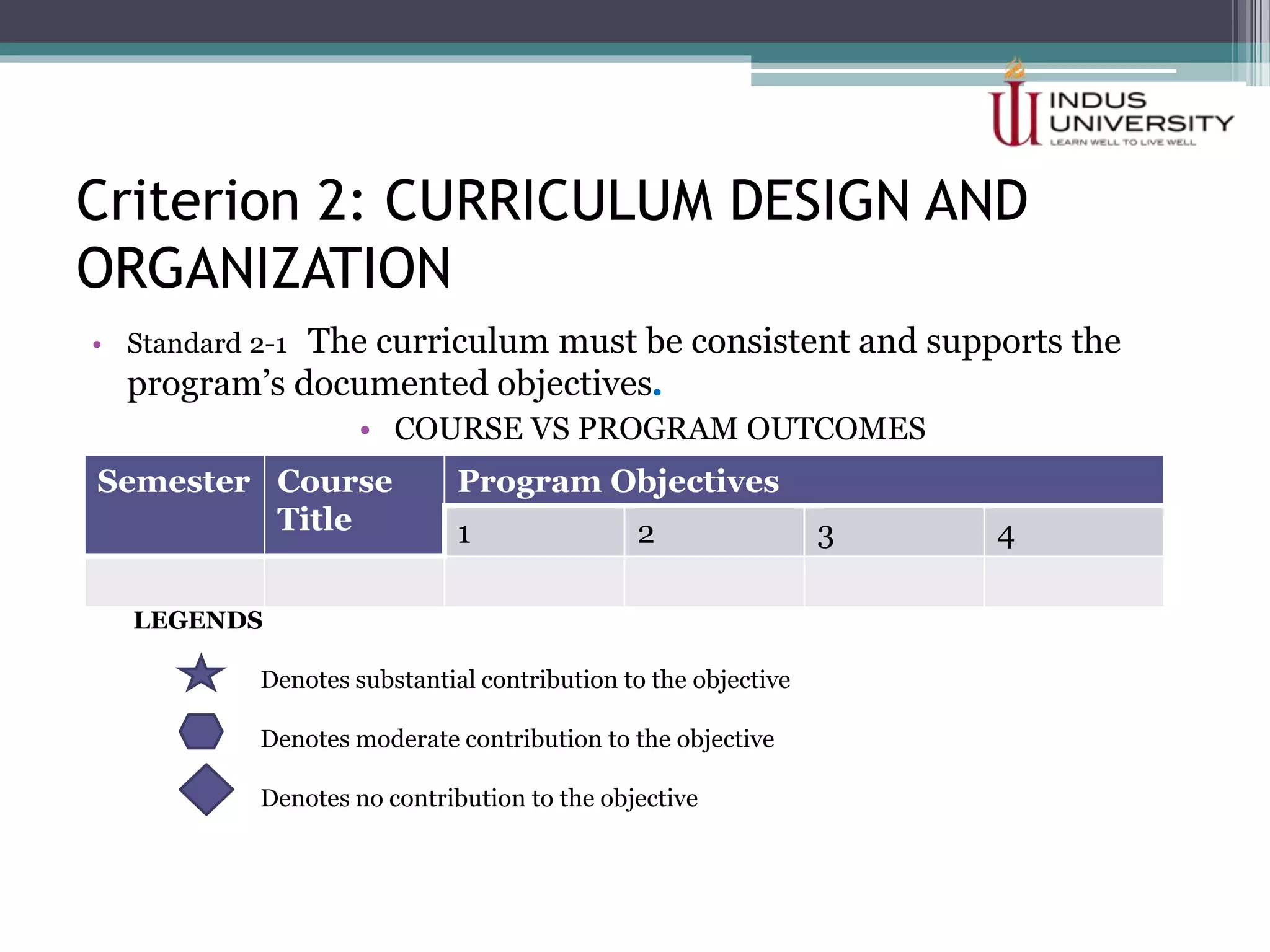
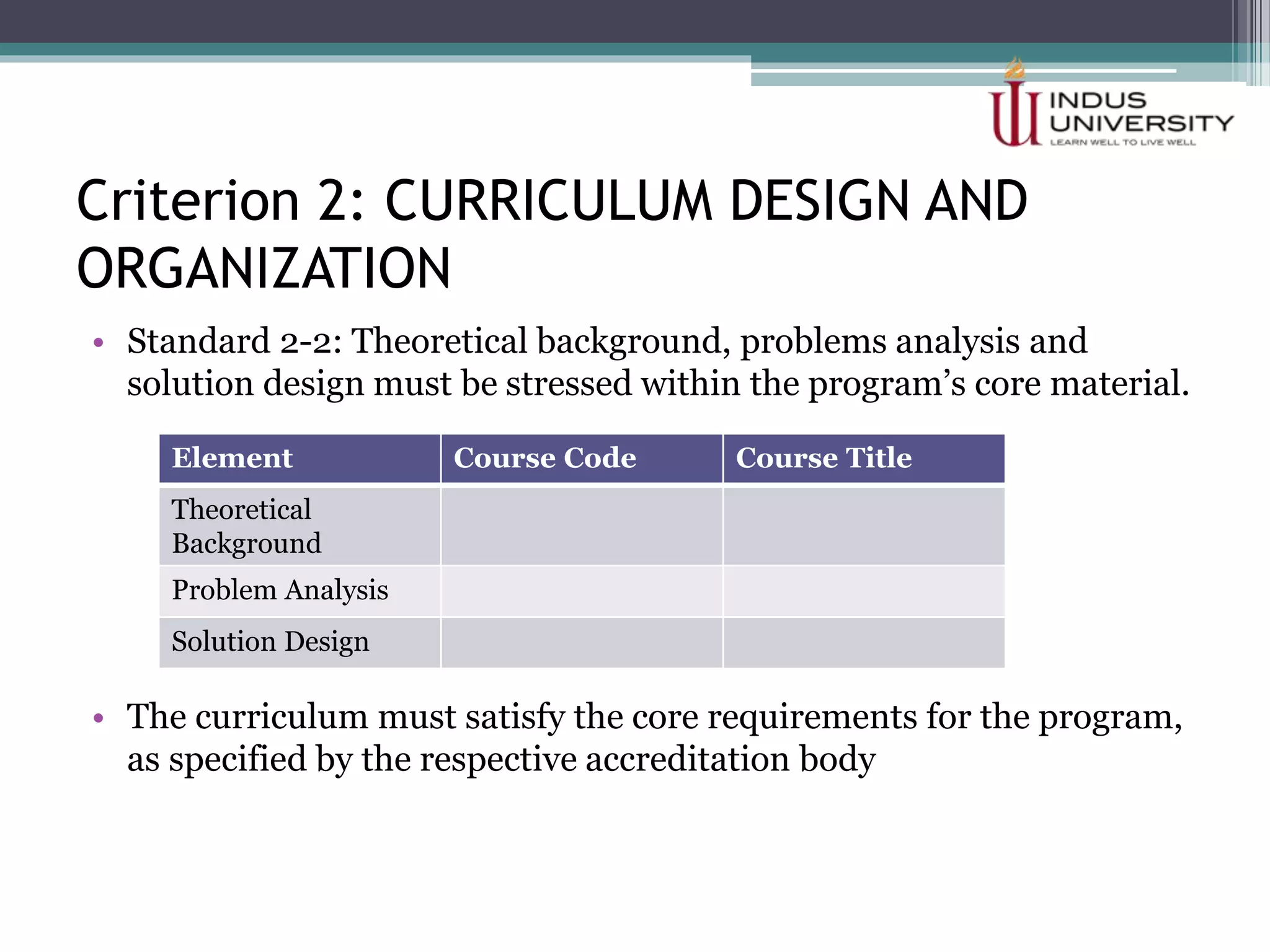
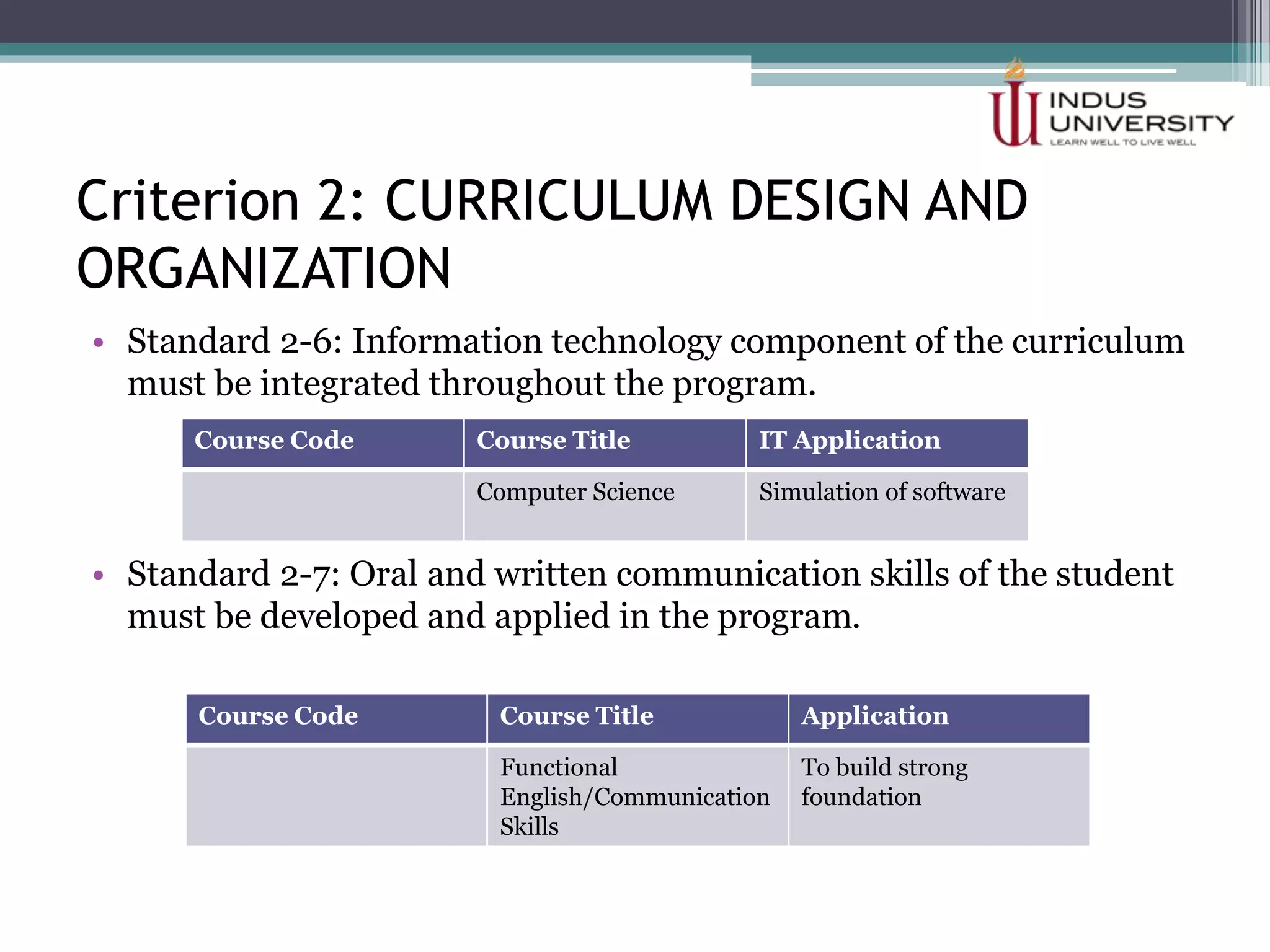
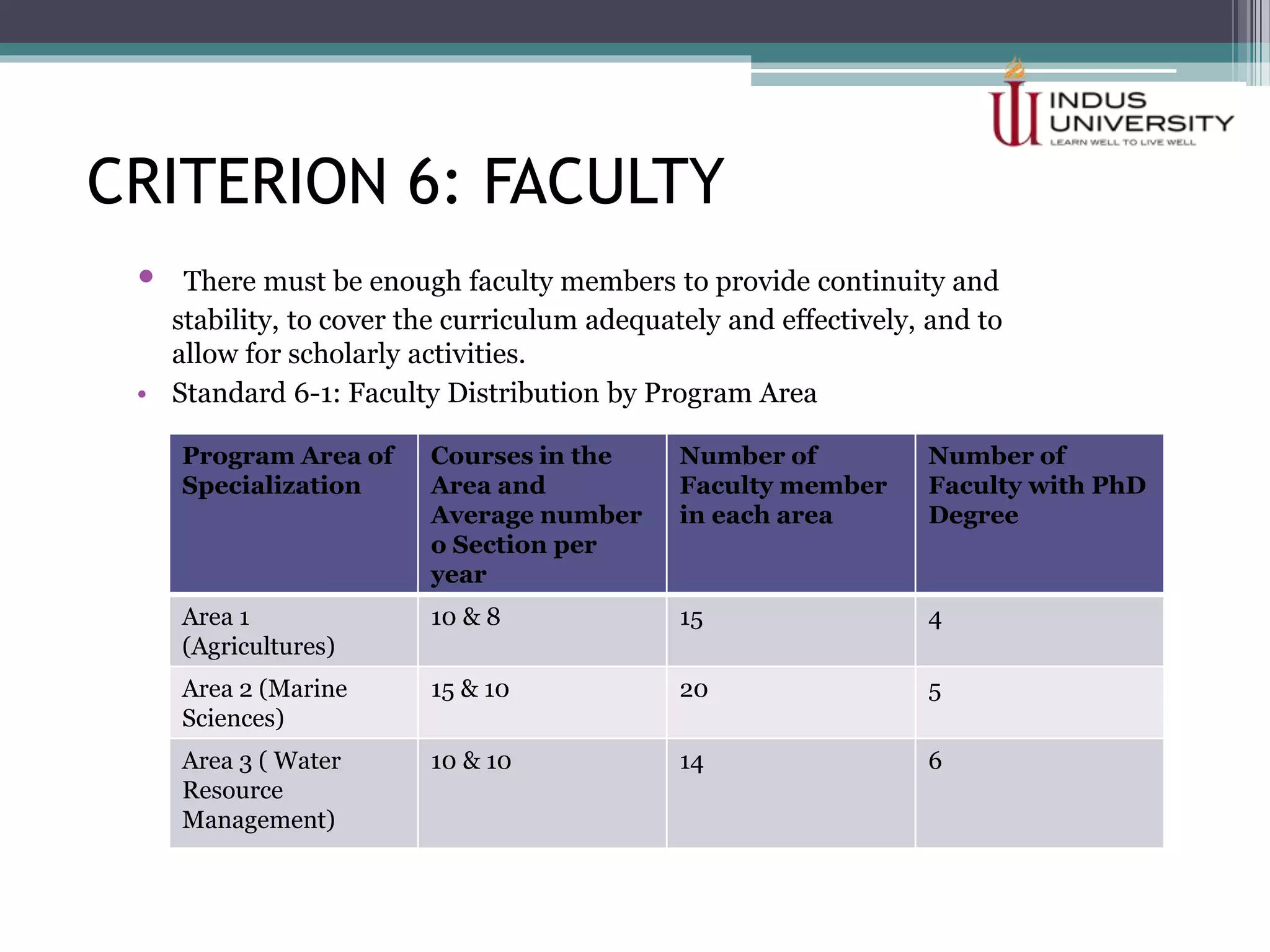
The self-assessment report summarizes Indus University's presentation on the concept and procedure of self-assessment reports to Lasbela University. It discusses the importance of quality assurance in higher education and outlines the objectives and components of conducting a self-assessment, including analyzing program missions and outcomes, curriculum, facilities, and other criteria. The presentation provides examples of how to measure objectives and outcomes both qualitatively and quantitatively and identify areas for improvement in order to enhance student learning and meet international standards.