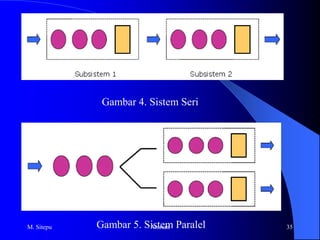
Queuing theory is used to determine optimal service levels by using mathematical formulas and simulations to calculate variables like wait times and average service times based on arrival rates and facility capacities. It was originally developed for telephone systems but is now used in various contexts like manufacturing, transportation, and more. Key aspects of queuing systems include arrival patterns, service disciplines, number of service channels, service times, system capacities, and customer abandonment behavior. Common queuing models include the single-channel M/M/1 model and multiple-channel M/M/s models.