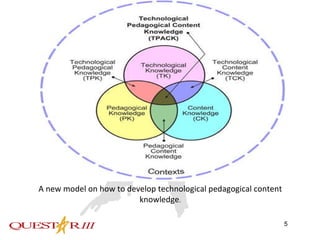
This document provides an introduction to the Technological Pedagogical Content Knowledge (TPACK) framework. It discusses the history and components of TPACK, which integrates knowledge of technology, pedagogy and content. Key aspects of TPACK include understanding how these three bodies of knowledge overlap and influence each other. The document also summarizes findings from research studies that show effective technology integration depends on the pedagogical approaches used, not just the technologies themselves.