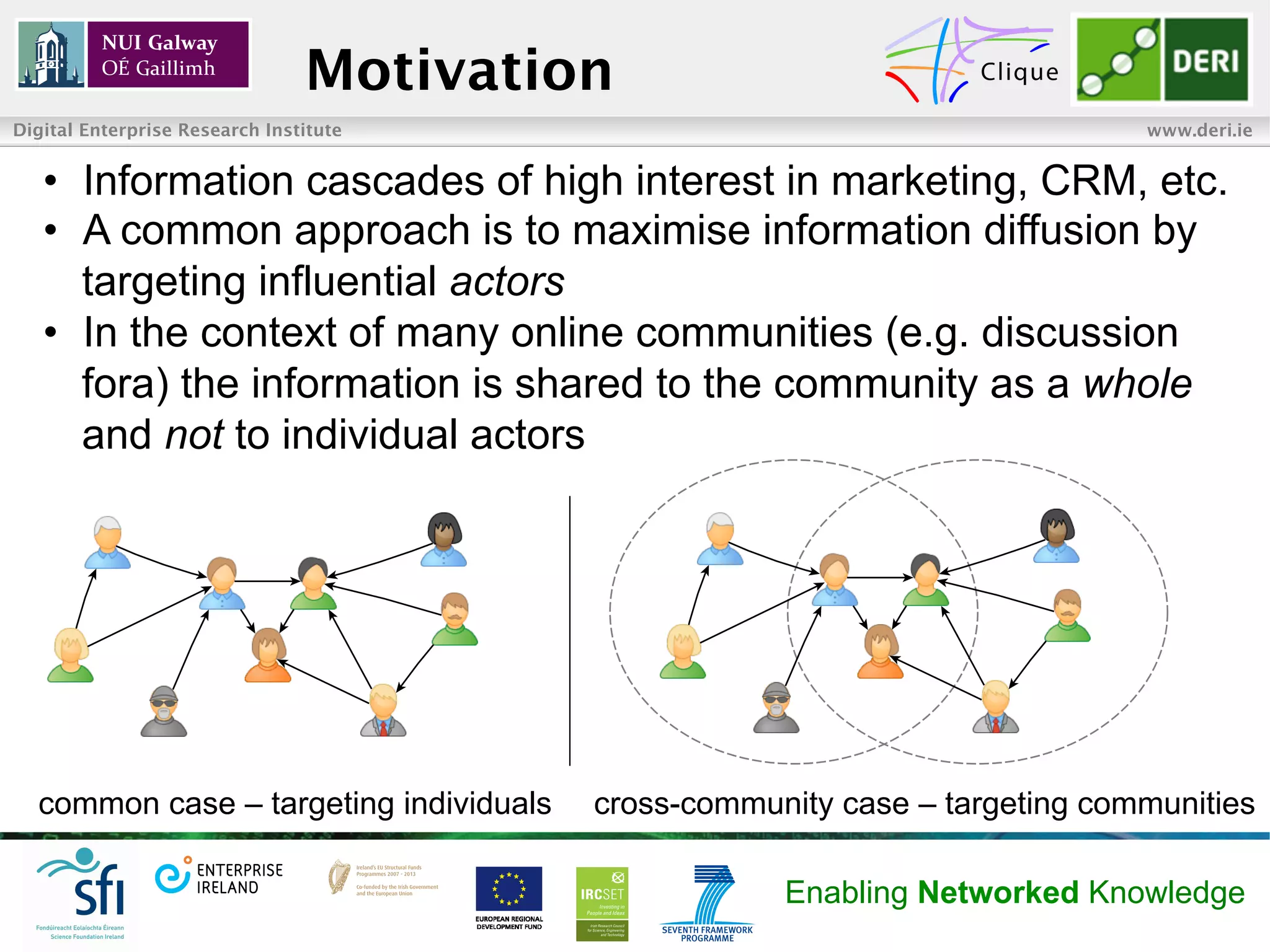
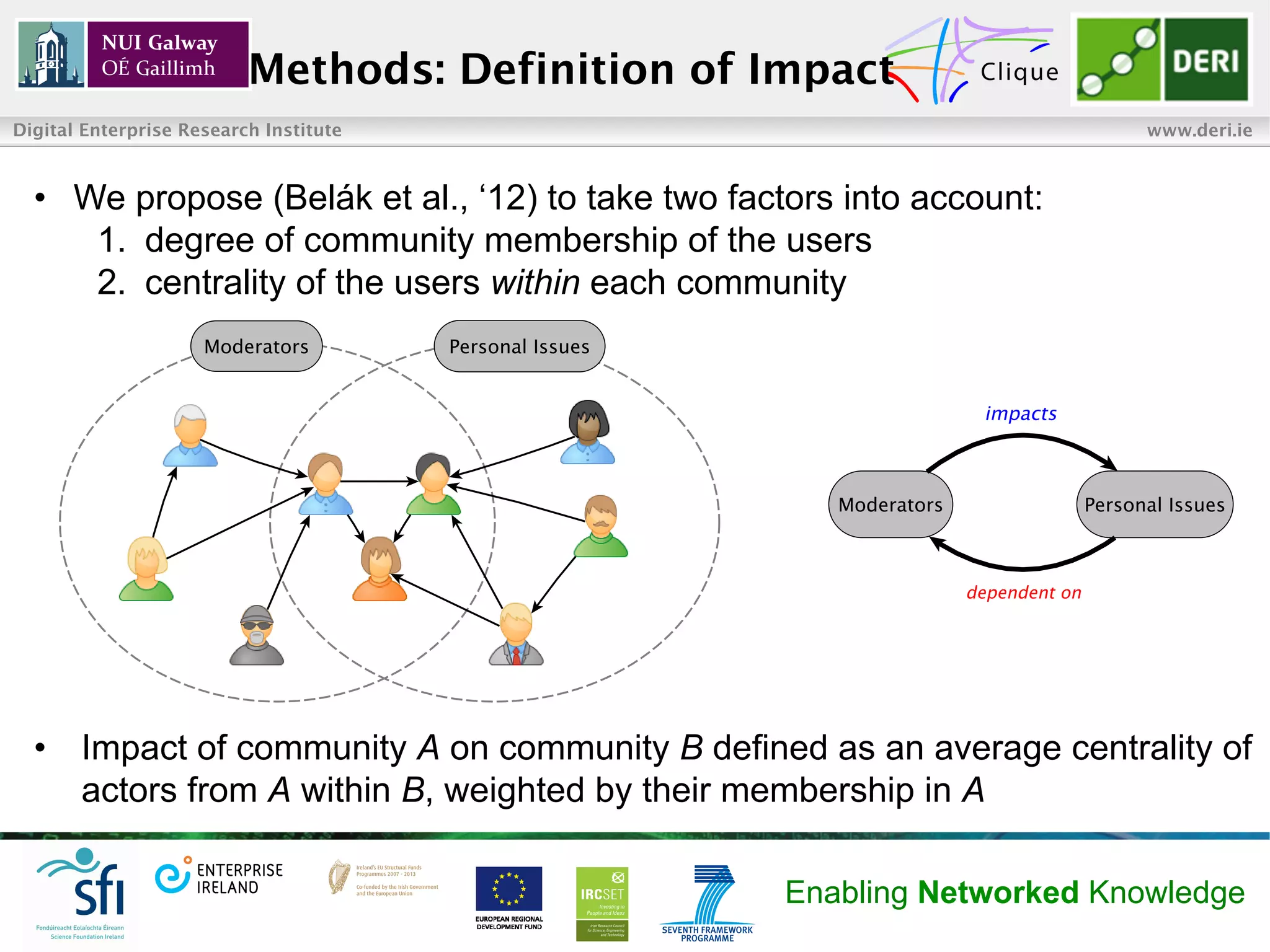
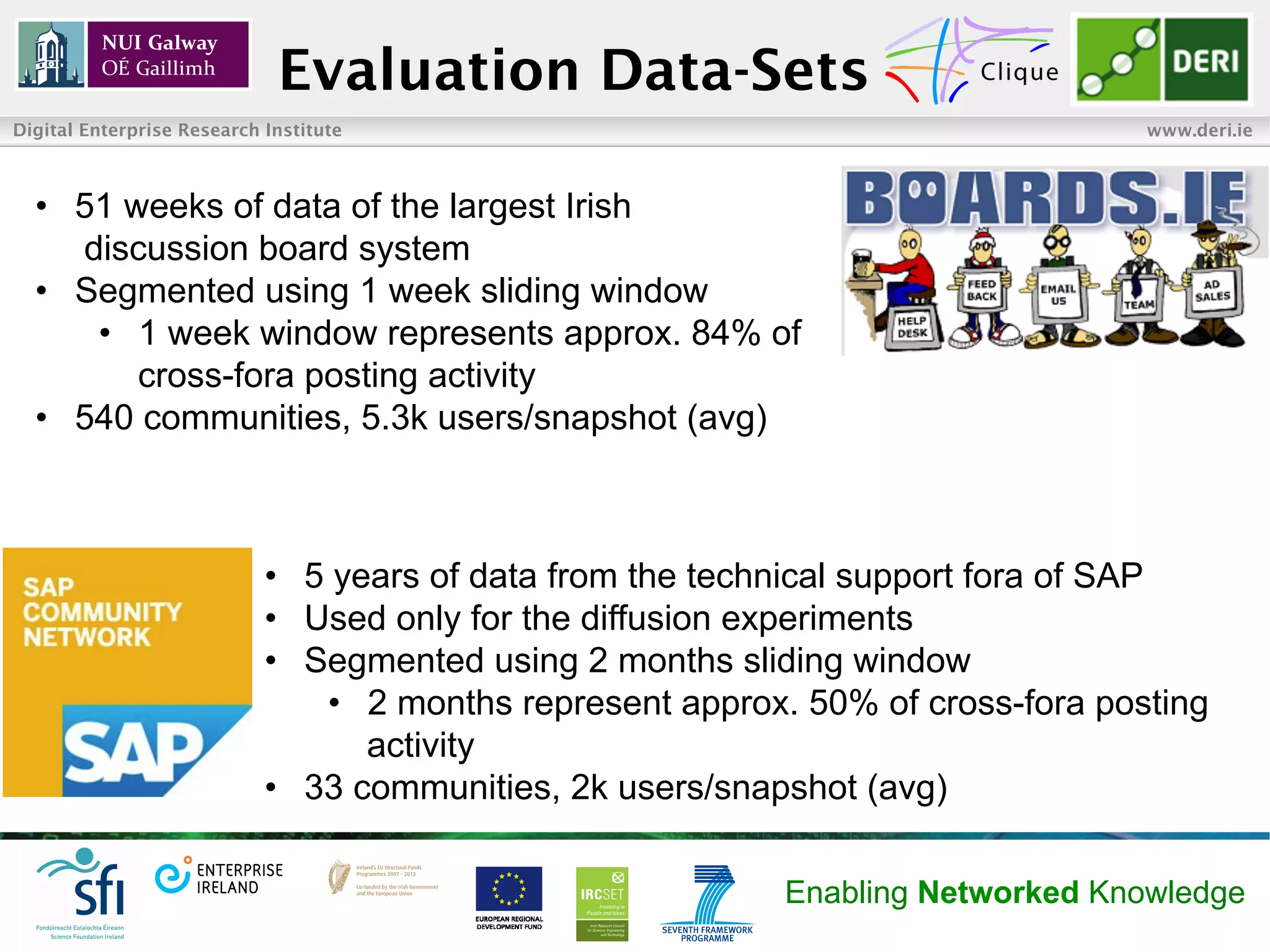
The document summarizes research on maximizing information diffusion across online communities. It aims to spread a message across an information flow network by targeting influential communities. The researchers define methods to measure community impact and propose targeting based on impact and entropy. Evaluation on two datasets shows their impact focus approach outperforms others for small numbers of targeted communities and seed users, achieving diffusion of information to 80% of users or communities.




![Results Highlights
Digital Enterprise Research Institute www.deri.ie
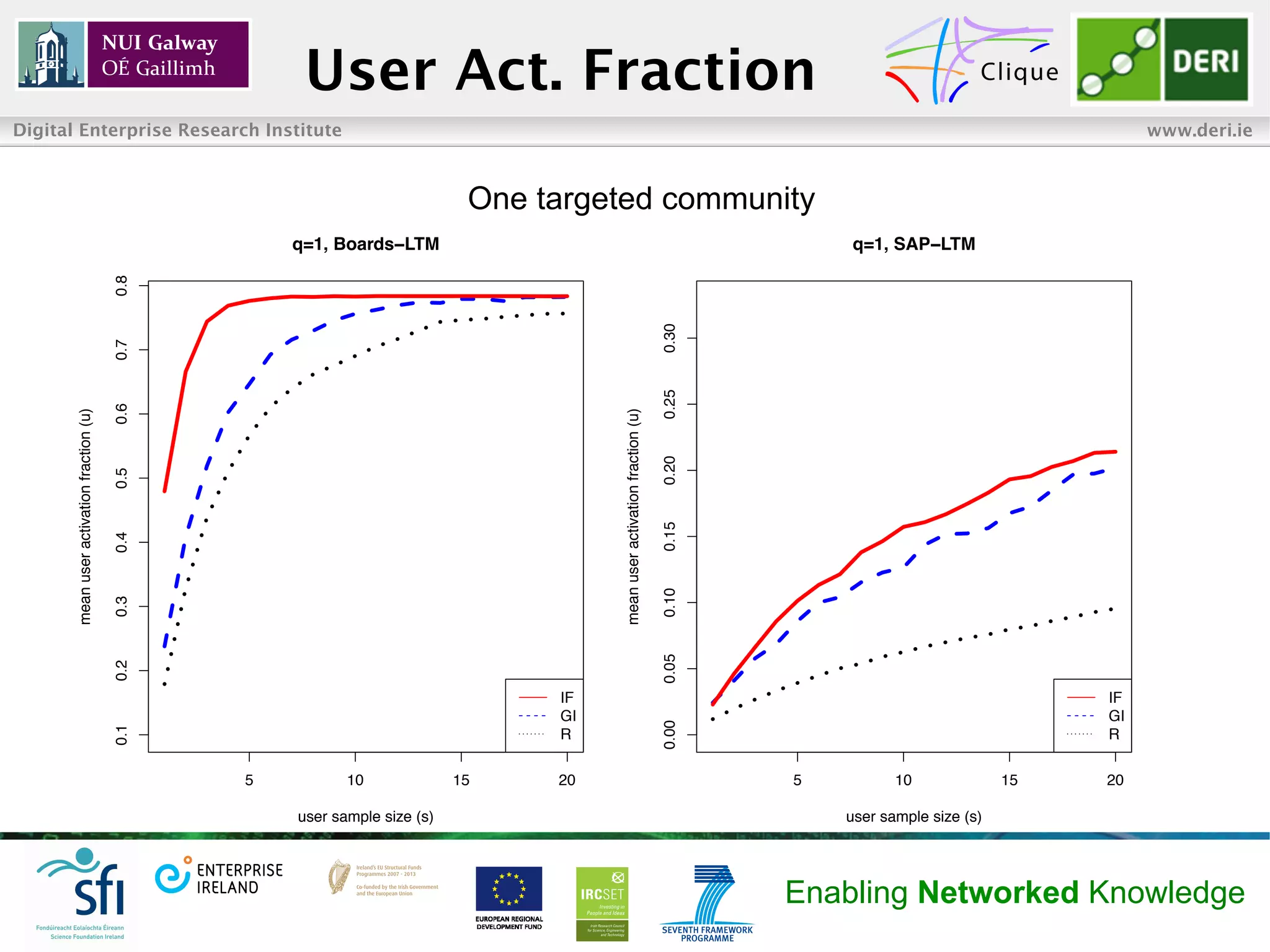
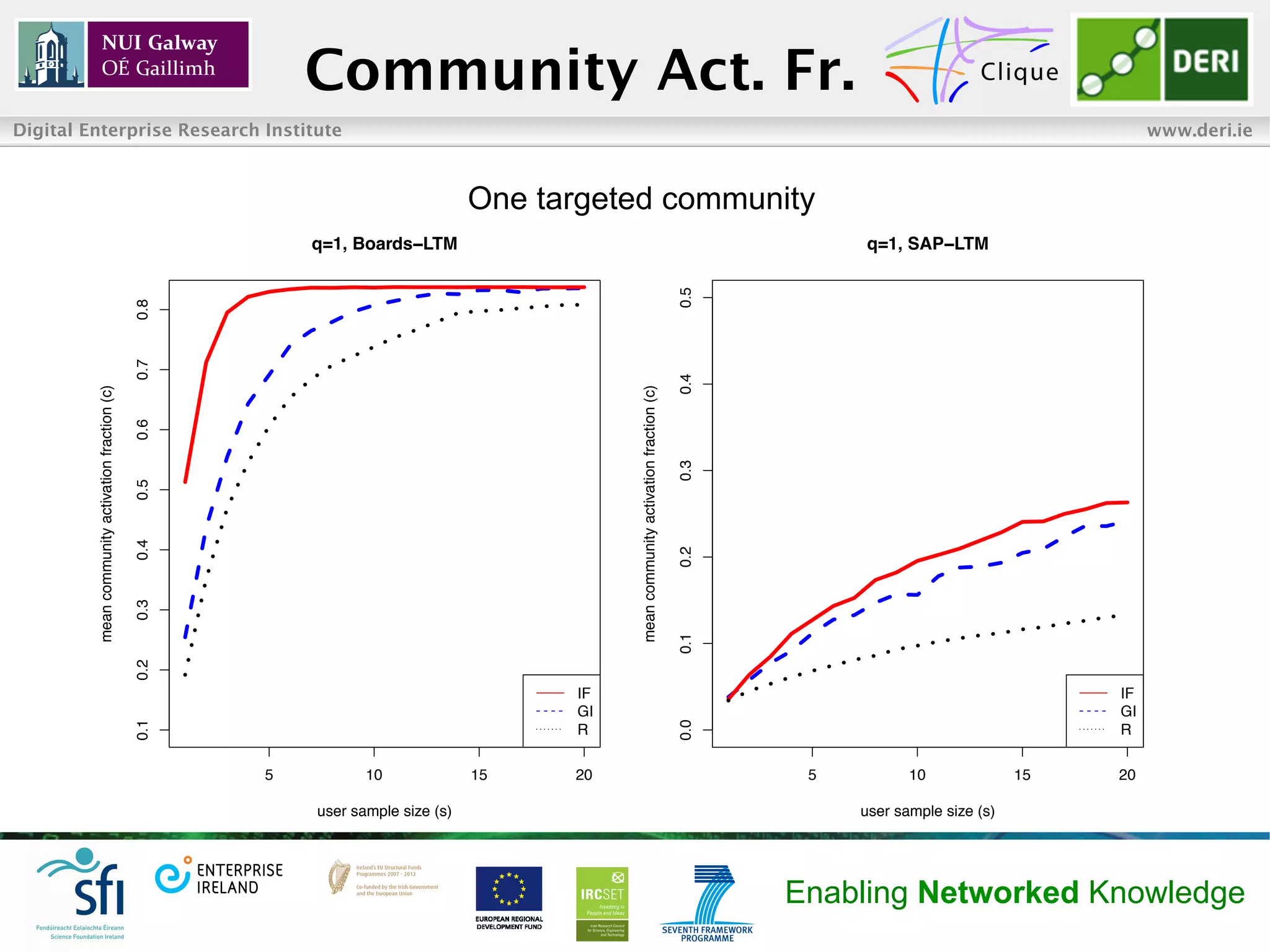
• Diffusion process became saturated at approximately 80% of users
or communities in Boards, and 30% in SAP
• More efficient to target few communities
• Impact Focus outperformed the other two strategies with respect to
both user and community activation fractions, namely for small
number of targeted communities (i.e. [1, 2]) and
seed users (i.e. [1, 20])
• Diminishing returns
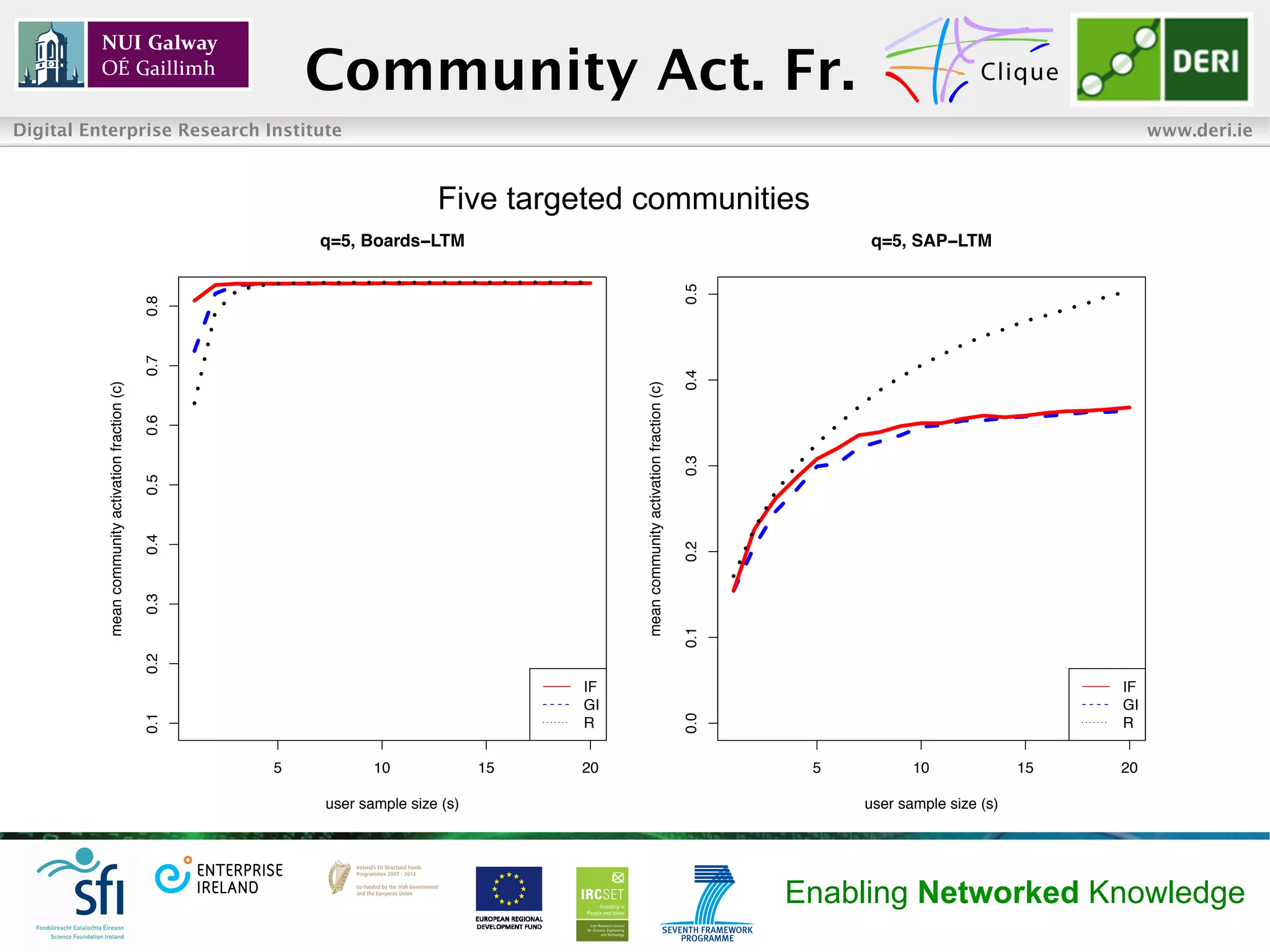
• For high number of targeted communities and seed users, random
strategy outperformed the other two with respect to community
activation fractions in SAP data-set
• SAP network fragmented into many small components, which
made it hard to reach peripheral communities
Enabling Networked Knowledge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2012augasonambelak-120920094858-phpapp02/75/Towards-Maximising-Cross-Community-Information-Diffusion-11-2048.jpg)

