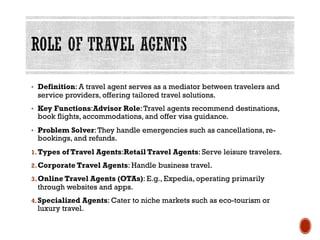
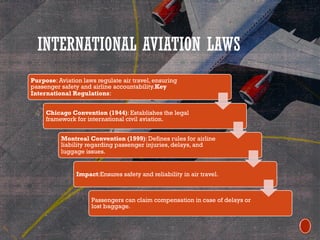
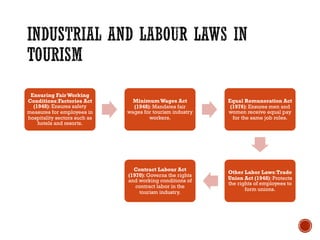
Tourism laws ensure a fair and regulated travel industry, focusing on traveler protection, business regulation, and comprehensive service from travel and tour agents. Key regulations address aviation, immigration, and sustainability, mandating safety, compliance, and eco-friendly practices. Compliance is crucial for tourism businesses, requiring various licenses and protections against consumer fraud and unfair treatment.