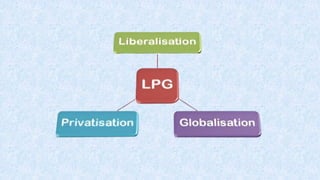
The LPG reforms in India, introduced in 1991, encompass liberalization, privatization, and globalization to address a balance of payments crisis and enhance economic growth. These reforms aimed to transition India from a closed economy with high state control to a more open market economy, fostering private sector participation and global trade. As a result, the reforms reduced government expenditures, improved foreign exchange reserves, and positioned India as a significant player in the global market.