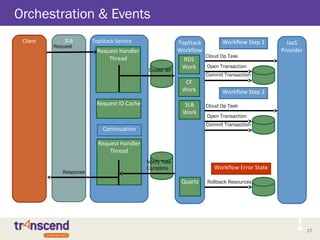
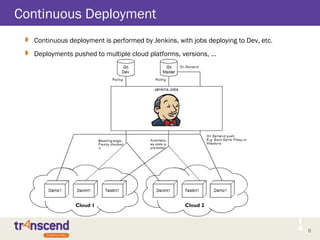
The document provides an overview of the TopStack architecture, which delivers Platform as a Service (PaaS) capabilities by extending Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) solutions. TopStack implements many popular AWS services and runs on private and public clouds. The focus for Q3 2013 is to complement OpenStack. TopStack uses common components like service registration, orchestration, logging, and configuration management. It offers services like load balancing, databases, queues and monitoring.


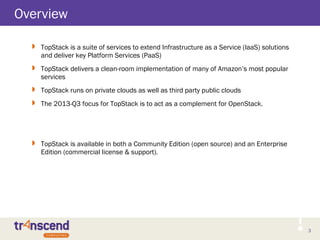






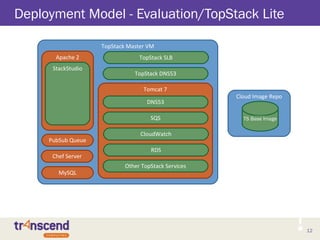
![13
TopStack SLB VM
TopStack Service VM2
Deployment Model - TopStack Enterprise
13
TopStack SLB
TopStack Service VM1
Tomcat 7
DNS53
SQS
CloudWatch
RDS
Other TopStack
StackStudio VM
Apache 2
StackStudio
Cloud Image Repo
Chef VM
Chef Server
[Optional]
DB VM
MySQL
Queue VM
PubSub Queue
DNS53 VM
DNS53
TS Base Image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topstackarchitecture-2013-q3-130817082054-phpapp01/85/TopStack-Product-Architecture-2013-Q3-13-320.jpg)
![14
Chef VM
TopStack Service VMn
Deployment Model - TopStack HA
14
TopStack Service VM2
StackStudio VM
Apache 2
StackStudio
TopStack Service VM1
TopStack ELB VM2TopStack ELB VM1
Cloud Image Repo
[Optional]
DB Active
MySQL
DB Standby
MySQL
Chef Cluster
Chef Server
Chef VM
Queue Cluster
PubSub Queue
Chef VM
DNS53 Cluster
DNS53
TS Base Image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topstackarchitecture-2013-q3-130817082054-phpapp01/85/TopStack-Product-Architecture-2013-Q3-14-320.jpg)