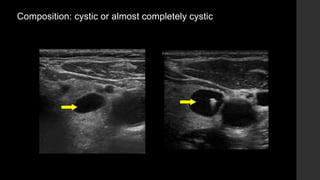
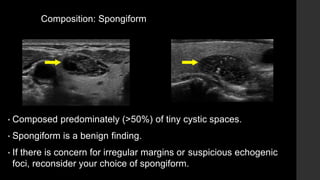
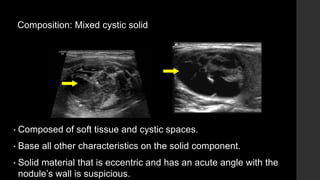
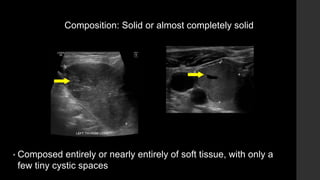
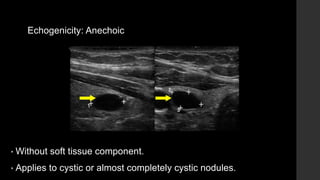
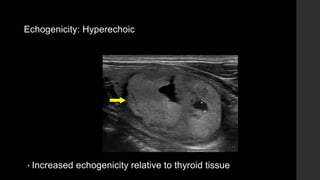
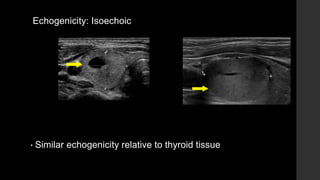
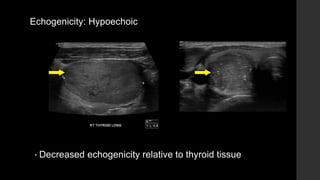
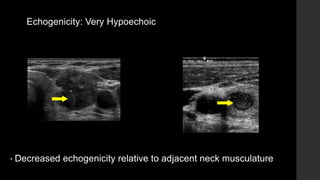
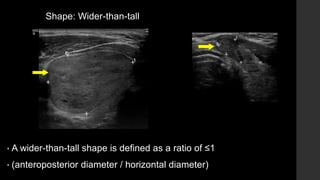
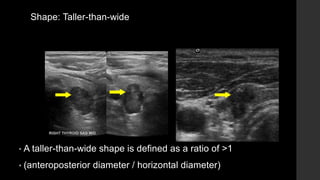
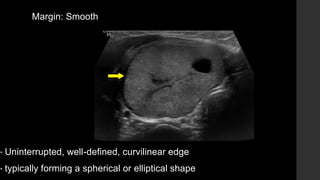
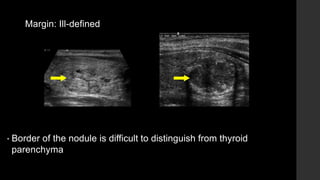
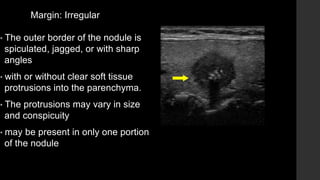
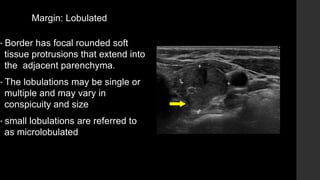
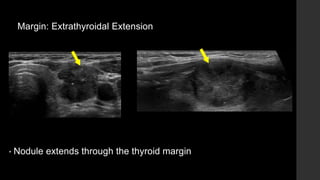
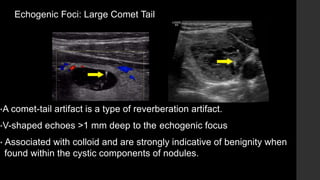
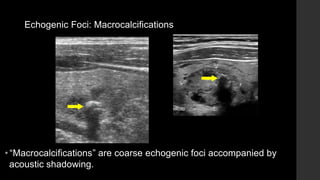
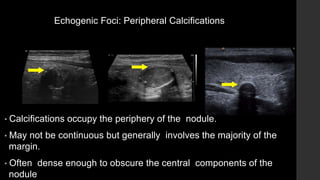
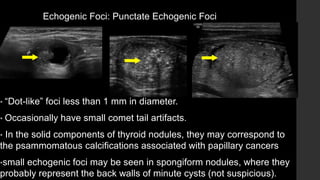
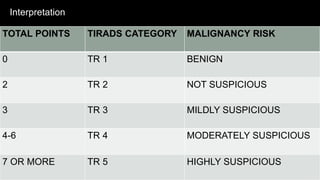
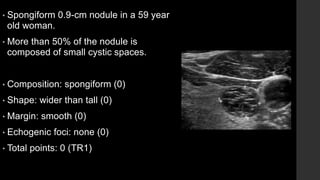
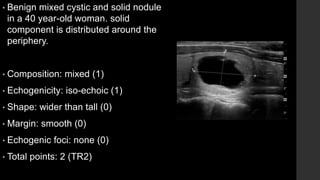
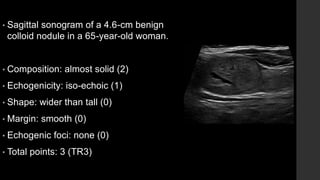
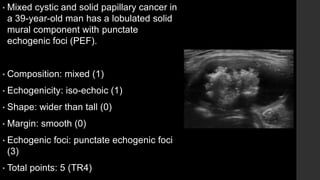
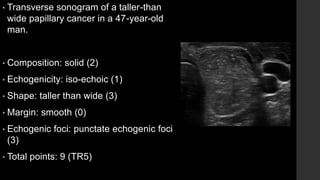
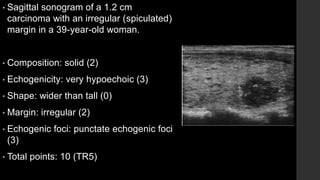
The TI-RADS system provides a standardized scoring and reporting system for thyroid nodules based on their ultrasound features and associated malignancy risk. The system stratifies nodules into 5 categories (TR1 to TR5) based on their scores in 5 categories: composition, echogenicity, shape, margin, and echogenic foci. The scoring helps determine whether fine needle aspiration or follow up ultrasound is recommended. Example cases are provided to illustrate how the system can be applied in clinical practice.