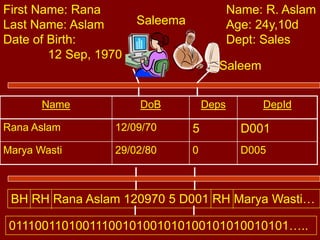
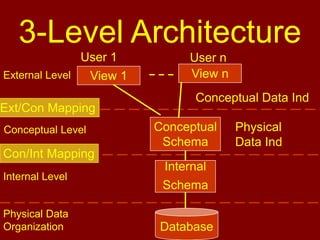
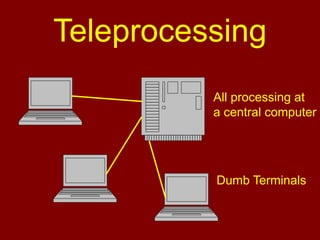
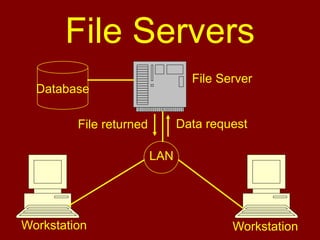
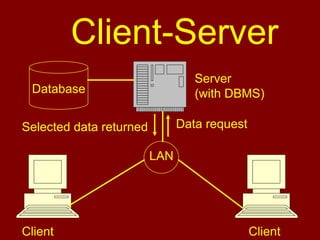
This document discusses database management systems and the three-level architecture. It covers the internal or physical view, which concerns the physical implementation of the database. It also discusses data independence, where changes to lower levels do not affect upper levels. The types of data independence are logical, where changes to the conceptual model do not affect external views, and physical, where changes to the internal model do not affect the conceptual model. Other topics covered include the functions of a DBMS, different DBMS environments like single-user, multi-user, and client-server, and an assignment for students on the three-level architecture.