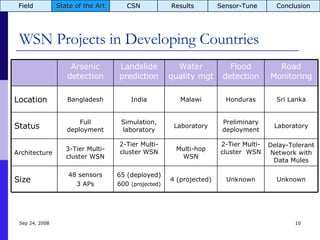
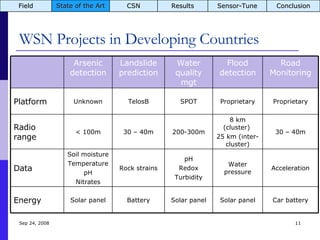
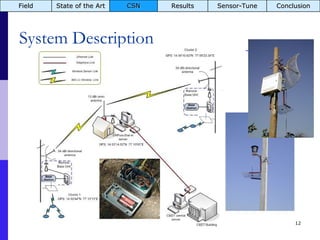
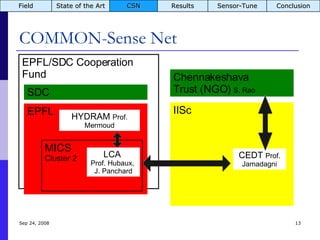
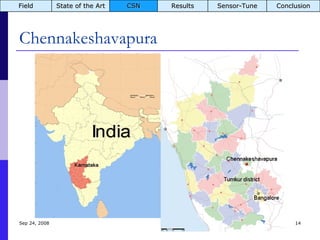
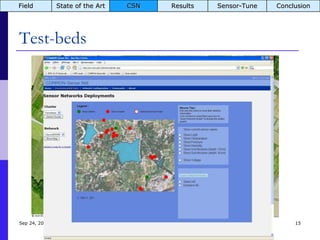
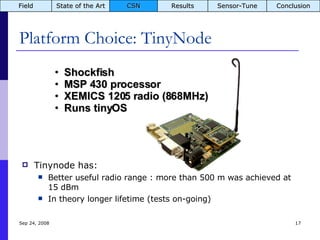
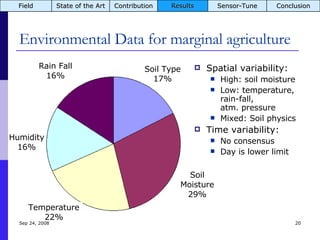
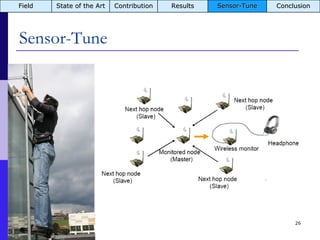
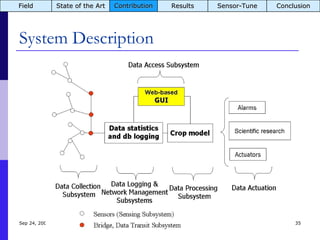
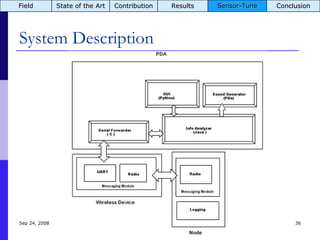
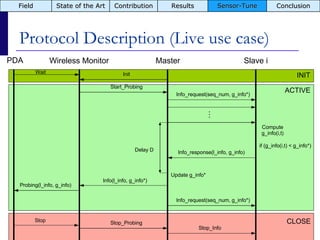
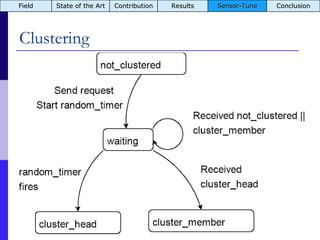
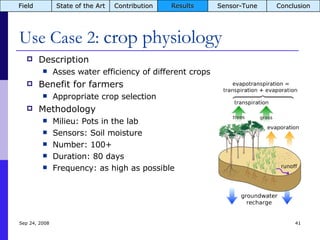
The document summarizes a presentation on the COMMON-Sense Net project, which aims to implement wireless sensor networks to help marginal farmers in India make better farming decisions. The project used a participatory design approach and deployed sensor nodes to collect environmental data. It identified potential use cases for agriculture scientists to analyze links between soil moisture and pest emergence, assess crop water efficiency, and evaluate underground drip irrigation. The project also developed a sonification interface to help non-specialists deploy and maintain sensor networks.





![ICT4D ICT4D: Information and Communication Technologies for Development ICT as an enabler for development [Heeks 2002, 2008], [Walsham 2001], [Negroponte 1998] Empowerment Fight against exclusion Prevention of corruption Common pitfalls of ICT4D projects [Heeks 2002, 2008] Design/actuality gaps Sustainability Scalability Design guidelines [Surana et al. 2008], [Heeks 2002, 2008] Use Hybrids Optimization of existing systems Financial self-sufficiency Operational self-sufficiency Jun 5, 2009 Field State of the Art CSN Results Sensor-Tune Conclusion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thesisnew-1222272669708434-8/85/Thesis-Slides-6-320.jpg)