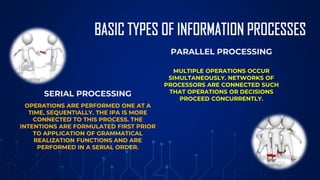
This document discusses two main approaches to language learning: the information processing approach and the social interaction approach. The information processing approach views language learning as analogous to information being processed by a computer, with inputs, memory storage, and retrieval. The social interaction approach emphasizes the role of social interactions like negotiation, gesture, imitation and child-directed speech between children and more knowledgeable individuals in facilitating language acquisition. The document also describes models within each approach, such as the parallel distributed processing model and competition model, and how they explain various aspects of language learning.