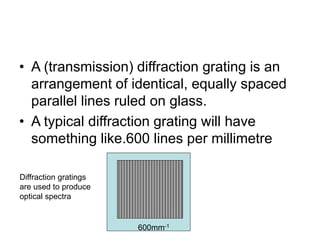
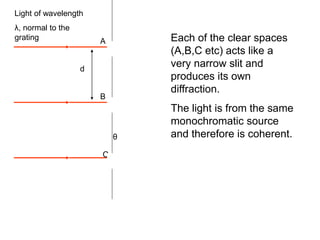
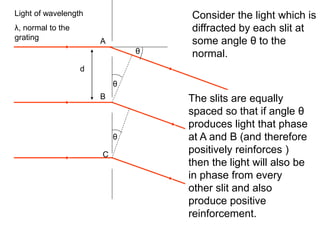
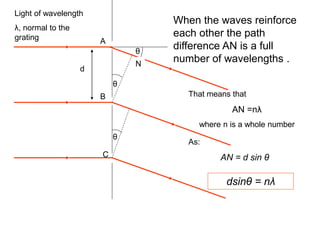
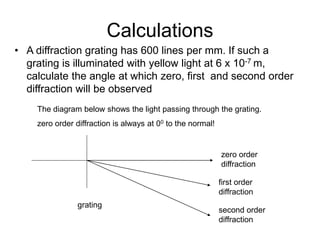
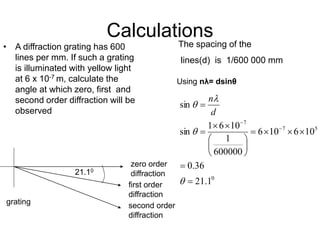
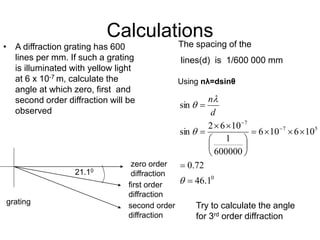
A diffraction grating is an arrangement of parallel, equally spaced lines that separates white light into its spectrum more effectively than a prism. Light passing through the grating will produce constructive interference at certain angles, called diffraction orders. For a grating with 600 lines per mm illuminated with yellow light of wavelength 6x10-7 m, the angles for zero, first, and second order diffraction can be calculated using the diffraction grating equation.