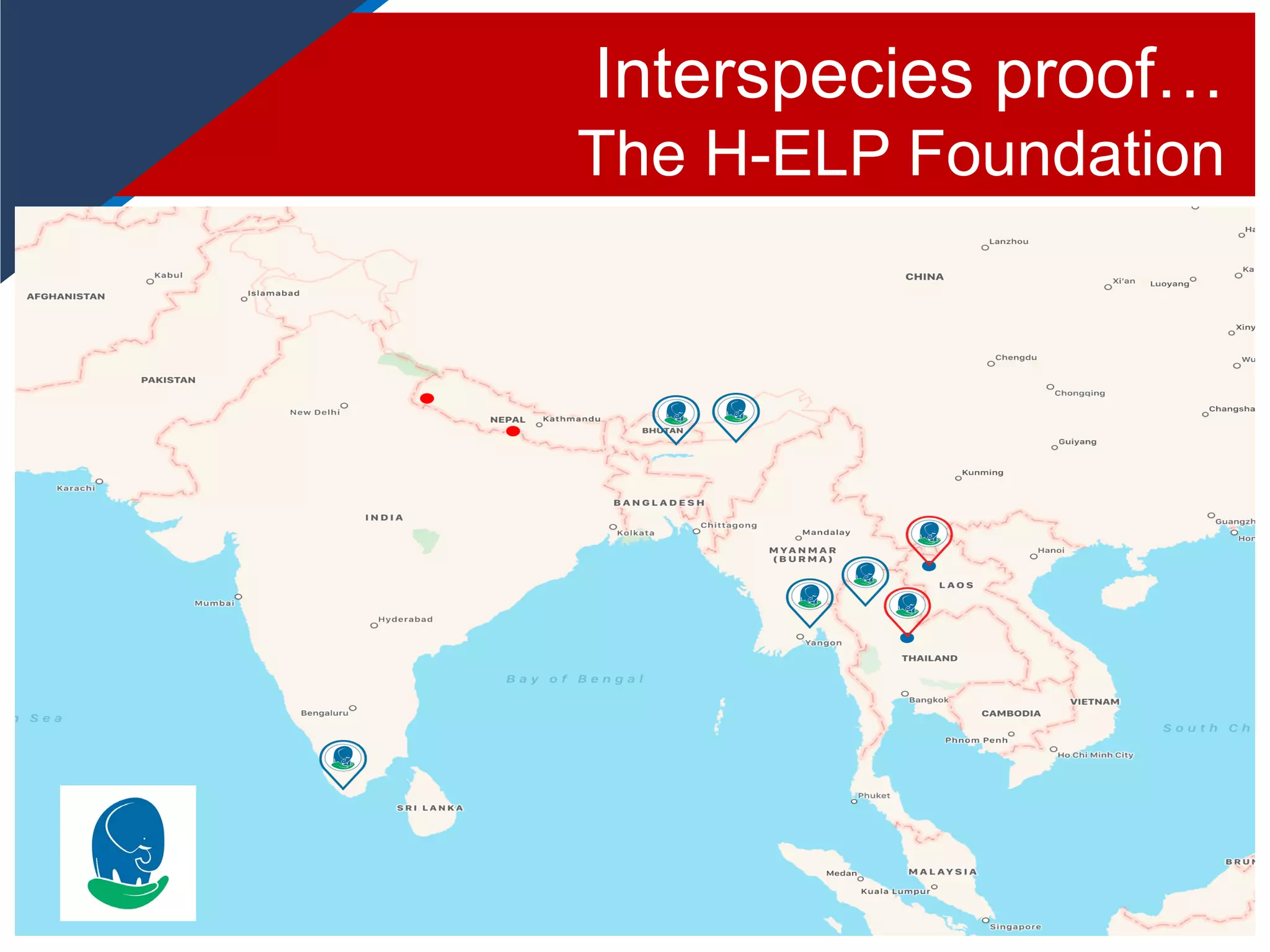
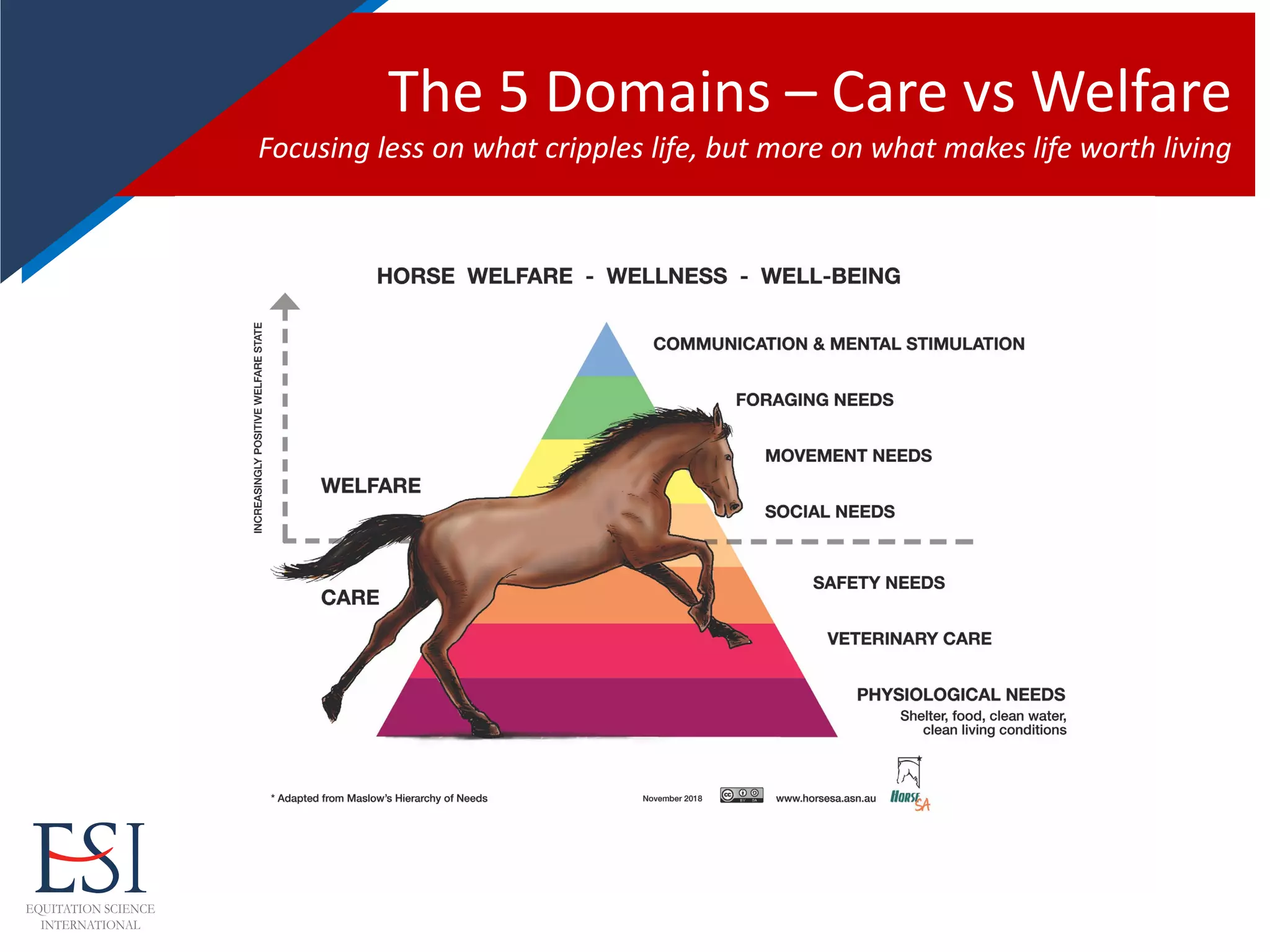
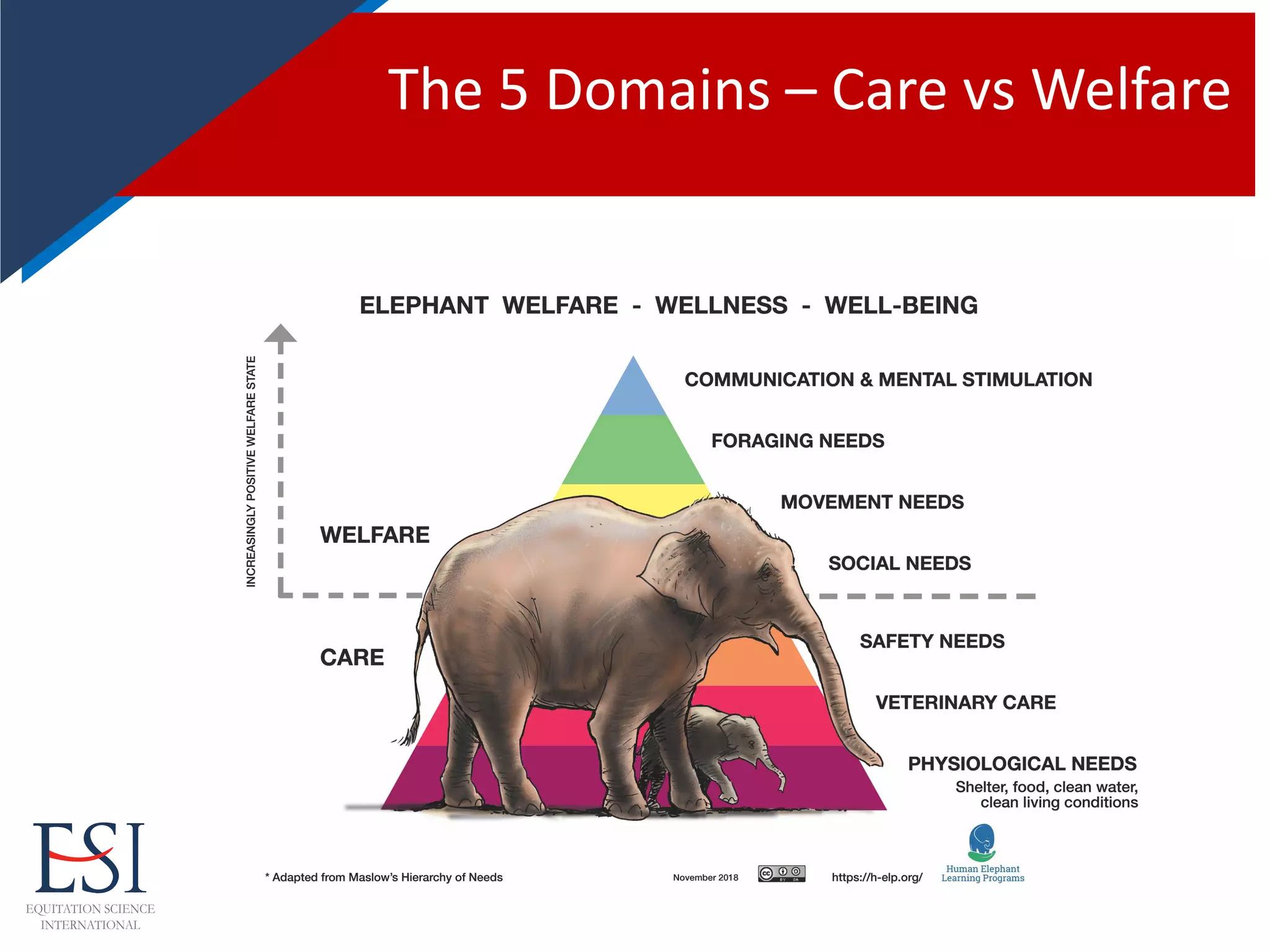
The document reflects on the evolution and challenges of evidence-based training in equitation science, emphasizing the transition from traditional methods to approaches rooted in psychology and animal behavior. It discusses the historical context of horse training, significant figures in the field, and the need for positive reinforcement techniques, while also addressing potential dysfunctions and conflict behaviors that may arise from improper training methods. Dr. Andrew McLean's contributions and advocacy for equitation science and animal welfare are highlighted throughout the narrative.









![Extinguishing the naughty horse…
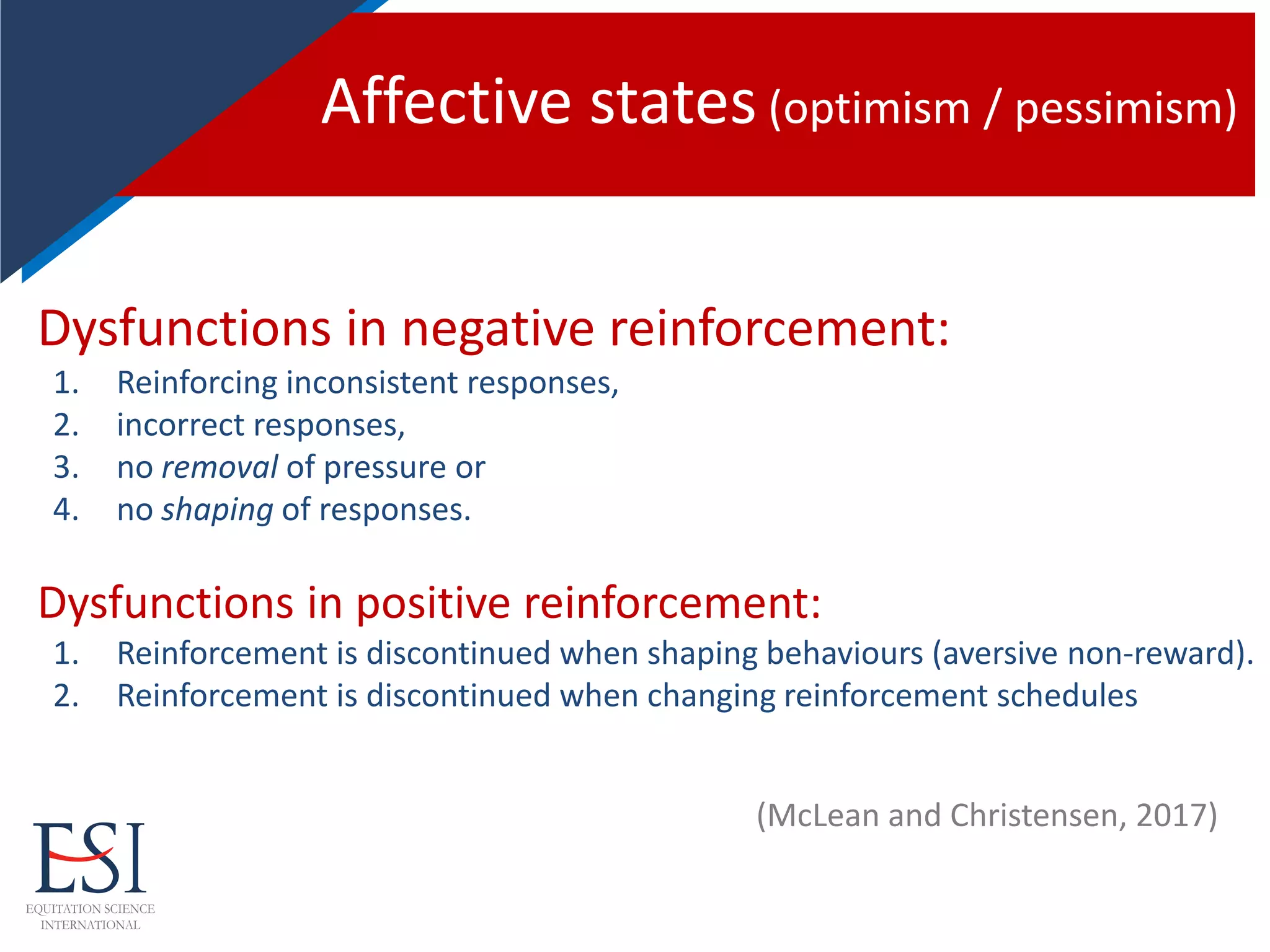
Training via negative reinforcement rules:
1. The strength of the aversive stimulus must meet the sensitivity of the individual
animal.
2. The aversive stimulus must be terminated at a right moment to avoid
punishment.
3. The animal should be in a sufficiently relaxed state to assess its situation and give
an adequate behavioural reaction.
4. Aversive tactile stimuli should be rapidly reduced to light versions of those stimuli
via classical conditioning.
Neglecting any of these conditions may lead to substantial emotional problems,
conflict behaviours, hyperactivity, or excessive fear in the horse-human relationship,
regardless of the training method
[How "natural" training methods can affect equine mental state? A critical approach - A review
Rozempolska-Rucińska et al, 2013 (Animal science papers and reports 31(3):185-19]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmcleanthewindsofchange-190214221601/75/The-Winds-of-Change-Reflections-on-the-international-adoption-of-evidenced-based-training-horsetraining-10-2048.jpg)


![Conflict Prevention
Co-author:
“First Training Principles” for
ISES
[www.equitationscience.com]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/andrewmcleanthewindsofchange-190214221601/75/The-Winds-of-Change-Reflections-on-the-international-adoption-of-evidenced-based-training-horsetraining-14-2048.jpg)