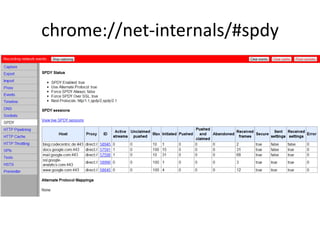
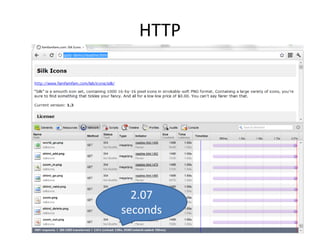
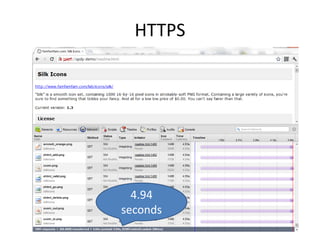
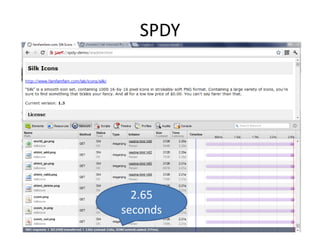
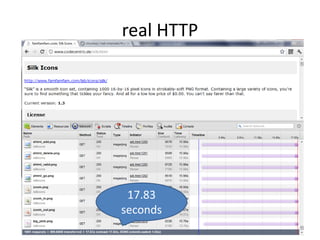
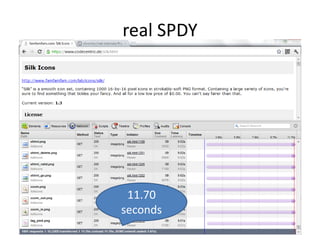
The document discusses the limitations of the current HTTP protocol and introduces SPDY, a Google proprietary protocol designed to address these issues by allowing multiple concurrent requests over a single TCP connection, compressing headers, and enabling server-initiated communications. It highlights challenges such as resource delays and redundant headers in traditional HTTP, while proposing SPDY's solutions to enhance web performance and security. Additionally, it includes technical implementation details and compatibility considerations for migrating to SPDY from traditional HTTP setups.
























![[root@centos57 modssl]# ./build_modssl_with_npn.sh
Using buildroot: /tmp/tmp.CooHIy8770
Downloading http://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.0.1-beta2.tar.gz
######################################################################## 100.0%
Downloading http://www.apache.org/dist/httpd/httpd-2.2.21.tar.gz
######################################################################## 100.0%
Downloading https://issues.apache.org/bugzilla/attachment.cgi?id=27969context=patch
######################################################################## 100.0%
Uncompressing openssl-1.0.1-beta2.tar.gz ... done
Uncompressing httpd-2.2.21.tar.gz ... done
Applying Apache mod_ssl NPN patch ...
patching file modules/ssl/ssl_private.h
patching file modules/ssl/ssl_engine_init.c
patching file modules/ssl/ssl_engine_io.c
patching file modules/ssl/ssl_engine_kernel.c
patching file modules/ssl/mod_ssl.c
patching file modules/ssl/mod_ssl.h
done
Configuring OpenSSL ... done
Building OpenSSL (this may take a while) ... done
Configuring Apache mod_ssl ... done
Building Apache mod_ssl (this may take a while) ... done
Generated mod_ssl.so at /root/modssl/mod_ssl.so.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spdy-120329021655-phpapp01/85/The-SPDY-Protocol-28-320.jpg)