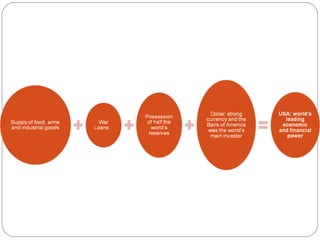
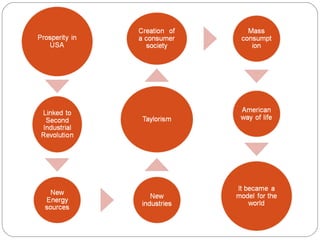
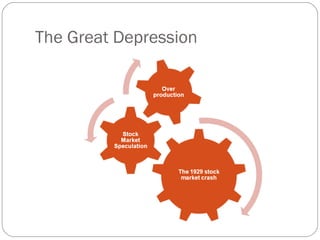
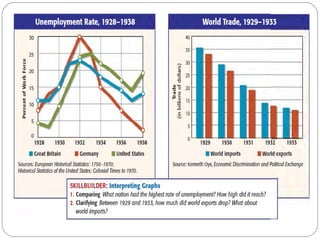
The 1920s saw economic problems in Europe including high unemployment, rising prices, and Germany's inability to pay war reparations which led to inflation and declining living standards. The Great Depression began in the late 1920s due to overproduction, low agricultural prices, and stock market speculation. It worsened in 1929 with the crash of the US stock market, causing banks to fail, industry to decline, unemployment to rise, and economic recession around the world. The Depression had international consequences as US banks withdrew money from Europe.