This document provides information about reflection and meta-programming in Ring, including functions to retrieve information about the program during runtime such as locals(), globals(), functions(), and cfunctions(). It also covers functions to retrieve information about classes, methods, and attributes like classes(), ismethod(), and attributes(). Additional functions covered include addattribute(), setattribute(), and mergemethods().

![CHAPTER
FORTYSIX
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
In previous chapters we learned about Functions and Recursion.
In this chapter we are going to learn about more Functional Programming (FP) concepts like
• Pure Functions
• First-class functions
• Higher-order functions
• Anonymous and nested functions.
• Equality of functions
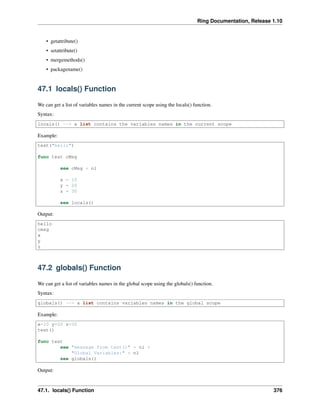
46.1 Pure Functions
We can create pure functions (functions that doesn’t change the state) by the help of the assignment operator to copy
variables (Lists & Objects) by value to create new variables instead of working on the original data that are passed to
the function by reference.
Example:
Func Main
aList = [1,2,3,4,5]
aList2 = square(aList)
see "aList" + nl
see aList
see "aList2" + nl
see aList2
Func Square aPara
a1 = aPara # copy the list
for x in a1
x *= x
next
return a1 # return new list
Output:
aList
1
2
3
4
5
370](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/401ring-190427182058/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-10-book-Part-41-of-212-3-320.jpg)
![Ring Documentation, Release 1.10
aList2
1
4
9
16
25
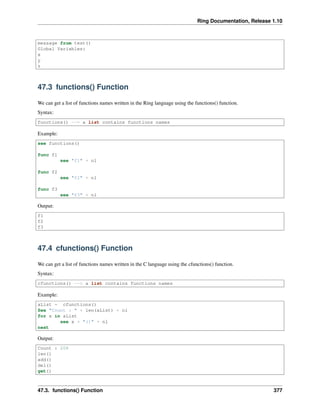
46.2 First-class Functions
Functions inside the Ring programming language are first-class citizens, you can pass functions as parameters, return
them as value or store them in variables.
We can pass/return the function by typing the function name as literal like “FunctionName” or :FunctionName for
example.
We can pass/return functions using the variable that contains the function name.
We can call function from variables contains the function name using the Call command
Syntax:
Call Variable([Parameters])
Example:
Func Main
see "before test2()" + nl
f = Test2(:Test)
see "after test2()" + nl
call f()
Func Test
see "Message from test!" + nl
Func Test2 f1
call f1()
See "Message from test2!" + nl
return f1
Output:
before test2()
Message from test!
Message from test2!
after test2()
Message from test!
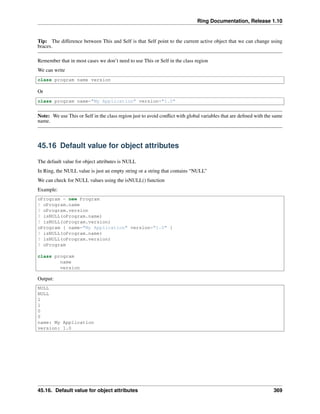
46.3 Higher-order Functions
Higher-order functions are the functions that takes other functions as parameters.
Example:
Func Main
times(5,:test)
46.2. First-class Functions 371](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/401ring-190427182058/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-10-book-Part-41-of-212-4-320.jpg)
![Ring Documentation, Release 1.10
Func Test
see "Message from the test function!" + nl
Func Times nCount,F
for x = 1 to nCount
Call F()
next
Output:
Message from the test function!
Message from the test function!
Message from the test function!
Message from the test function!
Message from the test function!
46.4 Anonymous and Nested Functions
Anonymous Functions are functions without names that can be passed as parameters to other functions or stored in
variables.
Syntax:
Func [Parameters] { [statements] }
Example:
test( func x,y {
see "hello" + nl
see "Sum : " + (x+y) + nl
} )
new great { f1() }
times(3, func { see "hello world" + nl } )
func test x
call x(3,3)
see "wow!" + nl
func times n,x
for t=1 to n
call x()
next
Class great
func f1
f2( func { see "Message from f1" + nl } )
func f2 x
call x()
Output:
hello
Sum : 6
46.4. Anonymous and Nested Functions 372](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/401ring-190427182058/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-10-book-Part-41-of-212-5-320.jpg)
![Ring Documentation, Release 1.10
wow!
Message from f1
hello world
hello world
hello world
Example:
Func Main
aList = [1,2,3,4]
Map (aList , func x {
return x*x
} )
see aList
aList = [4,9,14,25]
Map(aList, :myfilter )
see aList
aList = [11,12,13,14]
Map (aList , func x {
if x%2=0
return "even"
else
return "odd"
ok
})
see aList
Func myfilter x
if x = 9
return "True"
else
return "False"
ok
Func Map aList,cFunc
for x in aList
x = call cFunc(x)
next
Output:
1
4
9
16
False
True
False
False
odd
even
odd
even
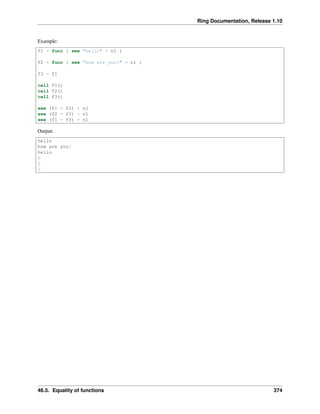
46.5 Equality of functions
We can test if function = function or not using the ‘=’ or ‘!=’ operators
46.5. Equality of functions 373](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/401ring-190427182058/85/The-Ring-programming-language-version-1-10-book-Part-41-of-212-6-320.jpg)