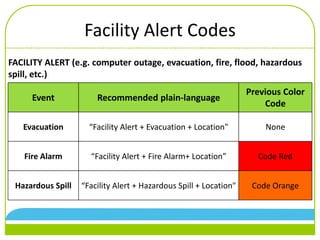
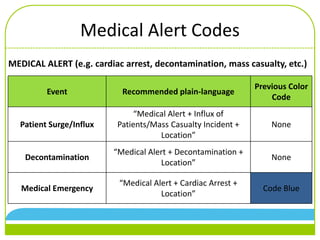
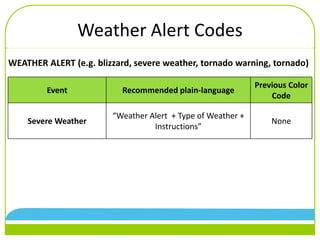
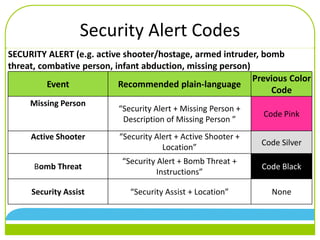
The document discusses changes to emergency codes to use plain language descriptions. It provides examples of plain language codes like "Security alert, missing person, 3rd floor east tower." The benefits are reducing confusion, allowing better understanding of the situation, and improving response times. The goals are for people to understand information and know how to respond. New codes are organized into facility, medical, weather, and security alerts. Specific codes are provided within each category. Emergency codes should now be called using a three part statement of alert category, code description, and location.