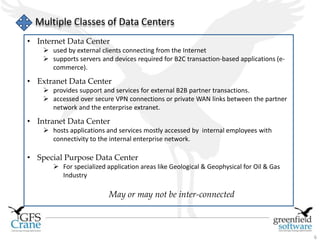
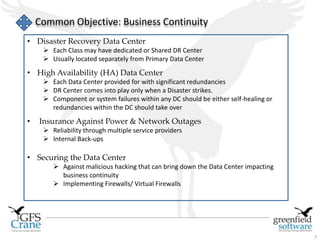
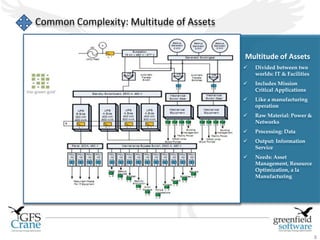
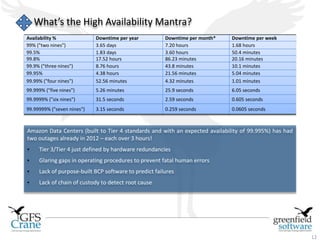
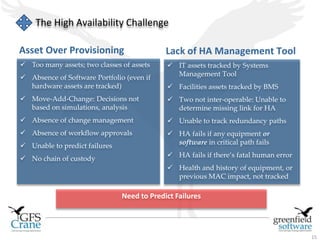
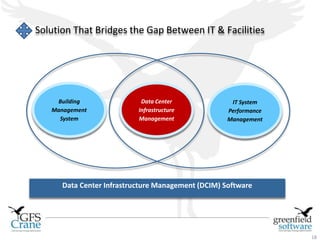
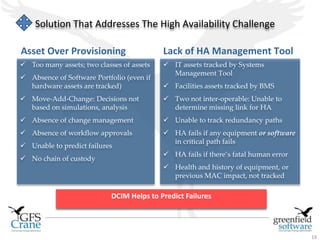
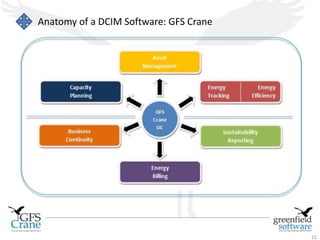
Greenfield Software is an Indian company focused on cloud-based infrastructure management, aiming to enhance operational and energy efficiencies in critical facilities. The document discusses modern data center types, the significance of high availability (HA), related challenges such as asset over-provisioning, and how effective management solutions like Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) can address these issues. Additionally, it highlights how failures in HA can lead to significant operational disruptions, using examples from major companies.