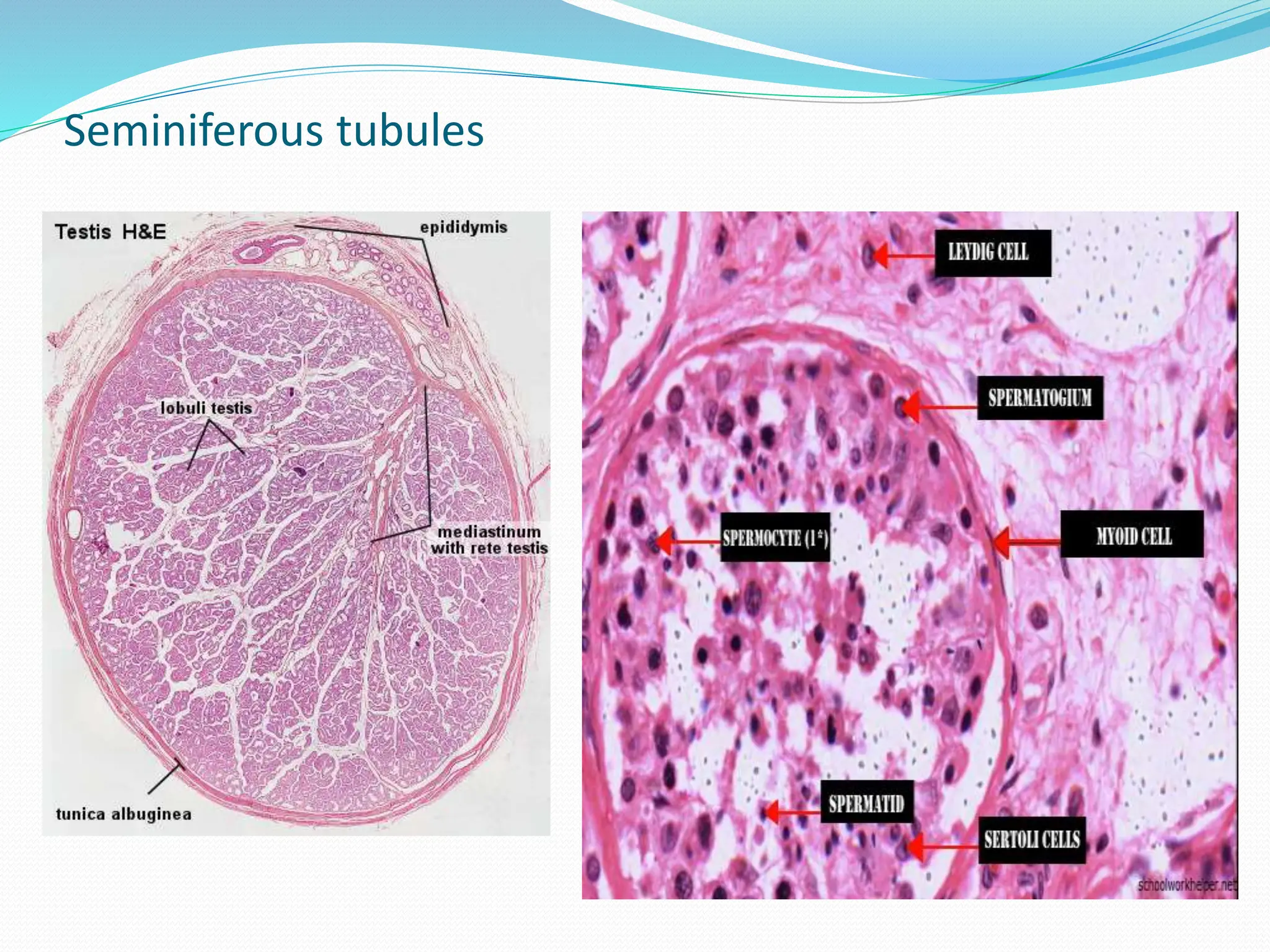
The document summarizes the male external and internal reproductive organs. It describes the penis, scrotum, testes, duct system including the epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct and urethra. It also discusses the process of spermatogenesis in the seminiferous tubules and sperm maturation in the epididymis. The accessory glands - prostate, seminal vesicles and bulbourethral glands are also described along with their secretions that combine to form semen.