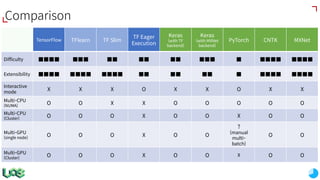
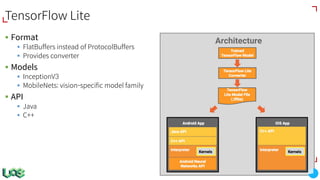
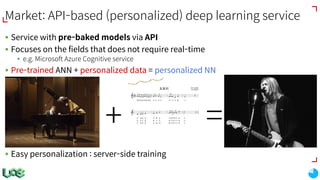
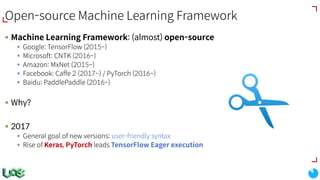
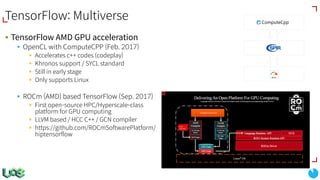
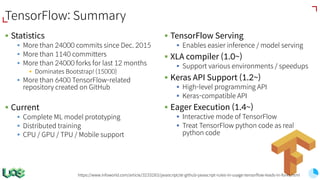
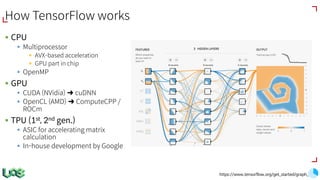
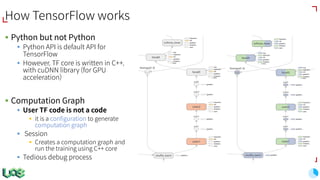
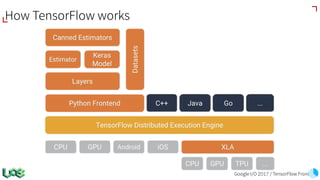
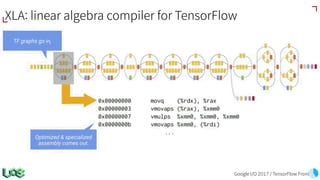
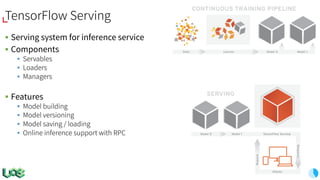
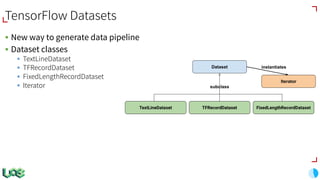
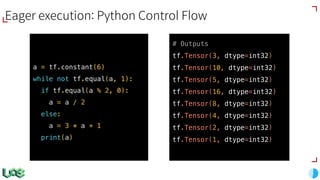
The document discusses the evolution and features of TensorFlow, an open-source software library developed by Google for machine learning. It covers various aspects such as types of machine learning, deep learning advancements, TensorFlow's architecture, API development, and the introduction of features like TensorFlow Serving and eager execution. The document also touches on market trends and the growing landscape of deep learning services.



















![Example: Decoding and resizing image data
# Reads an image from a file, decodes it into a dense tensor, and resizes it
# to a fixed shape.
def _parse_function(filename, label):
image_string = tf.read_file(filename)
image_decoded = tf.image.decode_image(image_string)
image_resized = tf.image.resize_images(image_decoded, [28, 28])
return image_resized, label
# A vector of filenames.
filenames = tf.constant(["/var/data/image1.jpg", "/var/data/image2.jpg", ...])
# `labels[i]` is the label for the image in `filenames[i].
labels = tf.constant([0, 37, ...])
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filenames, labels))
dataset = dataset.map(_parse_function)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-31-320.jpg)

![Example: Session
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[1, 1])
m = tf.matmul(x, x)
print(m)
# Tensor("MatMul:0", shape=(1, 1),
dtype=float32)
with tf.Session() as sess:
m_out = sess.run(m, feed_dict={x: [[2.]]})
print(m_out)
# [[4.]]
x = [[2.]]
m = tf.matmul(x, x)
print(m)
# tf.Tensor([[4.]], dtype=float32,
shape=(1,1))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-33-320.jpg)
![Example: Instant error
x = tf.gather([0, 1, 2], 7)
InvalidArgumentError: indices = 7 is not in [0, 3) [Op:Gather]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-34-320.jpg)
![Example: removing metaprogramming
x = tf.random_uniform([2, 2])
with tf.Session() as sess:
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
for j in range(x.shape[1]):
print(sess.run(x[i, j]))
x = tf.random_uniform([2, 2])
for i in range(x.shape[0]):
for j in range(x.shape[1]):
print(x[i, j])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-35-320.jpg)
![def square(x):
return tf.multiply(x, x) # Or x * x
grad = tfe.gradients_function(square)
print(square(3.)) # tf.Tensor(9., dtype=tf.float32
print(grad(3.)) # [tf.Tensor(6., dtype=tf.float32))]
Eager execution: Gradients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-37-320.jpg)
![def square(x):
return tf.multiply(x, x) # Or x * x
grad = tfe.gradients_function(square)
gradgrad = tfe.gradients_function(lambda x: grad(x)[0])
print(square(3.)) # tf.Tensor(9., dtype=tf.float32)
print(grad(3.)) # [tf.Tensor(6., dtype=tf.float32)]
print(gradgrad(3.)) # [tf.Tensor(2., dtype=tf.float32))]
Eager execution: Gradients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-38-320.jpg)
![def log1pexp(x):
return tf.log(1 + tf.exp(x))
grad_log1pexp = tfe.gradients_function(log1pexp)
print(grad_log1pexp(0.))
Eager execution: Custom Gradients
Works fine, prints [0.5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-39-320.jpg)
![def log1pexp(x):
return tf.log(1 + tf.exp(x))
grad_log1pexp = tfe.gradients_function(log1pexp)
print(grad_log1pexp(100.))
Eager execution: Custom Gradients
[nan] due to numeric
instability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-40-320.jpg)
![@tfe.custom_gradient
def log1pexp(x):
e = tf.exp(x)
def grad(dy):
return dy * (1 - 1 / (1 + e))
return tf.log(1 + e), grad
grad_log1pexp = tfe.gradients_function(log1pexp)
# Gradient at x = 0 works as before.
print(grad_log1pexp(0.)) # [0.5]
# And now gradient computation at x=100 works as well.
print(grad_log1pexp(100.)) # [1.0]
Eager execution: Custom Gradients](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-41-320.jpg)
![tf.device() for manual placement
with tf.device(“/gpu:0”):
x = tf.random_uniform([10, 10])
y = tf.matmul(x, x)
# x and y reside in GPU memory
Eager execution: Using GPUs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20171119devfestseoulshare-171221135029/85/The-Flow-of-TensorFlow-42-320.jpg)