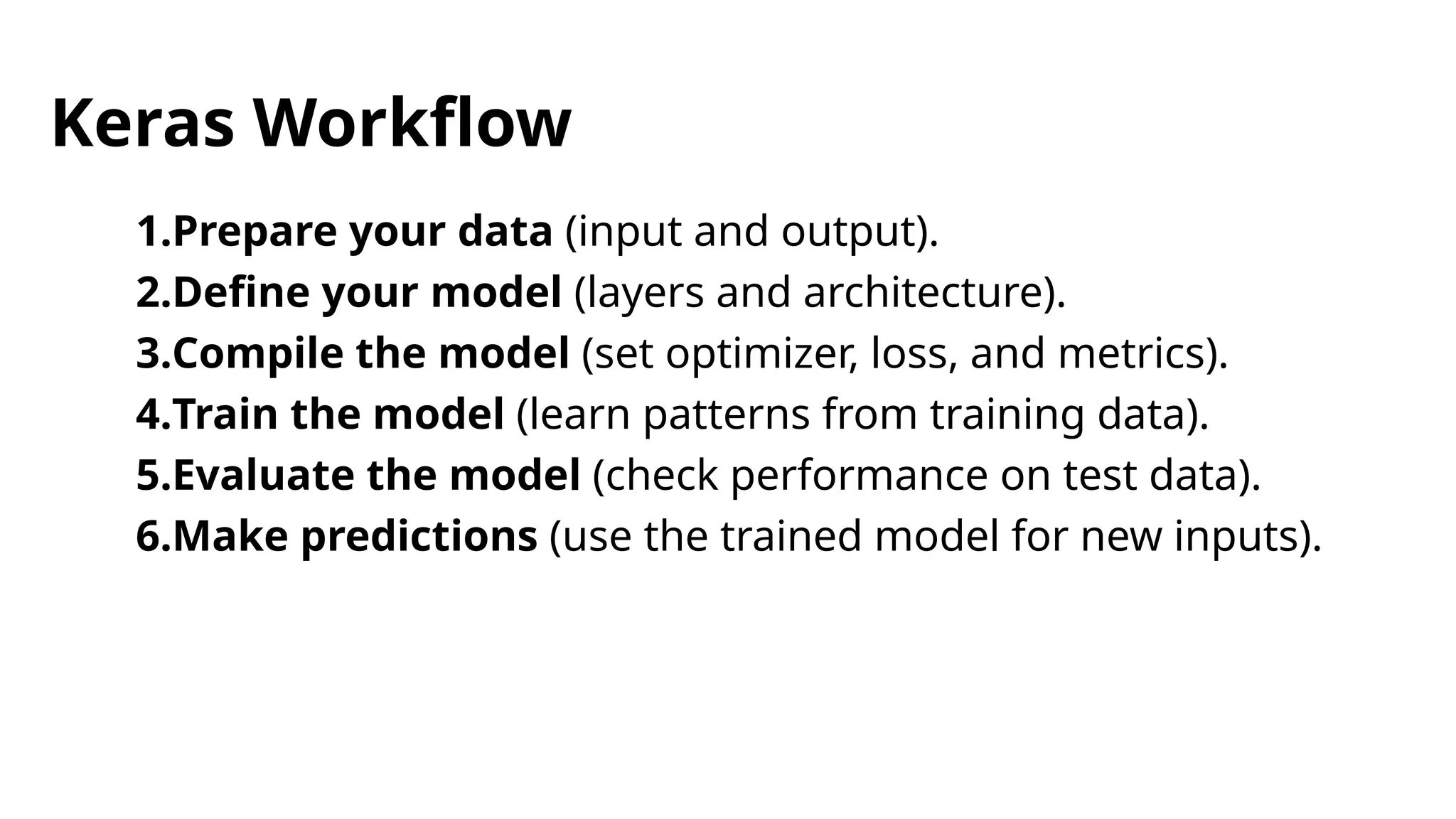
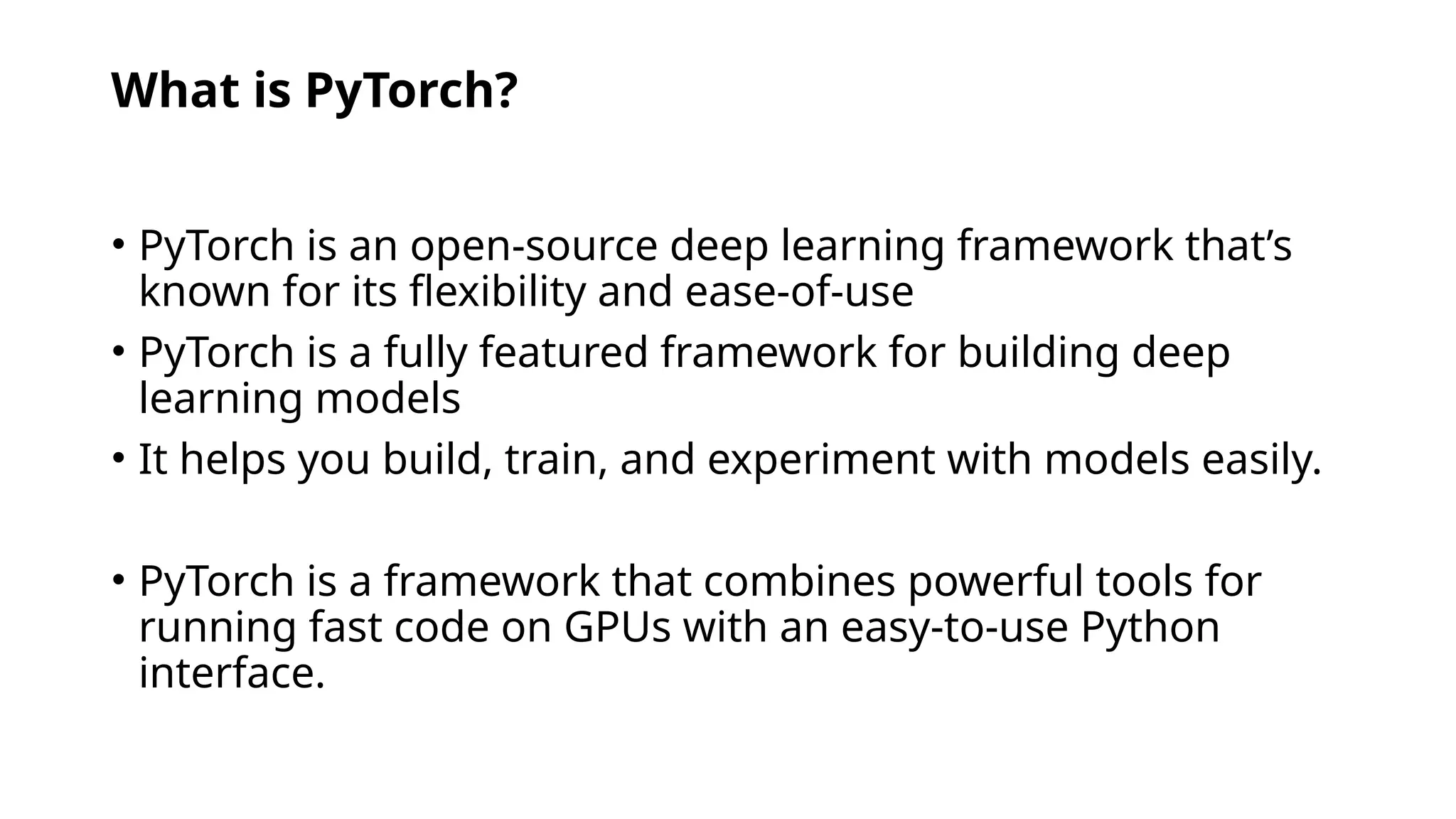
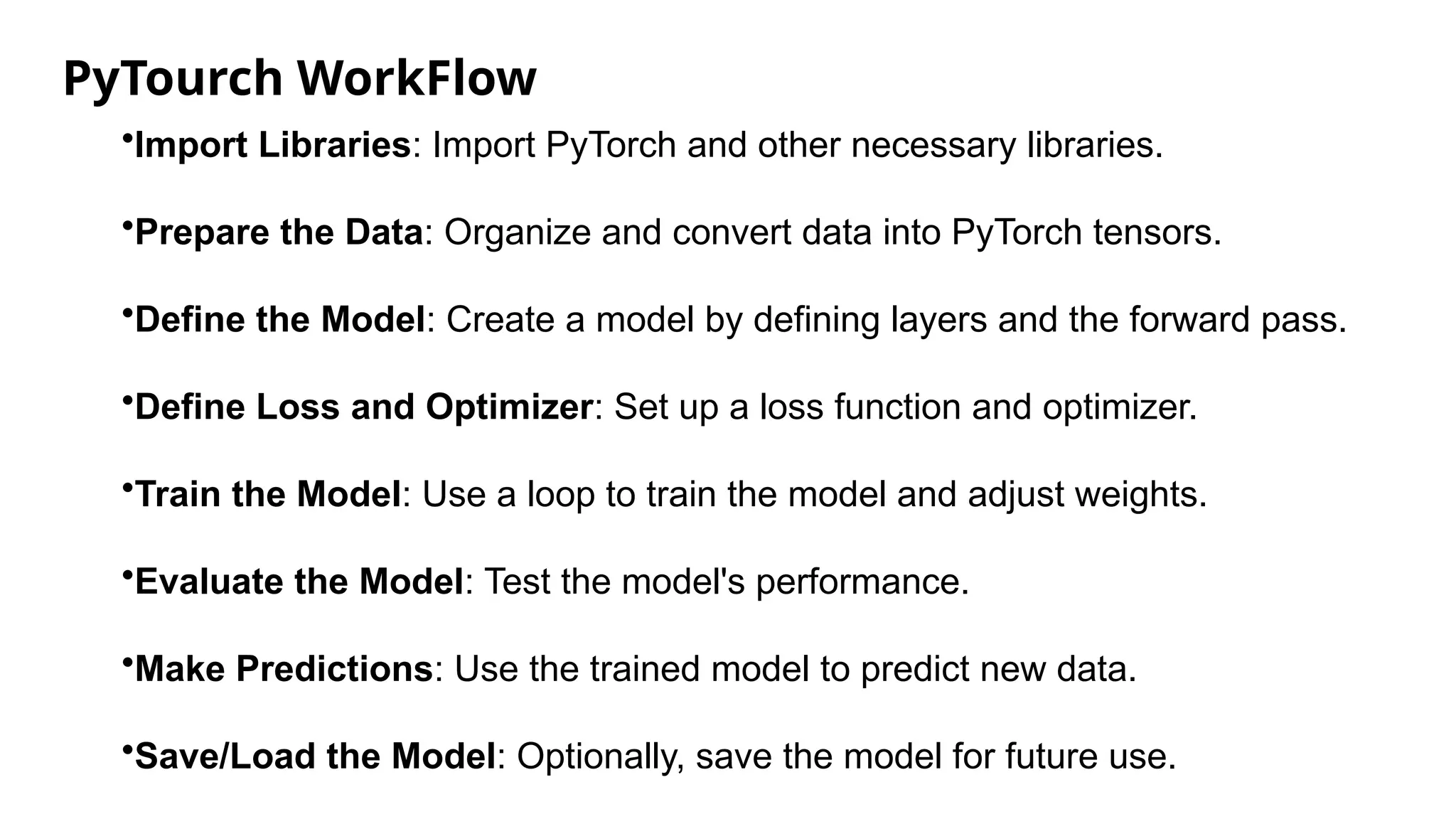
TensorFlow is an open-source library developed by Google for building machine learning and deep learning models, supporting various devices and programming languages. It excels in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning. Scikit-learn and Keras are additional libraries that focus on traditional machine learning and high-level model building, respectively, each offering distinct features and workflows.