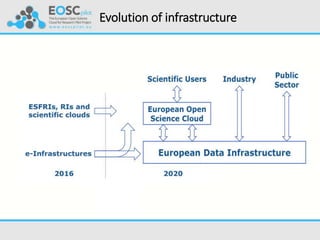
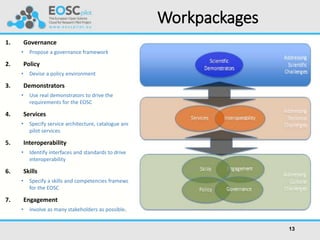
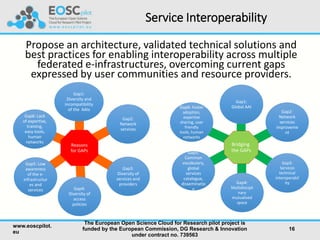
The European Open Science Cloud (EOSC) aims to enhance data sharing across research communities by creating an open science infrastructure that overcomes existing fragmentation and interoperability challenges. Key initiatives include the establishment of a governance framework, development of demonstrators for various scientific domains, and fostering engagement among stakeholders to build an open science culture. The project is supported by a €10 million funding for 33 partners to develop services and policies promoting data reuse and collaboration across disciplines.