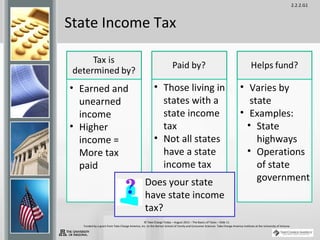
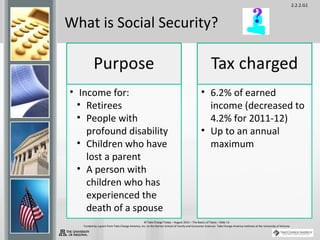
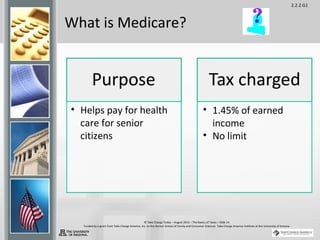
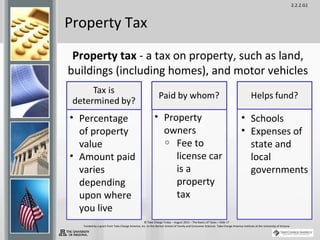
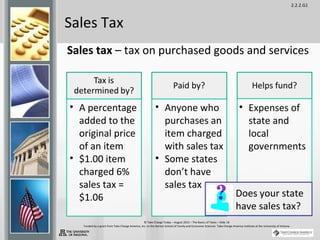
Taxes are sums of money demanded by governments to support government services and facilities. They are paid by taxpayers and fund things like roads, schools, police, and fire departments. There are several types of taxes including income tax, payroll tax, property tax, sales tax, and excise tax. Understanding taxes is an important part of money management as they play a role in both earning and spending and are typically one of the largest household expenses.