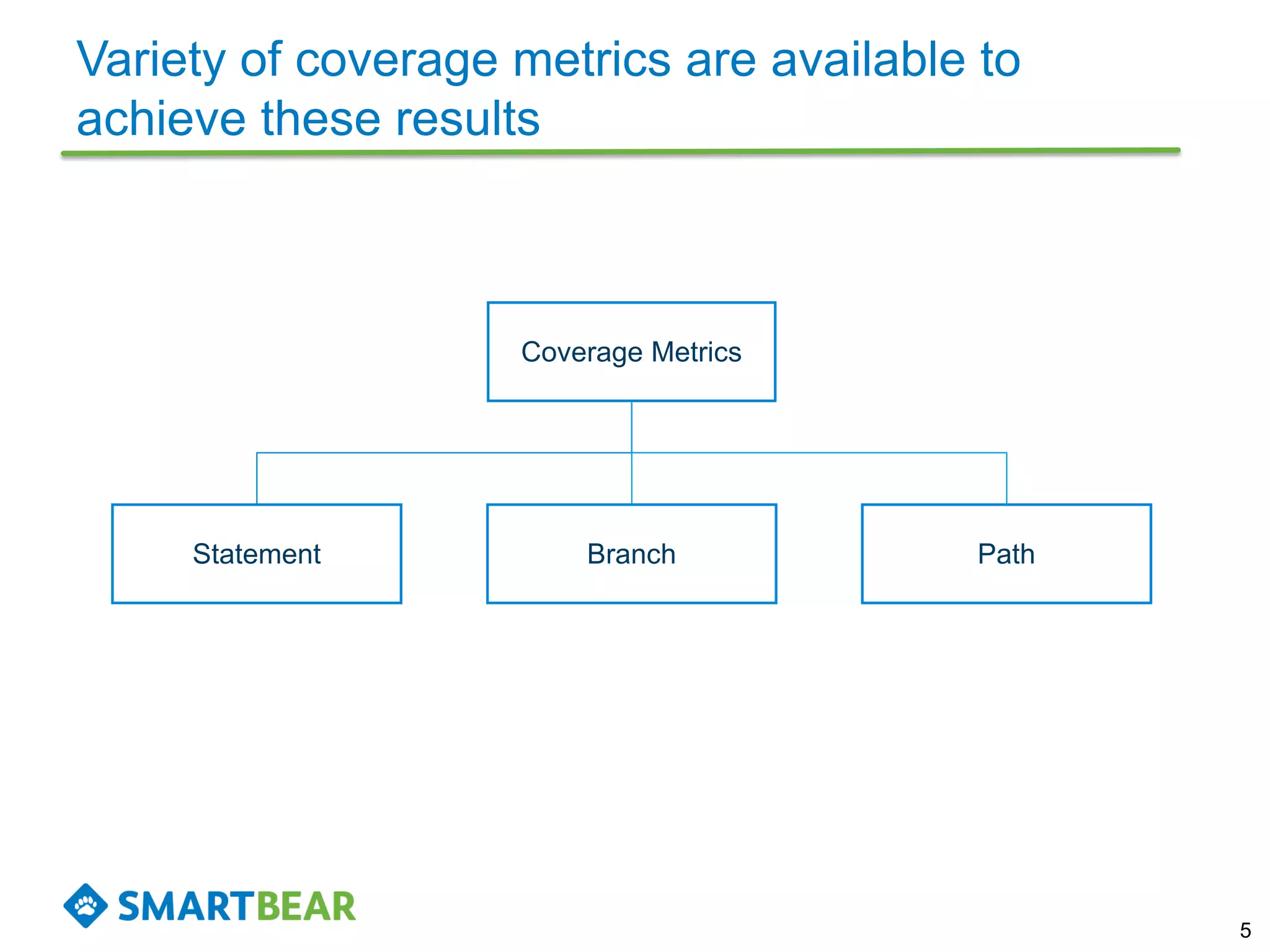
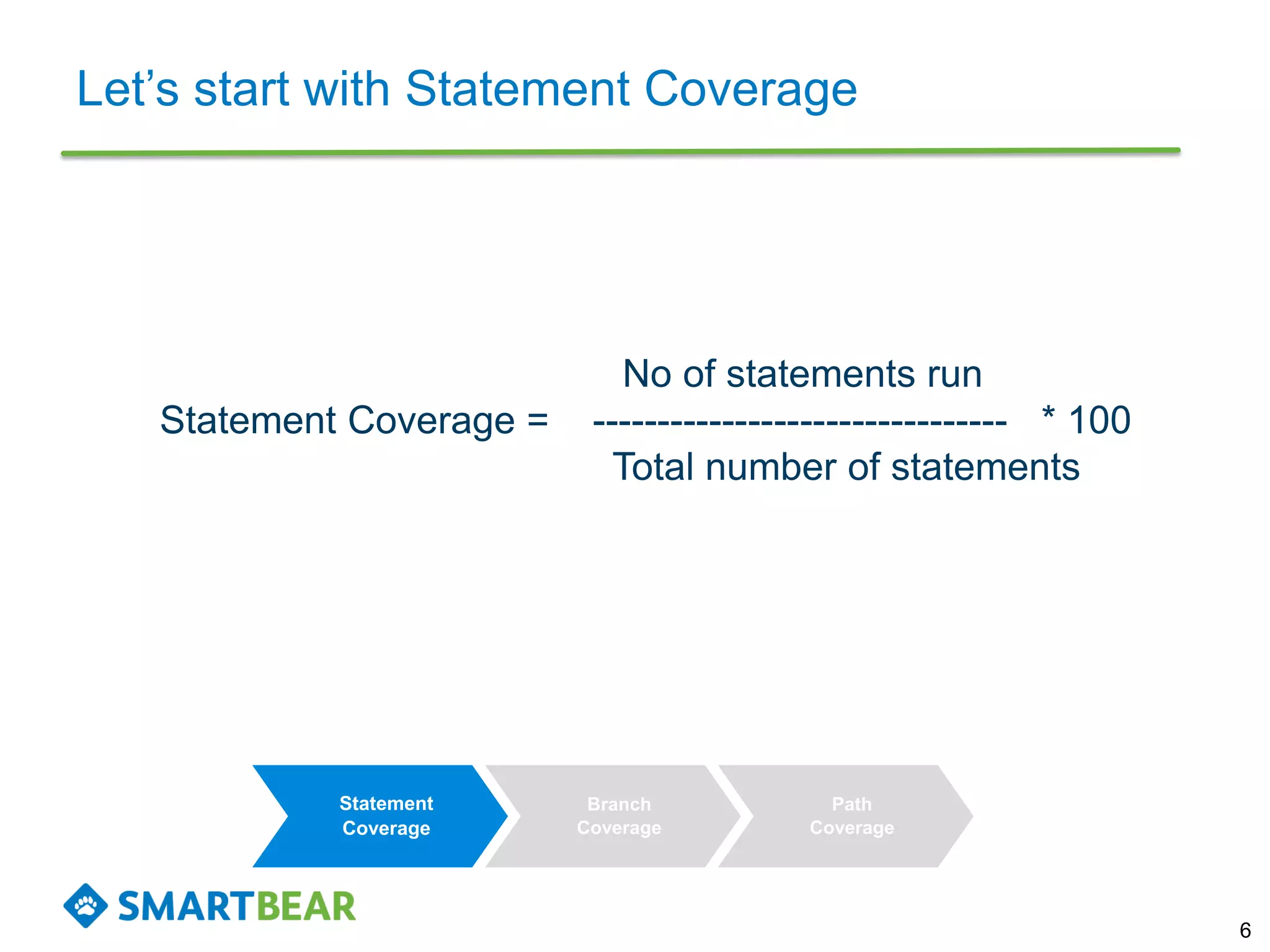
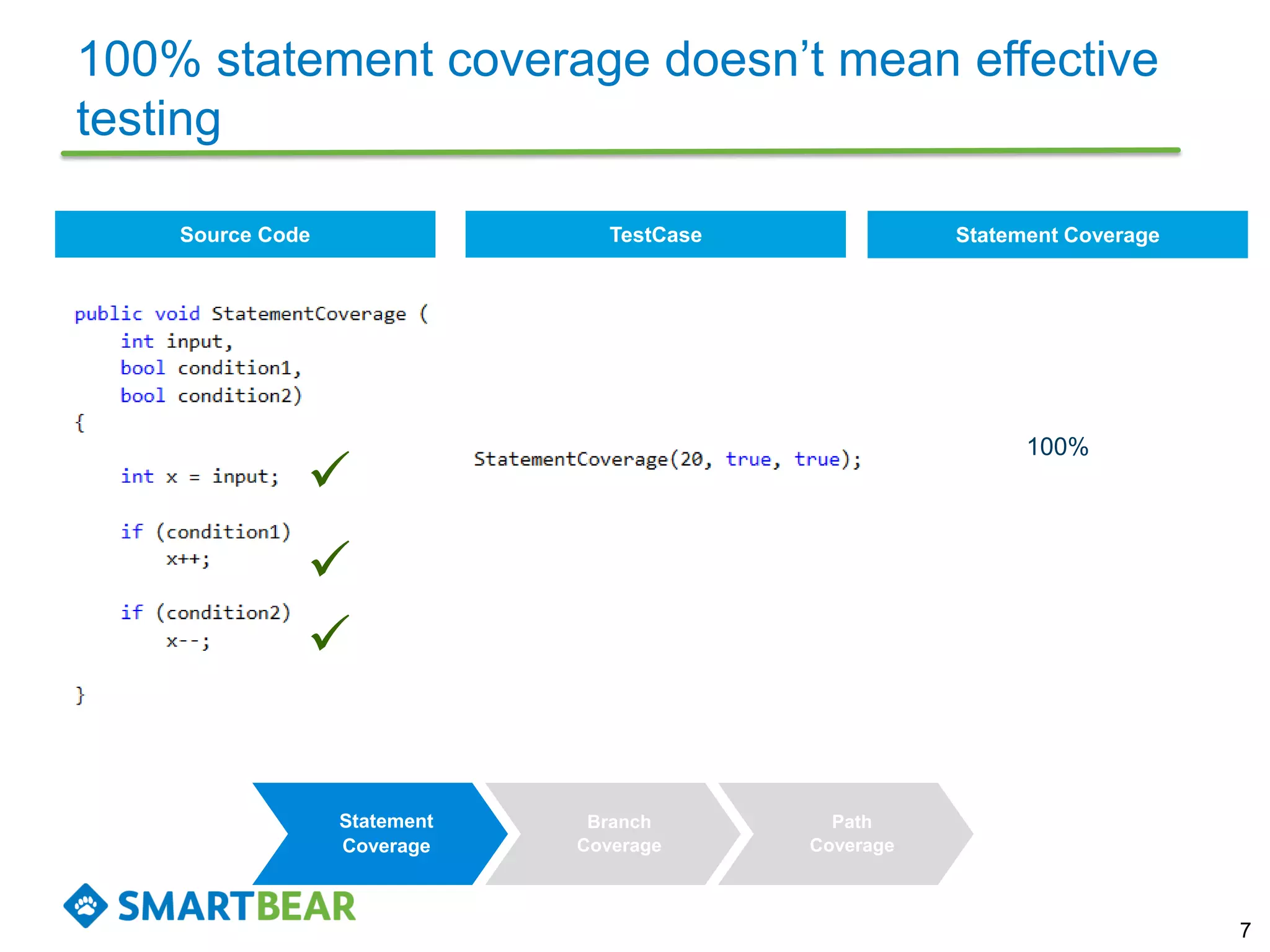
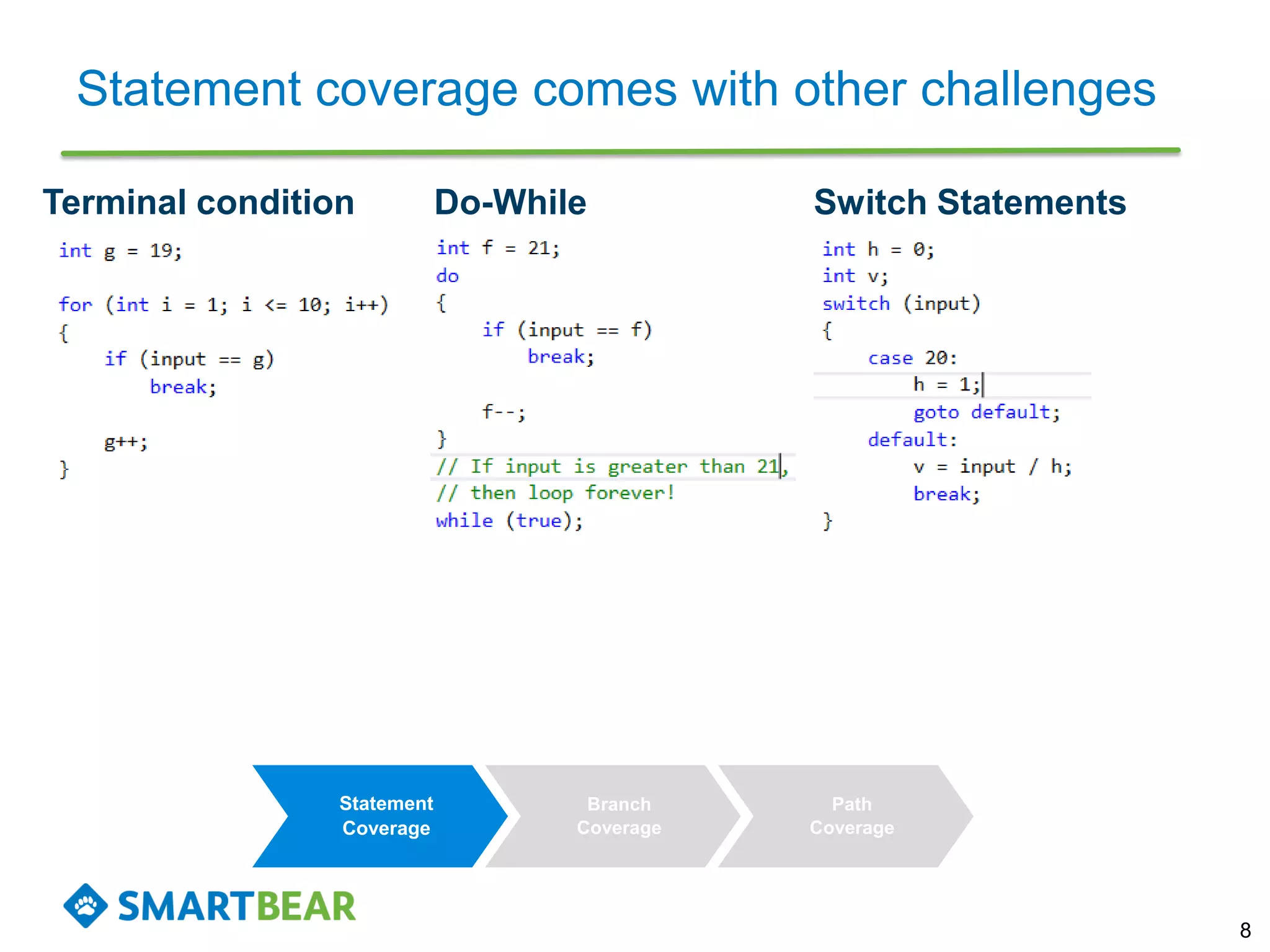
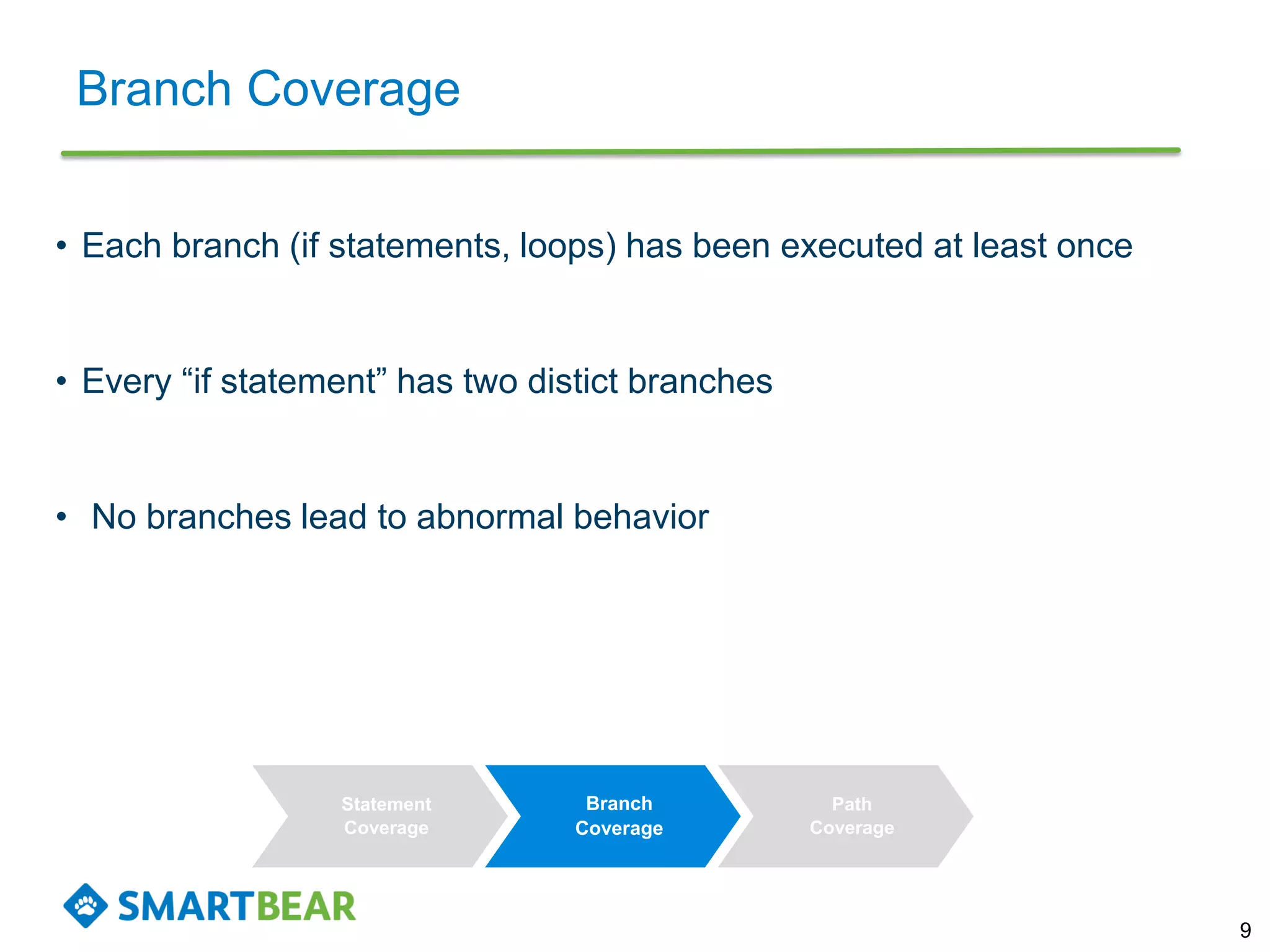
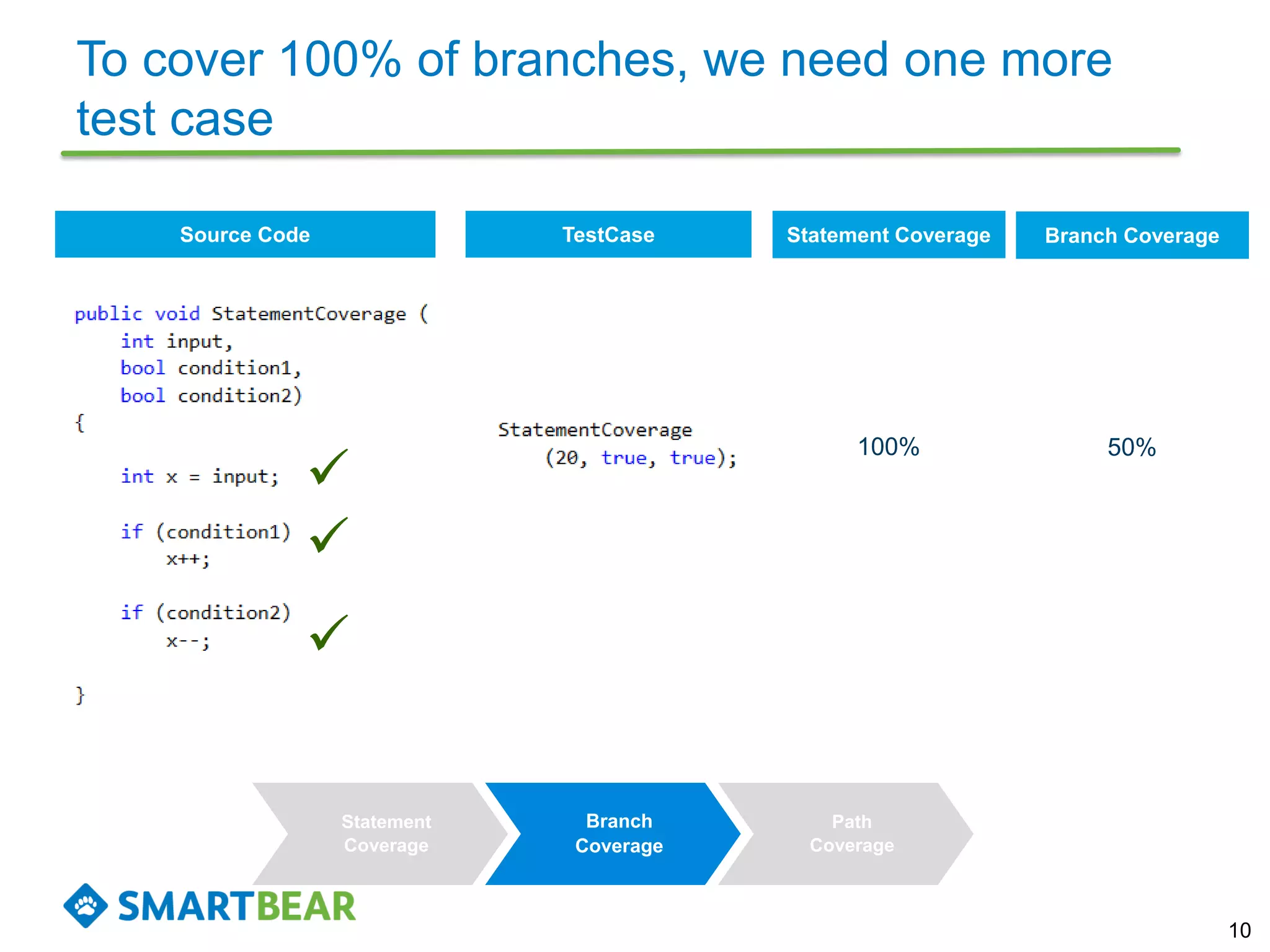
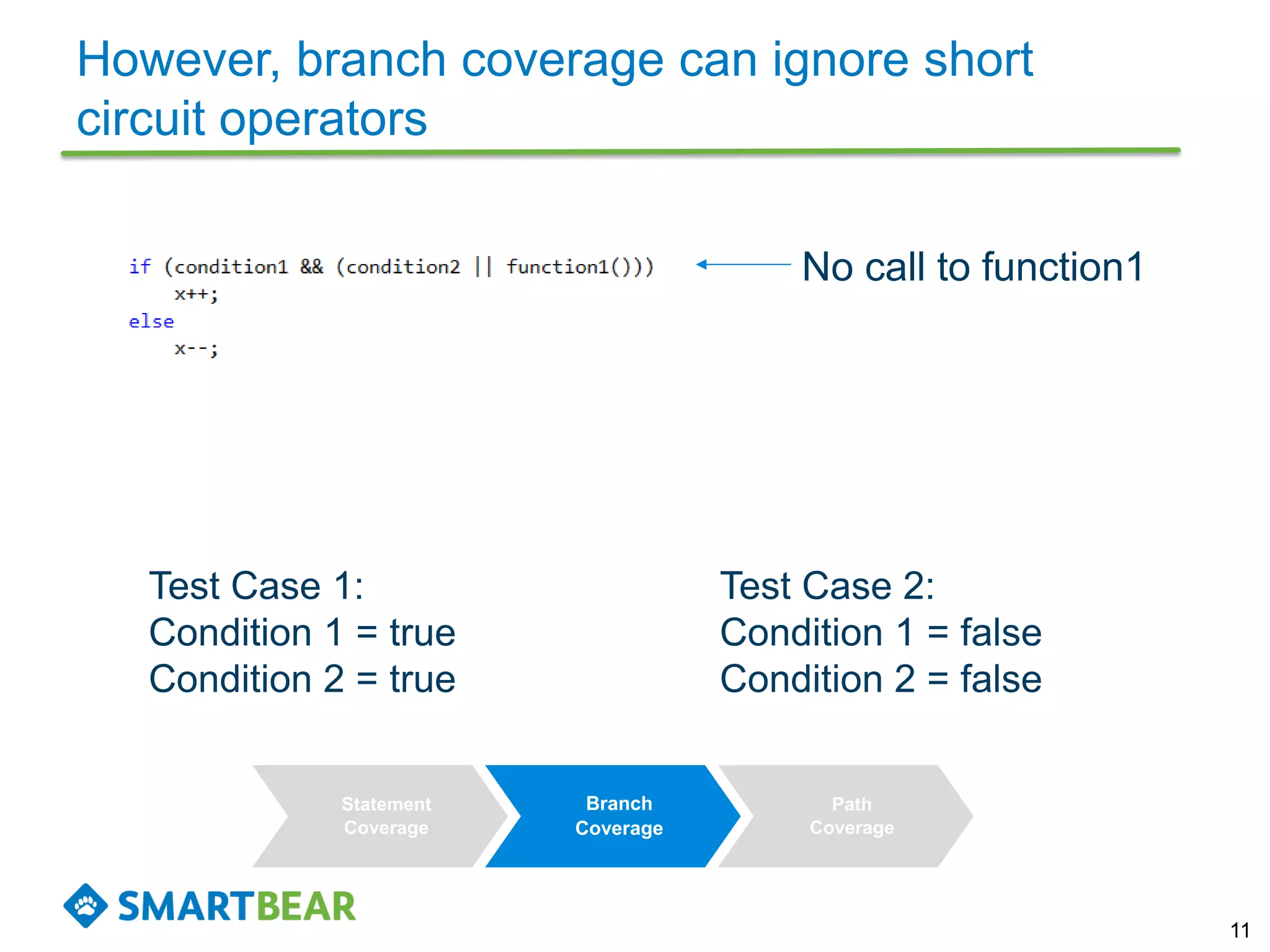
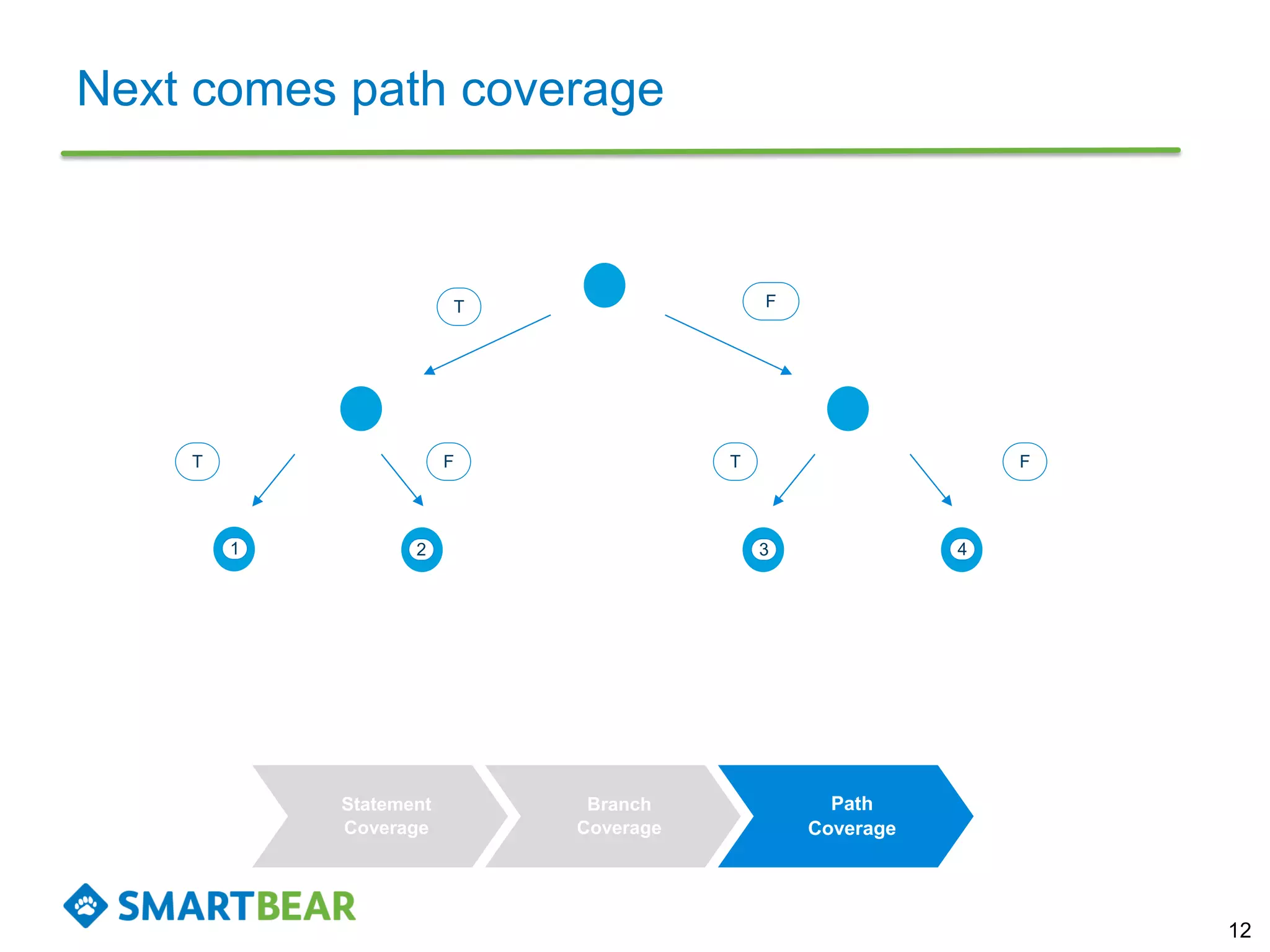
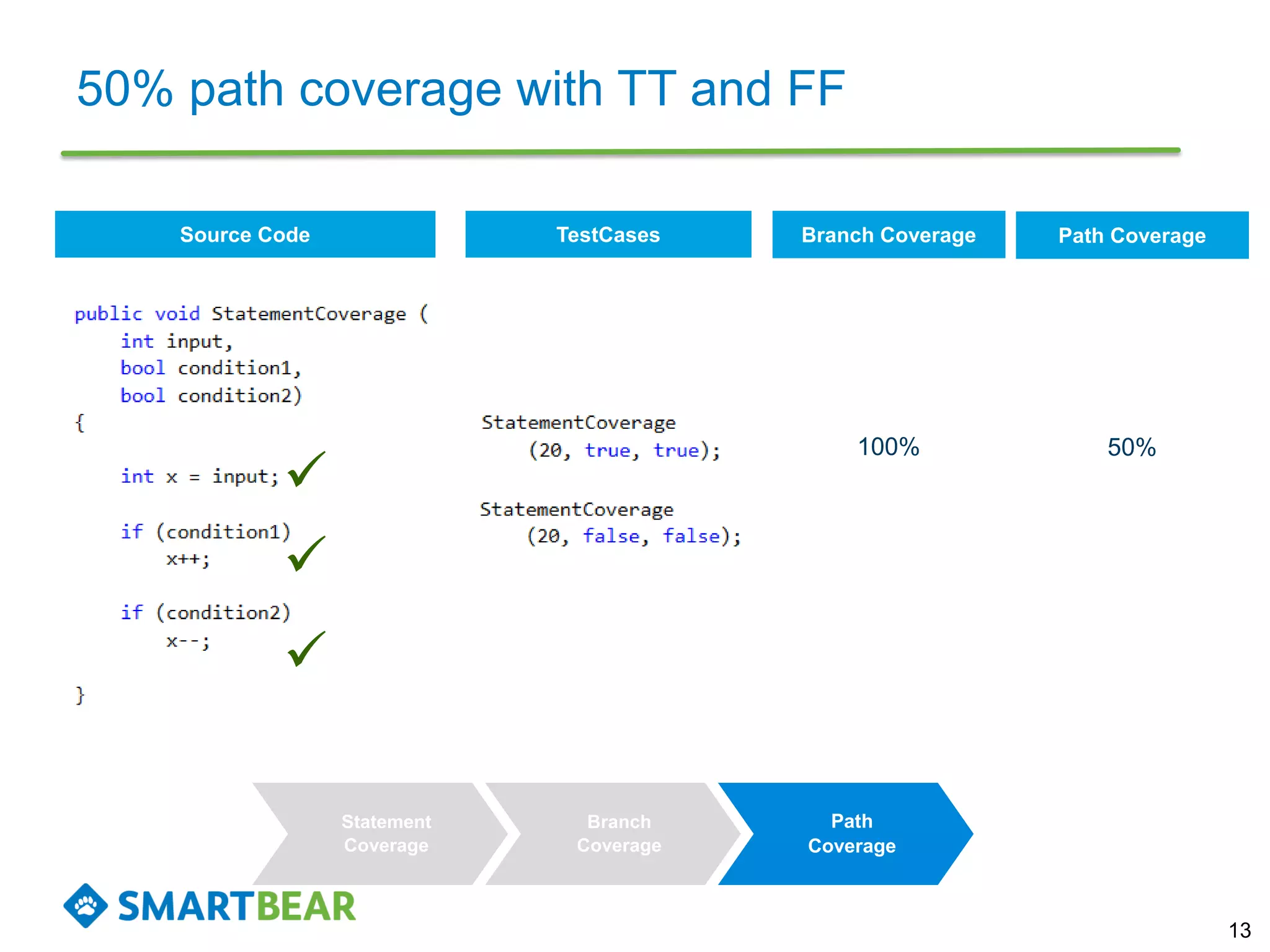
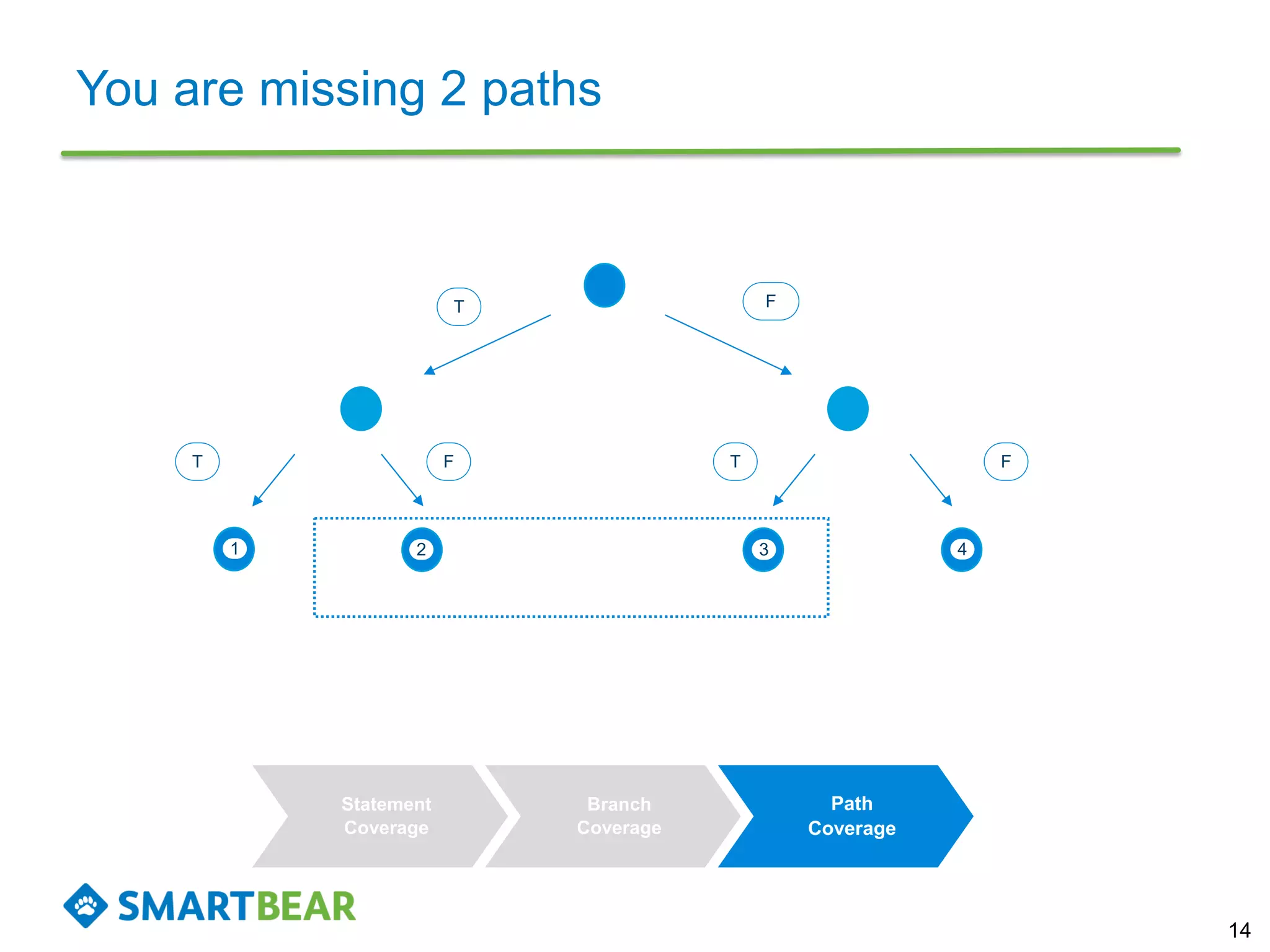
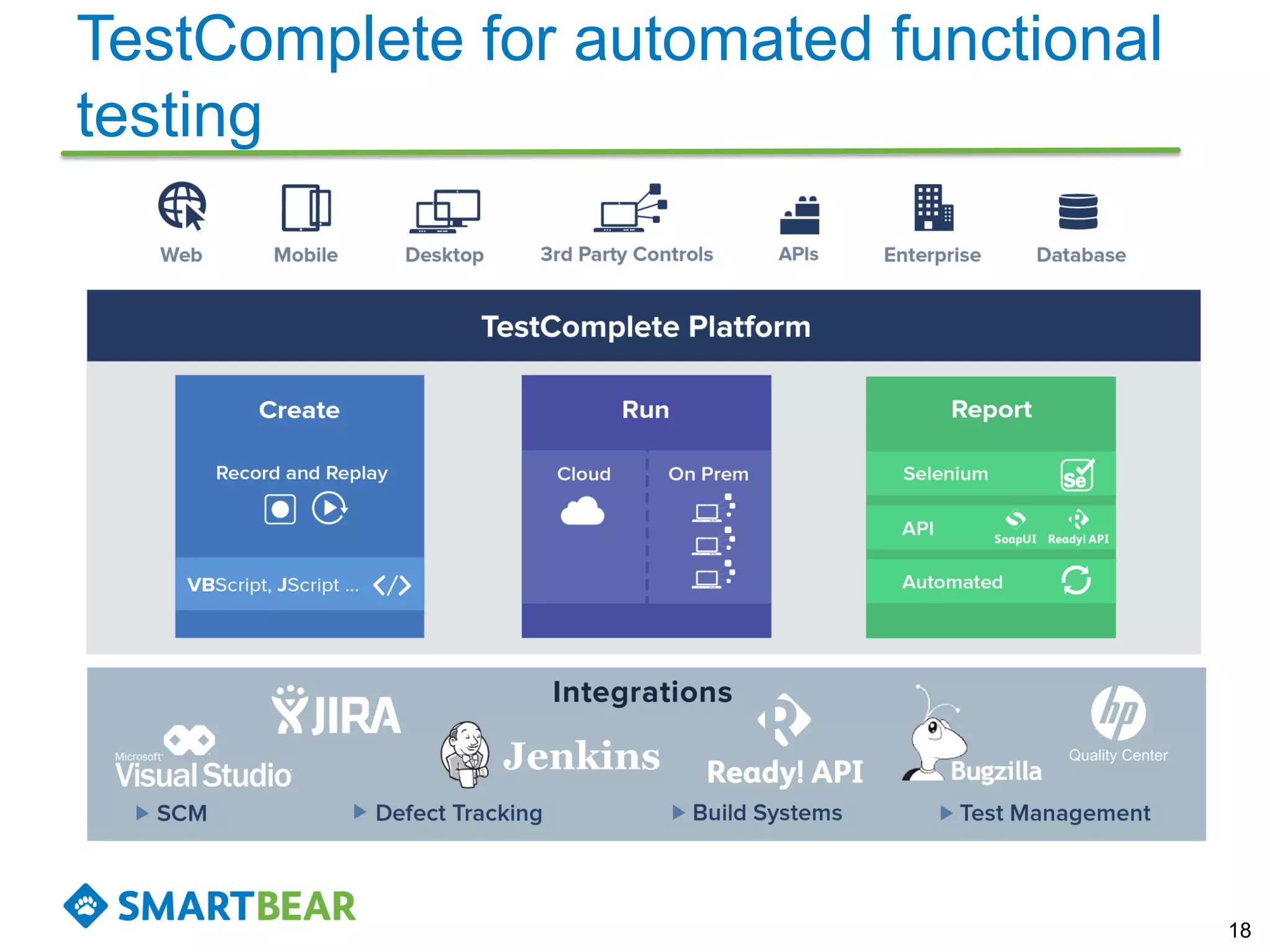
The document discusses the importance of coverage metrics in software testing, highlighting three main types: statement coverage, branch coverage, and path coverage. It emphasizes that high coverage percentages do not guarantee effective testing and warns against focusing solely on metrics without considering overall quality. The document also suggests strategies for achieving meaningful coverage by identifying early issues and testing various parts of the application.