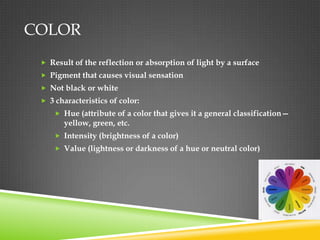
This document provides definitions for key terms used in understanding literature and art. For art vocabulary, it defines concepts like color, line, shade, space, brushstroke, perspective, background, and focal point. For literary vocabulary, it outlines themes in fiction and non-fiction works, figurative language, denotation vs connotation, setting, mood vs tone, types of irony, style, humor, and perspective vs point of view. The purpose is to introduce 8th grade students to important concepts and vocabulary used for analyzing and discussing both visual art and literature.