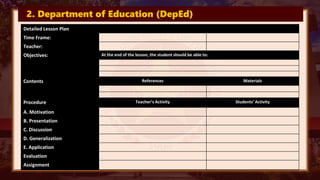
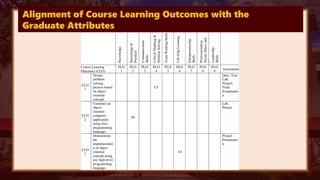
This document discusses productivity software applications that can be used for language teaching and learning. It identifies several uses of applications like MS Word, presentation software, and spreadsheets. It provides examples of how these applications can be used to create learning plans, assessments, templates and graphic organizers. It also discusses how presentation software can help develop language macro skills like reading, writing, speaking and listening. Specific productivity applications are identified for creating and sharing documents, presentations and spreadsheets for language learning. Basic instructional design for preparing presentations is also outlined.