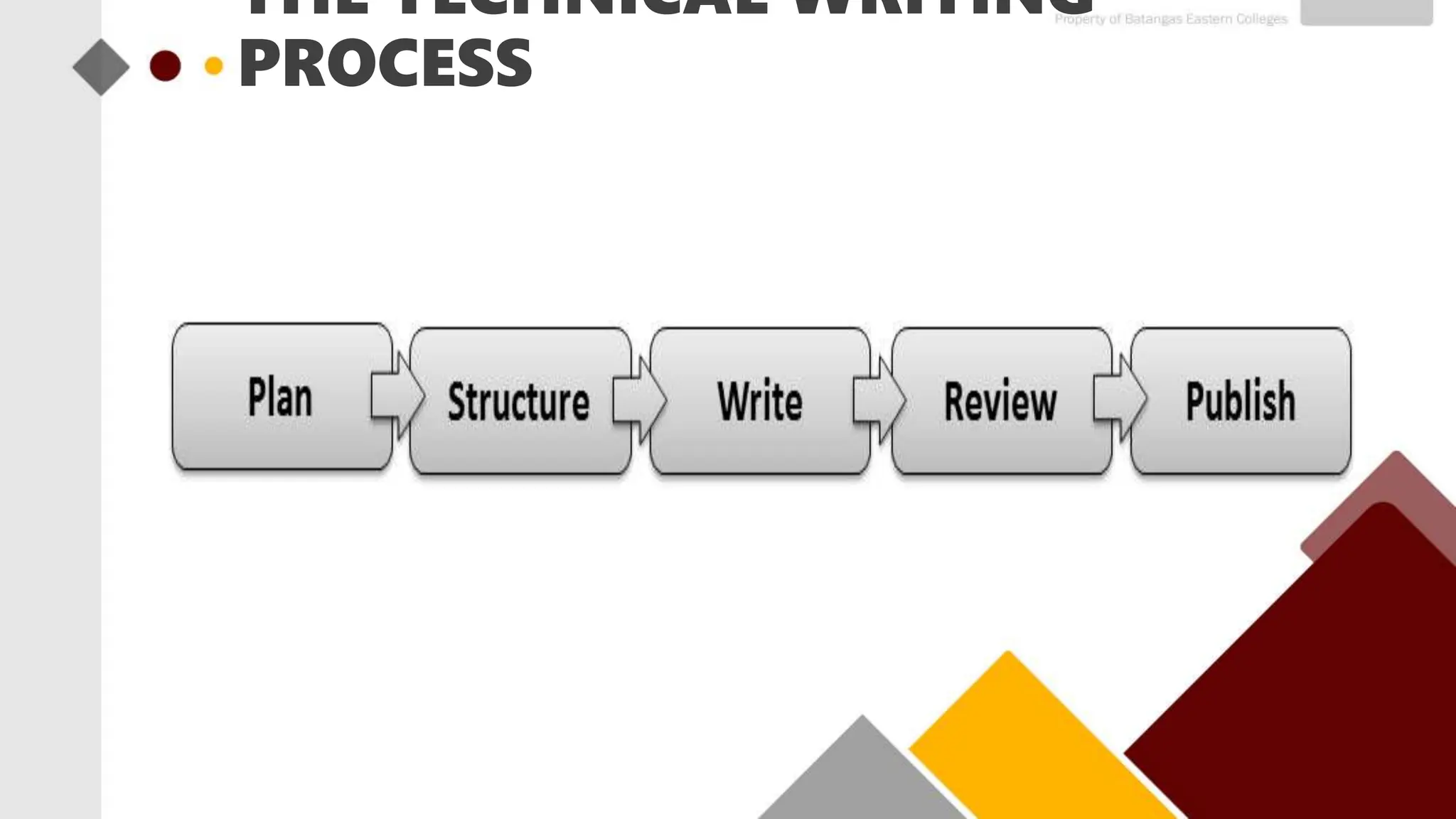
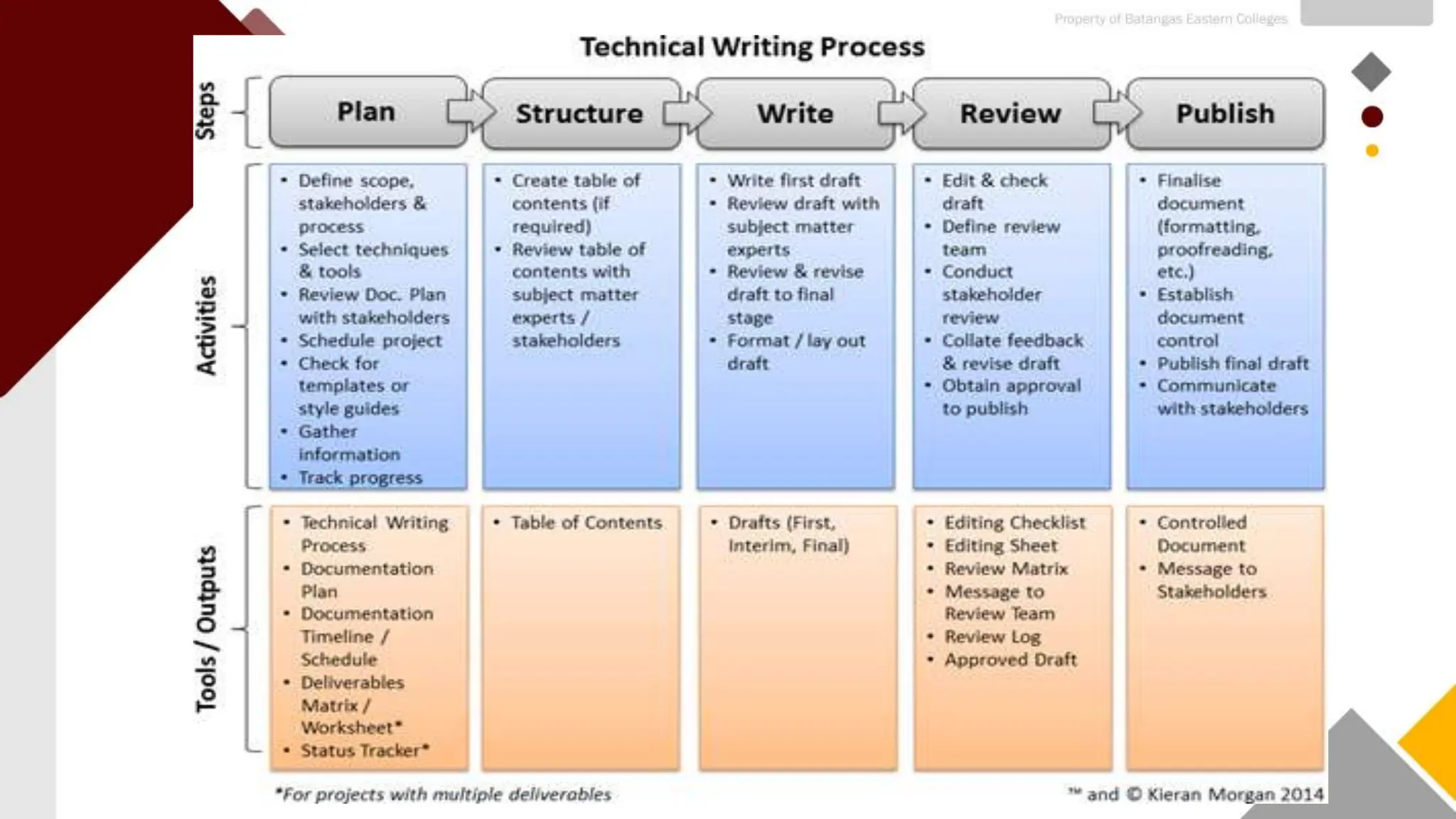
This document provides an overview of the technical writing process. It is divided into three main stages: pre-writing, drafting/writing, and post-writing/editing. The pre-writing stage involves planning, outlining, and gathering information. The drafting/writing stage is where the actual writing takes place. Considerations during this stage include structure, style, and appropriate language. The post-writing/editing stage focuses on revising content, organization, grammar, and style through activities like peer review and proofreading. The overall process helps technical writers create well-structured documents and overcome challenges through systematic planning, writing, and review.