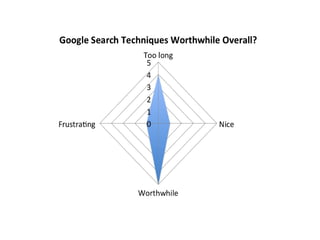
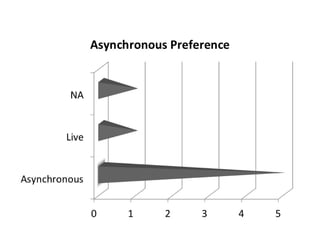
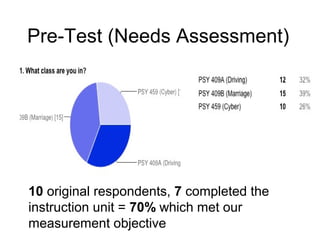
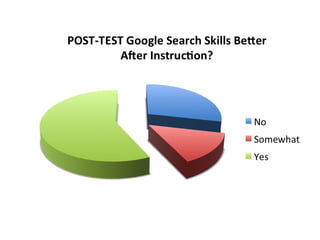
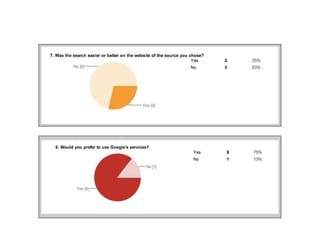
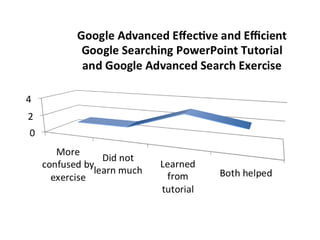
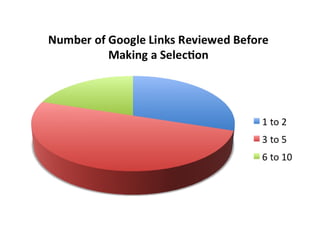
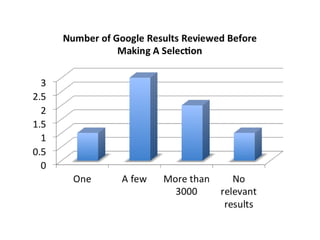
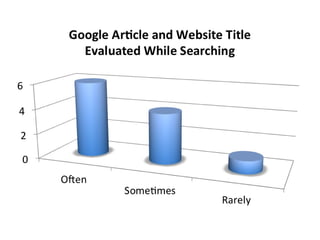
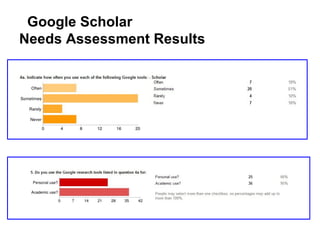
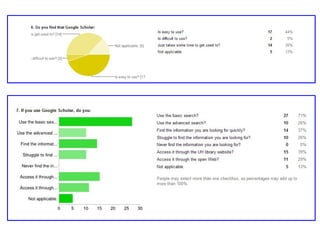
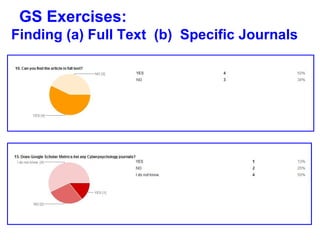
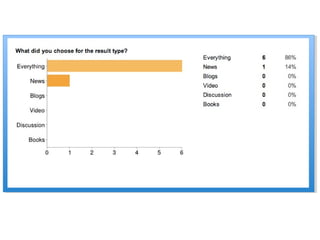
This document provides instructions and resources for students to complete exercises on using Google Advanced Search and Google Scholar Advanced Search techniques. It includes links to guides on advanced search tools, evaluating web resources, and APA citation style to assist students. It outlines exercises for students to practice personalized searches, finding full-text articles and specific journals, and provides examples of student responses evaluating the search tools. A survey found that 70% of students found the exercises worthwhile overall.









![Examples: Open-Ended Question
Results
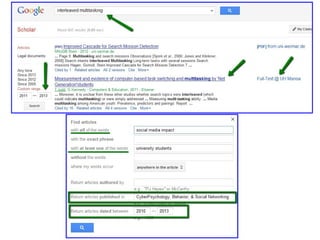
• Google Advanced Search
o “I got over 400,000 results … first two are the wikipedia articles
about technostress and cyberpsychology … also a lot of different
sources that … provide definitions of both terms.”
• Google Scholar Advanced Search
o “I got 23,200 results. There were more results that discussed
techostress.”
• Strengths/Weaknesses of each tool
o “Google Advanced Search is better for a basic overview of the
topic while Google Scholar is better for a more in-depth
understanding.”
• Which is the better “discovery” tool for research
o “The Google Scholar Advanced Search would be better for
content, but Google Advanced Search would be better for …
[discovery] … because it is not limited to articles and
publication.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/teachinginformationtechnologyliteracyoutcomesassessment-130527135914-phpapp01/85/Teaching-information-technology-literacy-outcomes-assessment-31-320.jpg)