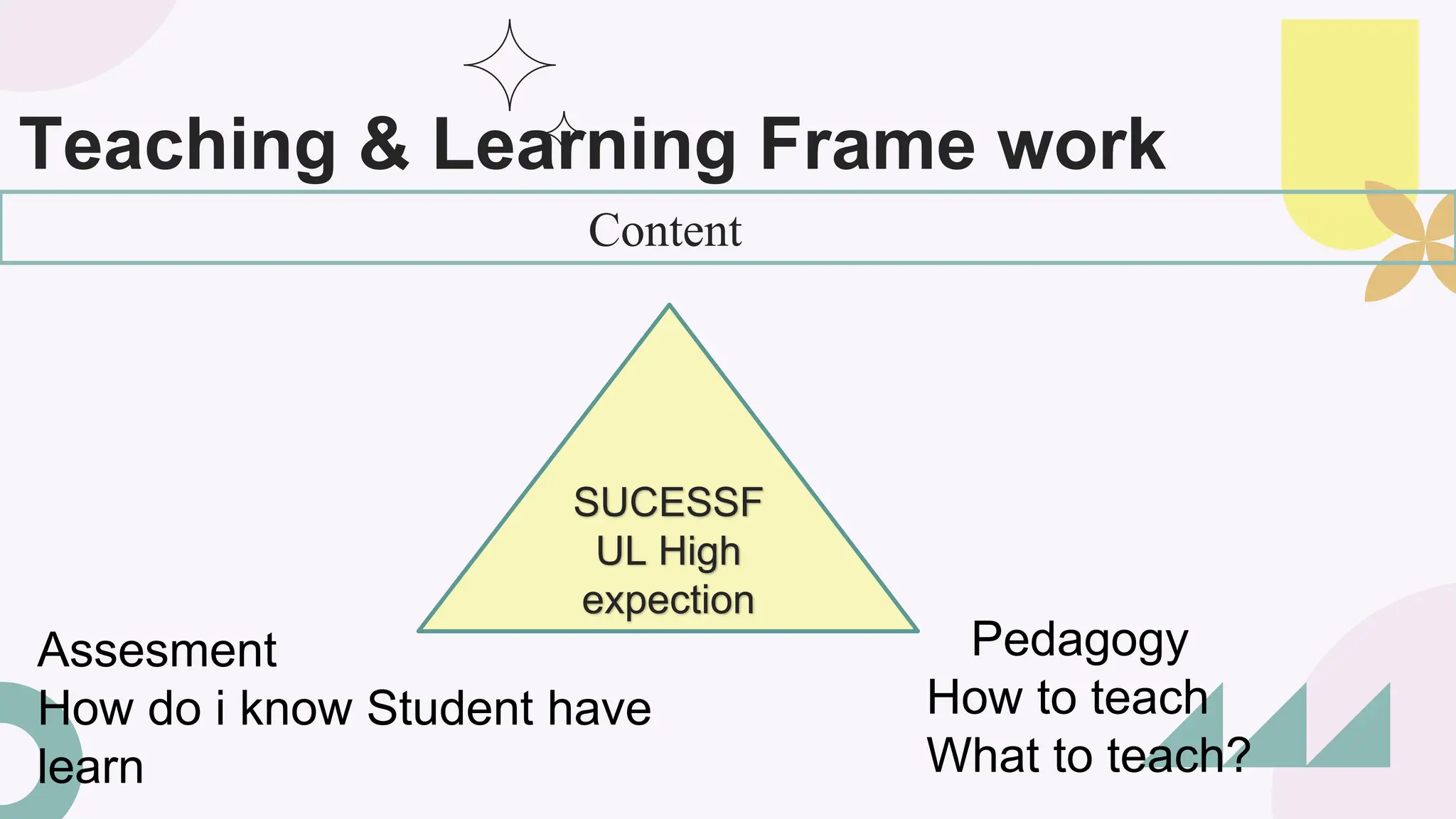
The document outlines various teaching and learning approaches, emphasizing the need to tailor strategies to meet diverse student needs. It highlights the importance of active learning, differentiated instruction, and technology integration while providing examples such as project-based learning and the flipped classroom model. Strategies for creating an inclusive and effective learning environment are also discussed, including assessment techniques and collaboration methods.