This document discusses strategies for teaching language construction and grammar. It outlines four approaches:
1) Studying structure and use, which focuses on language forms, meanings, and functions.
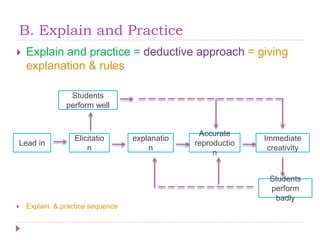
2) Explain and practice, taking a deductive approach by first explaining rules and then having students practice.
3) Discovery and practice, using an inductive approach where students discover language patterns on their own.
4) Research and practice, where students research language independently using resources like dictionaries.
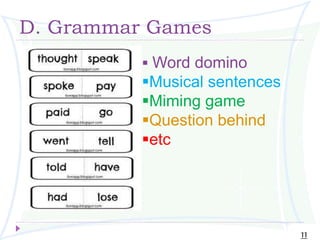
The document also provides specific techniques for each approach, such as choosing study activities, introducing grammar deductively or inductively, and using games to practice grammar.


![Teaching Language Construction
• A1. Language study in lesson sequences
• A2. Choosing study activities
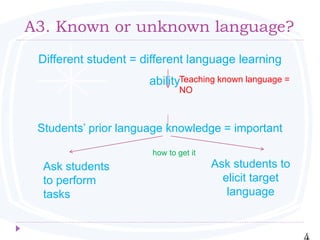
• A3. Known or unknown language?
A. Studying structure and
use
• B1. Explaining things
• B2. Practice (accurate reproduction)
B. Explain and Practice
C. Discovery [and practice]
• Language research on students’ ownD. Research [and practice]
• Deductive
• Inductive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ringgitgroup-170509150251/85/Teaching-and-Learning-Strategy-Teaching-Language-Construction-Grammar-3-320.jpg)



![C. Discover [and Practice]
Inductive approach
Discovery activities
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ringgitgroup-170509150251/85/Teaching-and-Learning-Strategy-Teaching-Language-Construction-Grammar-10-320.jpg)
![D. Research [and Practice]
Ask students to:
Consult a dictionary
Use search engines (like Google)
When students research the language on their own,
they are far more likely to remember what they find
out than if they sit passively and are given words.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ringgitgroup-170509150251/85/Teaching-and-Learning-Strategy-Teaching-Language-Construction-Grammar-11-320.jpg)