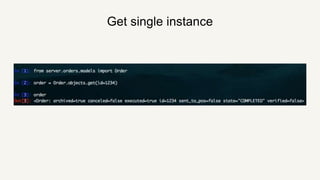
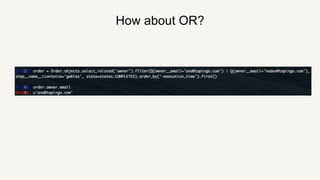
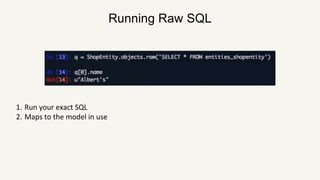
This document provides a summary of Django ORM and querying in Django. It begins with an introduction to ORM and how it works in Django using models. It then discusses querying Django models, including getting single and multiple instances, filtering with keywords like NOT and OR. More advanced querying techniques like annotating, aggregation, and running raw SQL are also covered. The document concludes with a discussion of working with real production data and using read replicas to gain insights while avoiding risks to the primary database.