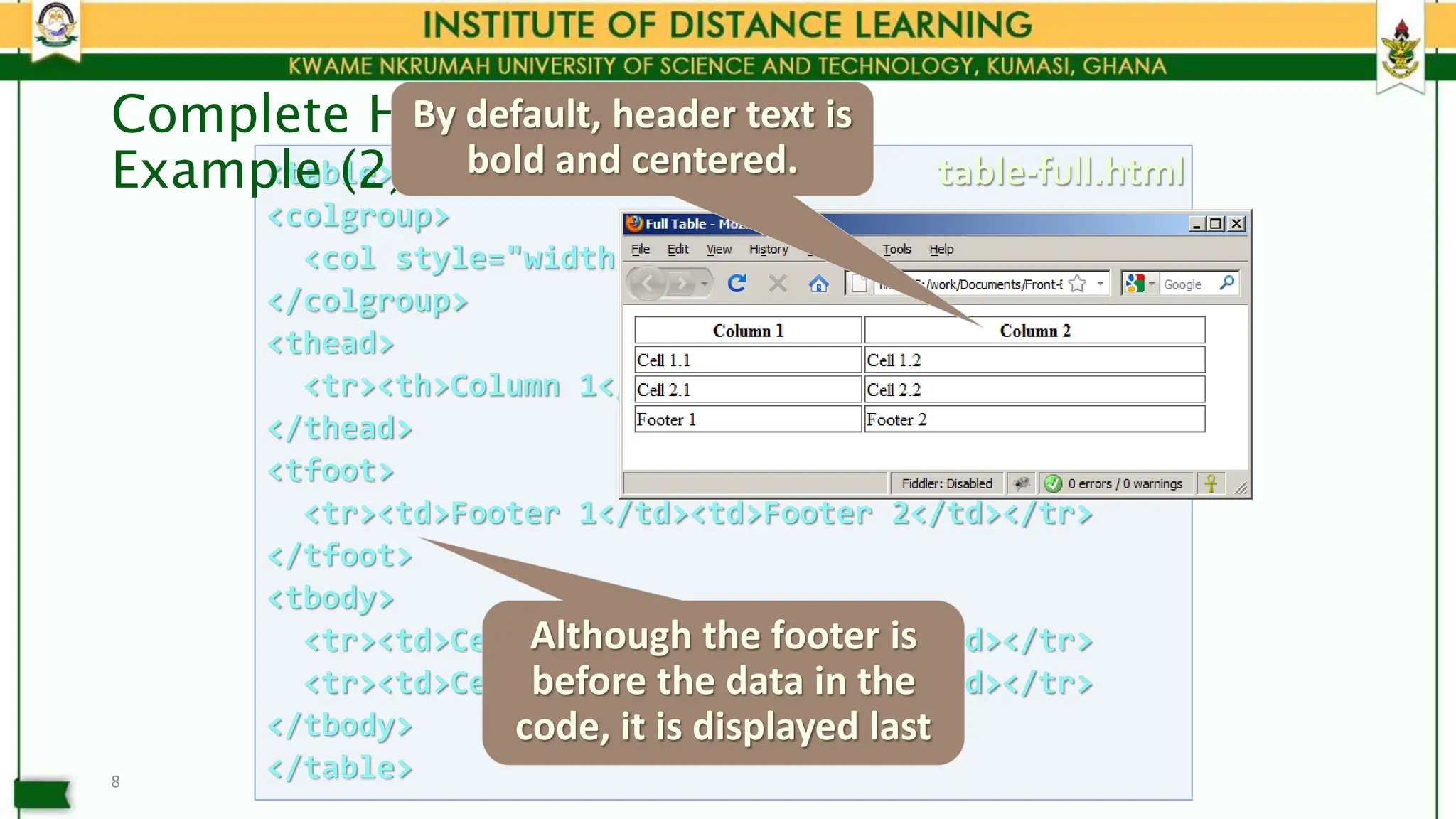
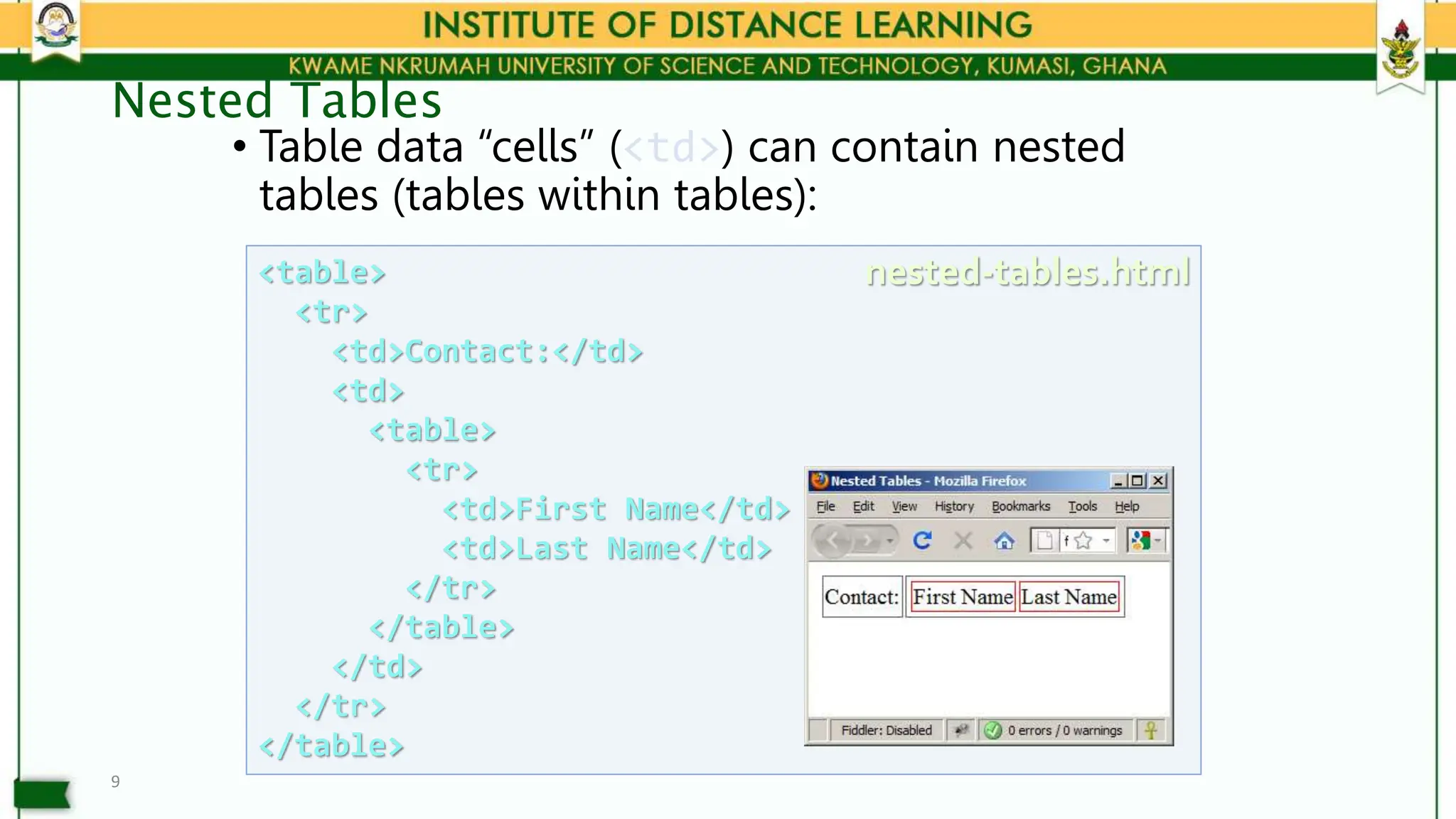
This document covers HTML tables and forms, explaining their structure, usage, and various attributes. It includes examples of simple and complete tables, nested tables, form elements and controls, as well as the deprecated <frameset> and <iframe> elements for displaying multiple documents. The lecture emphasizes proper usage of tables for data representation and forms for user input collection.



![ rowspan
Defines how
many rows the
cell occupies
colspan
Defines how
many columns
the cell occupies
Column and Row Span
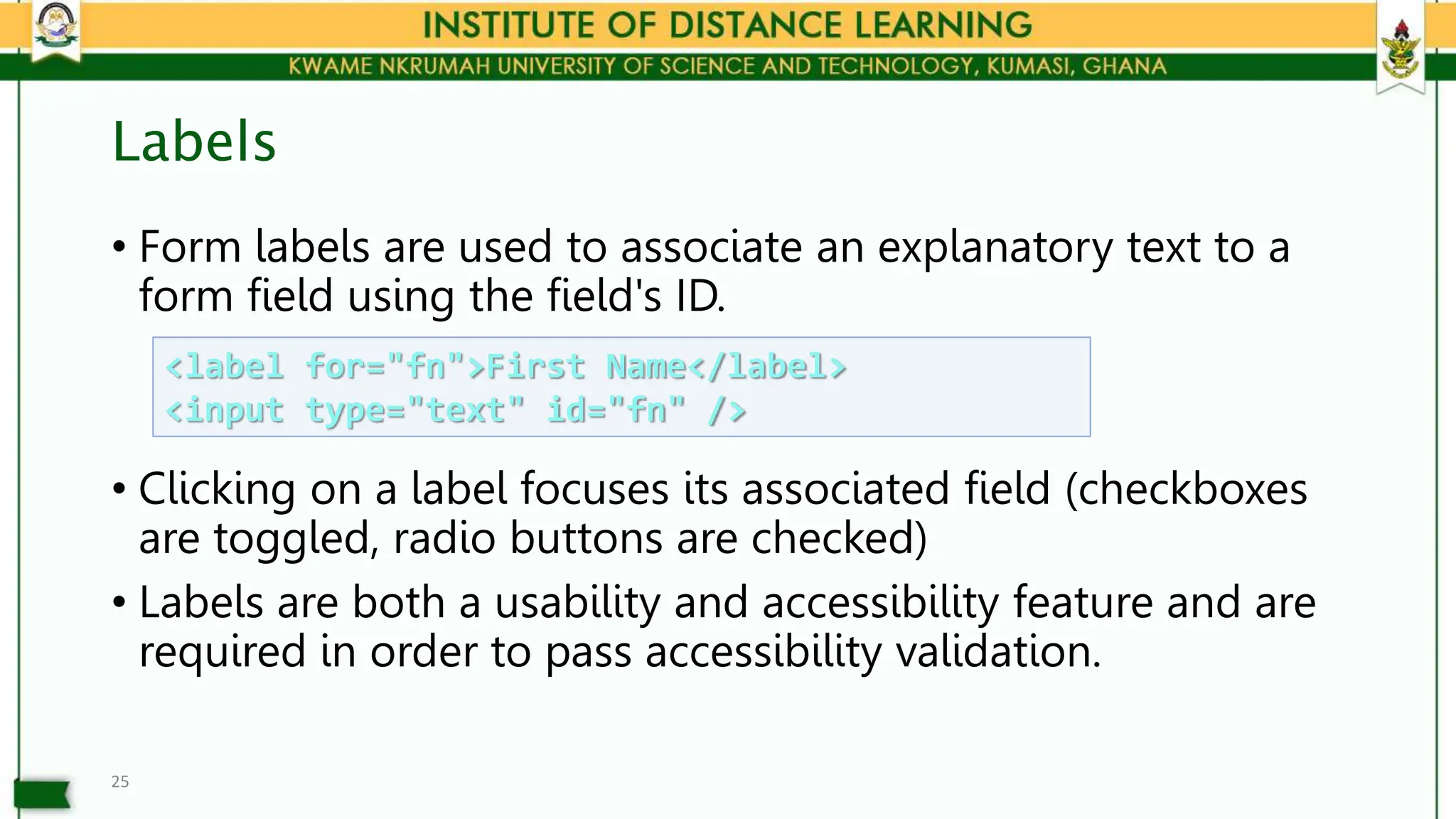
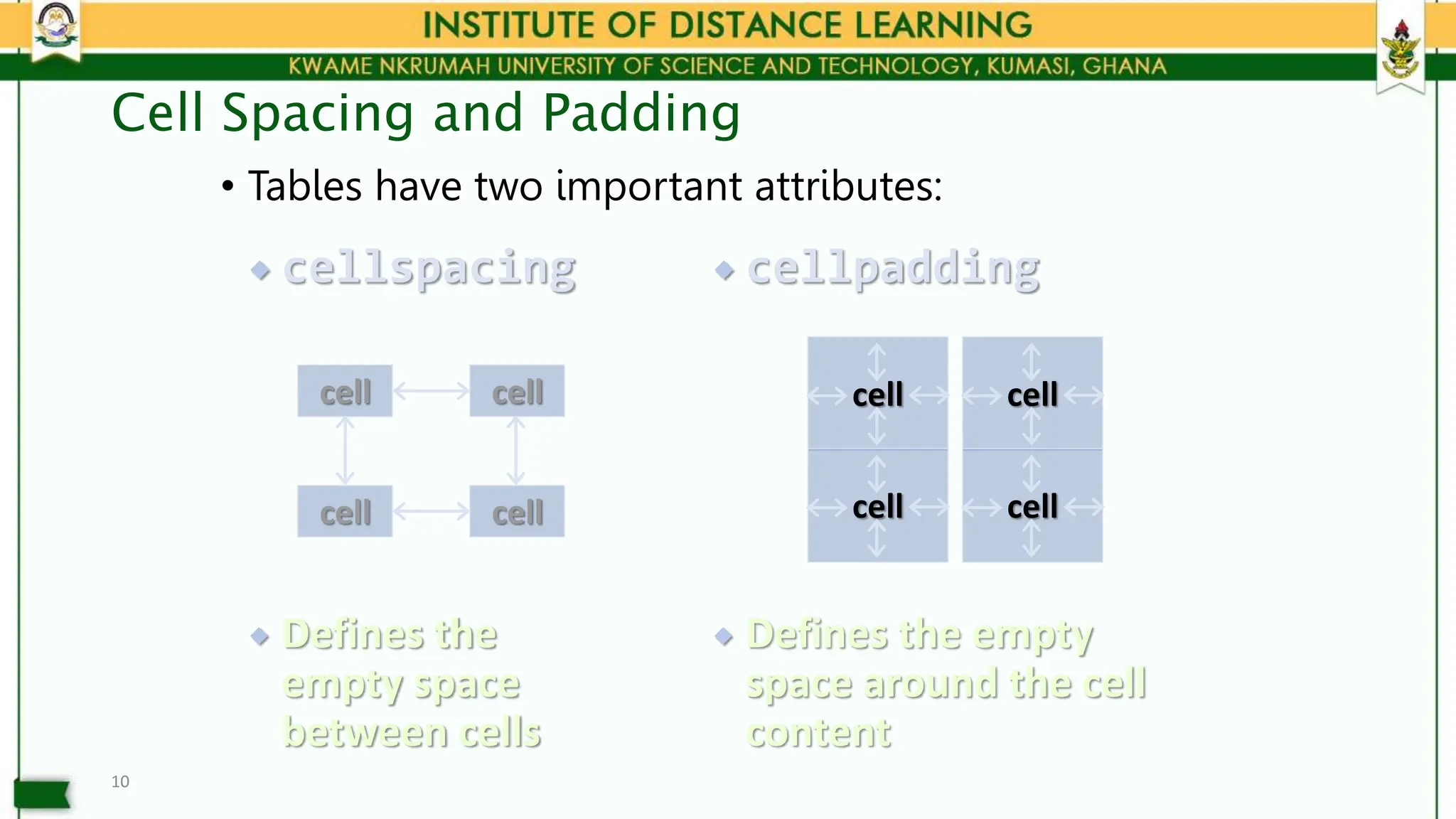
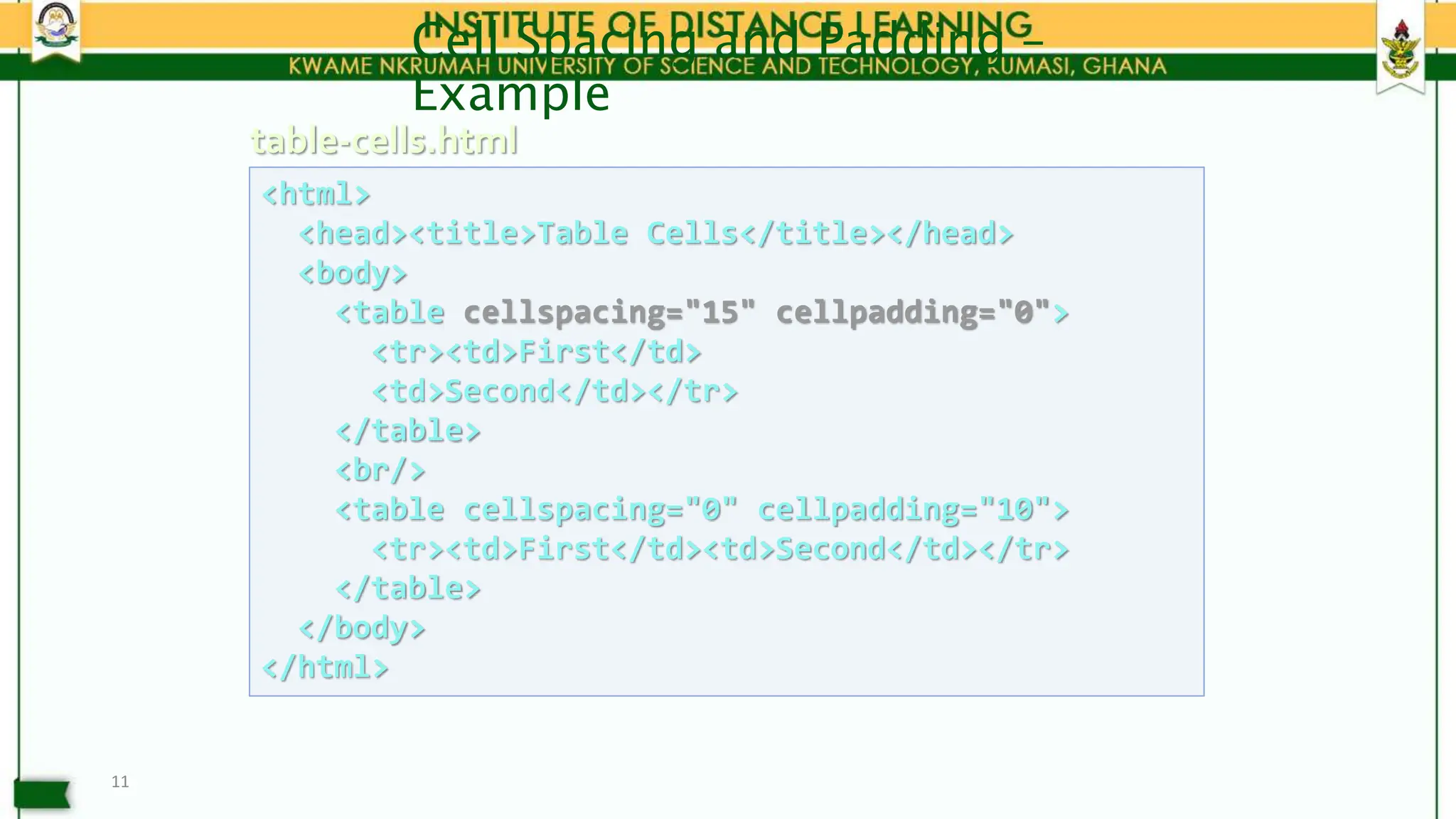
• Table cells have two important attributes:
13
cell[1,1] cell[1,2]
cell[2,1]
colspan="1"
colspan="1"
colspan="2"
cell[1,1]
cell[1,2]
cell[2,1]
rowspan="2" rowspan="1"
rowspan="1"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csm399unit3tablesfnframes-240419175250-cf24e378/75/Tables-and-their-padding-in-HTML-etc-pptx-14-2048.jpg)
![Column and Row Span – Example
14
<table cellspacing="0">
<tr class="1"><td>Cell[1,1]</td>
<td colspan="2">Cell[2,1]</td></tr>
<tr class=“2"><td>Cell[1,2]</td>
<td rowspan="2">Cell[2,2]</td>
<td>Cell[3,2]</td></tr>
<tr class=“3"><td>Cell[1,3]</td>
<td>Cell[2,3]</td></tr>
</table>
table-colspan-rowspan.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csm399unit3tablesfnframes-240419175250-cf24e378/75/Tables-and-their-padding-in-HTML-etc-pptx-15-2048.jpg)
![<table cellspacing="0">
<tr class="1"><td>Cell[1,1]</td>
<td colspan="2">Cell[2,1]</td></tr>
<tr class=“2"><td>Cell[1,2]</td>
<td rowspan="2">Cell[2,2]</td>
<td>Cell[3,2]</td></tr>
<tr class=“3"><td>Cell[1,3]</td>
<td>Cell[2,3]</td></tr>
</table>
Column and Row Span –
Example (2)
15
table-colspan-rowspan.html
Cell[2,3]
Cell[1,3]
Cell[3,2]
Cell[2,2]
Cell[1,2]
Cell[2,1]
Cell[1,1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csm399unit3tablesfnframes-240419175250-cf24e378/75/Tables-and-their-padding-in-HTML-etc-pptx-16-2048.jpg)